- United States presidential election, 1988
-
United States presidential election, 1988 
1984 ← November 8, 1988 → 1992 

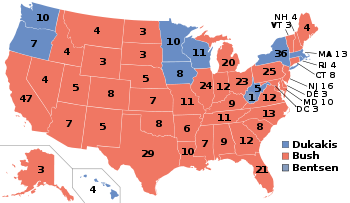
Nominee George H. W. Bush Michael Dukakis Party Republican Democratic Home state Texas Massachusetts Running mate Dan Quayle Lloyd Bentsen Electoral vote 426 111 States carried 40 10 + DC Popular vote 48,886,597 41,809,476 Percentage 53.4% 45.7%
Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Bush/Quayle, Blue denotes those won by Dukakis/Bentsen. Lloyd Bentsen for President (and Michael Dukakis for V.P.) received one electoral vote from a West Virginia faithless elector. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state.
President before election
Elected President
The United States presidential election of 1988 featured no incumbent president, as President Ronald Reagan was unable to seek re-election after serving the maximum two terms allowed by the Twenty-second Amendment. Reagan's Vice President, George H. W. Bush, won the Republican nomination, while the Democrats nominated Michael Dukakis, Governor of Massachusetts. Bush capitalized on a good economy, a stable international stage, and on Reagan's popularity, while Dukakis's campaign suffered from several miscues. The result was a third consecutive Republican landslide.
Contents
Nominations
Democratic Party nomination
Democratic candidates
- Michael Dukakis, governor of Massachusetts[1]
- Jesse Jackson, reverend and civil rights leader from South Carolina[2]
- Al Gore, U.S. senator from Tennessee[3]
- Dick Gephardt, U.S. representative from Missouri[4]
- Paul Simon, U.S. senator from Illinois[5]
- Gary Hart, former U.S. senator from Colorado[6]
- Bruce Babbitt, former governor of Arizona[7]
- Joe Biden, U.S. senator from Delaware[8]
- Lyndon LaRouche, activist from Virginia[9]
- David Duke, activist from Louisiana[10]
- James Traficant, U.S. representative from Ohio[11]
- Douglas Applegate, U.S. representative from Ohio[12]
- Andy Martin, perennial candidate from Connecticut[13]
Candidates gallery
-
Reverend Jesse Jackson of South Carolina (campaign)
-
Senator Paul Simon of Illinois
-
Former Governor Bruce Babbitt of Arizona
-
Andy Martin of Connecticut
In the 1984 presidential election the Democrats had nominated Walter Mondale, a traditional New Deal-type liberal as their candidate. When Mondale was defeated in a landslide, party leaders became eager to find a new approach to win the presidency. After Reagan's image was tarnished in the Iran-Contra scandal, and after the Democrats won back control of the Senate in the 1986 congressional elections, the party's leaders felt more optimistic about winning the Presidency in 1988.
One goal of the party was to find a new, fresh candidate who could move beyond the traditional New Deal-Great Society ideas of the past and offer a new image of the Democrats to the public. To this end party leaders tried to recruit the New York Governor, Mario Cuomo, to be a candidate. Cuomo had impressed many Democrats with his stirring keynote speech at the 1984 Democratic Convention, and they believed that he would be a strong candidate. However, Cuomo chose not to run. As a result, the Democratic frontrunner for most of 1987 was former Colorado Senator Gary Hart. He had made a strong showing in the 1984 presidential election and, after Mondale's defeat, had positioned himself as the moderate centrist many Democrats felt their party would need to win.
However, questions and rumors about possible extramarital affairs dogged Hart's campaign. One of the great myths is that Senator Hart challenged the media to "put a tail" on him. In fact, Hart had told reporters from The New York Times who questioned him about these rumors that, if they followed him around, they would "be bored". However, in a separate investigation, the Miami Herald had received an anonymous tip from a friend of Donna Rice that Rice was involved with Hart. It was only after Hart had been discovered that the Herald reporters found Hart's quote in a copy of the New York Times magazine. After the Herald's findings were publicized, many other media outlets picked up the story and Hart's ratings in the polls plummeted. On May 8, 1987, a week after the Donna Rice story broke, Hart dropped out of the race. His campaign chair, Representative Patricia Schroeder tested the waters for about four months after Hart's withdrawal, but decided in September 1987 that she would not run.[14] In December 1987, Hart surprised many political pundits by resuming his presidential campaign. However, the allegations of adultery had delivered a fatal blow to his candidacy, and he did poorly in the primaries before dropping out again.
Senator Ted Kennedy of Massachusetts had been considered a potential candidate, but he ruled himself out of the 1988 campaign in the fall of 1985. Two other politicians mentioned as possible candidates, both from Arkansas, didn't join the race: Senator Dale Bumpers and Governor (and future President) Bill Clinton. (Clinton said in 2007 he changed his mind the day before he was to announce a run, he felt that he wasn't ready for the Presidency in 1988, and that he would wait until 1992 or 1996 before trying.)[citation needed]
Joe Biden's campaign also ended in controversy after the Delaware Senator was accused of plagiarizing a speech by Neil Kinnock, then-leader of the British Labour Party. Though Biden had correctly credited the original author in all speeches but one, the one where he failed to make mention of the originator was caught on video and parlayed into a political hit piece by the Dukakis campaign.[15] In the video Biden is filmed repeating a stump speech by Kinnock, with only minor modifications. This would lead him to drop out of the race. Dukakis later revealed that his campaign was responsible for leaking the tape, and two members of his staff resigned. The Delaware Supreme Court's Board on Professional Responsibility would later clear Biden of the law school plagiarism charges.[16]
Al Gore, a Senator from Tennessee, also chose to run for the nomination. Turning 40 in 1988, he would have been the youngest man ever to contest the Presidency on a major party ticket since William Jennings Bryan in 1900 , and the youngest president ever if elected, younger than John F. Kennedy at election age and Theodore Roosevelt at age of assumption of office.
Primaries
After Hart withdrew from the race, no clear frontrunner emerged before the primaries and caucuses began. The Iowa caucus was won by Dick Gephardt, who had been sagging heavily in the polls until, three weeks before the vote, he began campaigning as a populist and his numbers surged. Illinois Senator Paul M. Simon finished a surprising second, and Massachusetts Governor Michael Dukakis finished third. In the New Hampshire primary, Dukakis came in first place, Gephardt fell to second, and Simon came in third. In an effort to weaken Gephardt's candidacy, both Dukakis and Tennessee Senator Al Gore ran negative television ads against Gephardt. The ads convinced the United Auto Workers, which had endorsed Gephardt, to withdraw their endorsement; this crippled Gephardt, as he relied heavily on the support of labor unions.
In the Super Tuesday races, Dukakis won six primaries, to Gore's five, Jesse Jackson five and Gephardt one, with Gore and Jackson splitting the Southern states. The next week, Simon won Illinois with Jesse Jackson finishing second. 1988 remains the race with the most candidates winning primaries since the McGovern reforms of 1971. Jackson captured 6.9 million votes and won 11 contests; seven primaries (Alabama, the District of Columbia, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, Puerto Rico and Virginia) and four caucuses (Delaware, Michigan, South Carolina and Vermont). Jackson also scored March victories in Alaska's caucuses and Texas's local conventions, despite losing the Texas primary. Briefly, after he won 55% of the vote in the Michigan Democratic caucus he had more pledged delegates than all the other candidates.
However, Jackson's campaign suffered a significant setback less than two weeks later when he was defeated handily in the Wisconsin primary by Michael Dukakis. Dukakis's win in New York and then in Pennsylvania effectively ended Jackson's hopes for the nomination.
Democratic Convention
The Democratic Party Convention was held in Atlanta, Georgia from July 18–21. In his first major national speech, Arkansas Governor Bill Clinton placed Dukakis's name in nomination. The speech lasted for so long that some delegates began booing to get him to finish.[17]
The most memorable speech given at the Democratic Convention was by Texas State Treasurer Ann Richards, who two years later was elected the state governor. Richards uttered the famous line: "Poor George [H.W. Bush], he can't help it, he was born with a silver foot in his mouth." Six years later, Bush's son and future President George W. Bush would defeat Richards in her re-election campaign for Texas Governor.
With only Jackson remaining as an active candidate to oppose Dukakis, the tally for president was:
The Balloting Presidential Ballot Vice Presidential Ballot Michael S. Dukakis 2,876.25 Lloyd M. Bentsen 4,162 Jesse L. Jackson 1,218.5 Richard H. Stallings 3 Joe Biden 2 Richard A. Gephardt 2 Gary W. Hart 1 Lloyd M. Bentsen 1 Jesse Jackson's supporters said that since their candidate had finished in second place, he was entitled to the vice presidential spot. Dukakis disagreed, and instead selected Senator Lloyd Bentsen of Texas. Bentsen's selection led many in the media to dub the ticket as the "Boston-Austin" axis, and to compare it to the more famous pairing of John F. Kennedy and Lyndon Johnson in the 1960 presidential campaign. Like Dukakis and Bentsen, Kennedy had been from Massachusetts and Johnson from Texas.
Bentsen was selected in large part to help win the large electoral vote of the state of Texas. Because of Bentsen's status as an elder statesman, more experienced in elected politics, some Democrats believed that Dukakis's selection of Bentsen as his running mate was a mistake; they noted that Bentsen, although only the vice-presidential candidate, appeared more "presidential" than did Dukakis. During the vice-presidential debate, Republican candidate and Senator Dan Quayle ignored a head-on confrontation with Bentsen (aside from the "Jack Kennedy" comparison) and spent his time attacking Dukakis.
Republican Party
Republican candidates
- George H. W. Bush, Vice President of the United States from Texas[18]
- Bob Dole, U.S. senator from Kansas[19]
- Pat Robertson, televangelist from Virginia[20]
- Jack Kemp, U.S. representative from New York[21]
- Pierre S. du Pont, IV, governor of Delaware[22]
- Alexander Haig, former Secretary of State from Pennsylvania[23]
- Ben Fernandez, former Special Ambassador to Parguay from California[24]
- Paul Laxalt, former Senator from Nevada[25]
- Donald Rumsfeld, former Secretary of Defense from Illinois[26]
- Harold E. Stassen, former Governor of Minnesota[27]
- Isabell Masters, perennial candidate from Kansas[28]
Candidates gallery
-
Televangelist Pat Robertson of Virginia
-
Governor Pierre S. du Pont, IV of Delaware
-
Former Secretary of State Alexander Haig
-
Former Senator Paul Laxalt of Nevada
-
Former Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld of Illinois
Vice President George H.W. Bush had the support of President Ronald Reagan, and pledged to continue Reagan's policies, but also pledged a "kinder and gentler nation" in an attempt to win over some more moderate voters.
Bush unexpectedly came in third in the Iowa caucus, which he had won in 1980, behind Dole and Robertson. Dole was also leading in the polls of the New Hampshire primary, and the Bush camp responded by running television commercials portraying Dole as a tax raiser, while Governor John H. Sununu campaigned for Bush. Dole did nothing to counter these ads and Bush won, thereby gaining crucial momentum, or what he called "Big Mo". Dole was bitter about his defeat in New Hampshire, going on TV to tell Bush to "stop lying about my record".[29]
Once the multiple-state primaries such as Super Tuesday began, Bush's organizational strength and fund raising lead were impossible for the other candidates to match, and the nomination was his. The Republican party convention was held in New Orleans, Louisiana. Bush was nominated unanimously. Bush selected U.S. Senator Dan Quayle of Indiana as his running mate.
In his acceptance speech, Bush made an energetic pledge, "Read my lips: No new taxes", a comment that would come to haunt him in the 1992 elections.
Other nominations
- David E. Duke - Populist Party: Former leader of the Louisiana Ku Klux Klan. Advocated a mixture of White nationalist/separatist policies and more traditionally conservative positions, such as opposition to most immigration from Latin America and affirmative action.
- Lenora Fulani - New Alliance Party: Focused on issues concerning unemployment, healthcare, and homelessness.
- Willa Kenoyer/Ron Ehrenreich - Socialist Party USA: Advocated a decentralist government approach with policies determined by the needs of the workers.
- Ron Paul/Andre Marrou - Libertarian Party: (campaign) Called for the adoption of a global policy on military nonintervention; wanted to end the federal government's involvement with education; criticized Reagan's "bailout" of the Soviet Union. Former member of the U.S. House of Representatives, first elected as a Republican from Texas in an April 1976 special election. Protested the War on Drugs in a letter to Drug Czar William Bennett.
General election
Campaign
During the election, the Bush campaign sought to portray Governor Dukakis as a "Massachusetts liberal" who was unreasonably left-wing. Dukakis was attacked for such positions as opposing mandatory recitation of the Pledge of Allegiance in schools, and being a "card carrying member of the ACLU" (a statement Dukakis made himself early in the primary campaign). Dukakis responded by saying that he was a "proud liberal" and that the phrase should not be a bad word in America. Bush (Yale '48) derided Dukakis (Swarthmore '55) for having "foreign-policy views born in Harvard Yard's boutique".[30] New York Times columnist Maureen Dowd asked "Wasn't this a case of the pot calling the kettle elite?" Bush explained however that, unlike Harvard, Yale's reputation was "so diffuse, there isn't a symbol, I don't think, in the Yale situation, any symbolism in it.... Harvard boutique to me has the connotation of liberalism and elitism", and said Harvard in his remark was intended to represent "a philosophical enclave" and not a statement about class.[31] Columnist Russell Baker opined that "Voters inclined to loathe and fear elite Ivy League schools rarely make fine distinctions between Yale and Harvard. All they know is that both are full of rich, fancy, stuck-up and possibly dangerous intellectuals who never sit down to supper in their undershirt no matter how hot the weather gets."[32]
The Dukakis camp tried to tie Bush to some of the recent scandals of the Reagan Administration, such as Iran-Contra, and argued that Republicans were too hawkish on foreign policy.
Governor Dukakis attempted to quell criticism that he was ignorant on military matters by staging a photo op in which he rode in an M1 Abrams tank outside a General Dynamics plant in Sterling Heights, Michigan.[33] The move ended up being a massive public relations blunder, with many mocking Dukakis's appearance as he stuck his smiling, helmeted head out one of the tank's hatches to wave to the crowd. Footage of Dukakis was used by the Bush campaign as evidence he would not make a good commander-in-chief, and "Dukakis in the tank" — or the "Snoopy Incident" — remains shorthand for backfired public relations outings.[34][35]
One reason for Bush's choice of running mate, Senator Dan Quayle, was to appeal to a younger generation of Americans. Quayle's good looks were praised by Senator John McCain: "I can't believe a guy that handsome wouldn't have some impact."[36] Quayle was not a seasoned politician, however, and made a number of embarrassing statements. The Dukakis team attacked Quayle's credentials, saying he was dangerously inexperienced to be first-in-line to the presidency.[37]
During the Vice Presidential debate, Quayle attempted to dispel such allegations by comparing his experience with that of former Senator John F. Kennedy, who had also been a young political rookie when running for the presidency. During the Vice Presidential debate, Quayle said, "I have as much experience in the Congress as Jack Kennedy did when he sought the presidency." (Kennedy had served fourteen years in Congress to Quayle's twelve). Dukakis's running mate, Lloyd Bentsen, responded, "Senator, I served with Jack Kennedy. I knew Jack Kennedy. Jack Kennedy was a friend of mine. Senator, you're no Jack Kennedy."[38]
Quayle responded, "That was really uncalled for, Senator", to which Bentsen said, "You are the one that was making the comparison, Senator, and I'm one who knew him well. And frankly I think you are so far apart in the objectives you choose for your country that I did not think the comparison was well-taken."
Quayle's reaction to Bentsen's comment was played and replayed by the Democrats in subsequent television ads as an announcer intoned, "Quayle: just a heartbeat away." Despite much press about the Kennedy comments, this did not reduce the Bush-Quayle lead in the polls. Quayle had sought to use the debate to criticize Dukakis as too liberal rather than go point for point with the more seasoned Bentsen. Bentsen's attempts to defend Dukakis received little recognition, with greater attention on the Kennedy comparison.
During the course of the campaign, Dukakis fired his deputy field director Donna Brazile after she spread rumors that Bush had an affair with his assistant Jennifer Fitzgerald.[39] (The relationship of George H.W. Bush and Jennifer Fitzgerald would be briefly rehashed during the 1992 campaign.)[40][41]
Dukakis was badly hurt by the Republican "Willie Horton", "Revolving Door", and "Boston Harbor" campaign ads, the latter of which attacked the governor's failure to clean up environmental pollution in the harbor. Dukakis was a supporter of a state prison furlough program, which had begun before he was governor. The program had resulted in the release (furlough) of convicted murderer Willie Horton, who then committed a rape and assault in Maryland. As Governor, Dukakis had vetoed a 1976 plan to bar inmates convicted of first-degree murder from the furlough program. The program was abolished by the state legislature in April 1988 after public outcry over the Willie Horton case.
A number of false rumors were reported in the media about Dukakis, including the claim by Idaho Republican Senator Steve Symms that Dukakis's wife Kitty had burned an American flag to protest the Vietnam War, as well as the claim that Dukakis himself had been treated for a mental illness. Lee Atwater was accused of having floated these rumors.[42]
Although Dukakis did well in the first presidential debate, Bush seemed to score a triumph in the second debate, with a Gallup Poll giving him a 49-43 lead.[43] Before the second debate, Dukakis had been suffering from the flu and spent quite a bit of the day in bed. His performance was poor and played to his reputation as being intellectually cold. The most memorable moment came when reporter Bernard Shaw asked Dukakis whether he would support the death penalty if his wife were raped and murdered. Dukakis's answer discussed the statistical ineffectiveness of capital punishment. Several commentators thought the question itself was unfair, in that it injected an irrelevant emotional element into the discussion of a policy issue, but many observers felt Dukakis's answer lacked the normal emotions one would expect of a person asked about a loved one's rape and death.[44] Tom Brokaw of NBC reported on his October 14 newscast: "The consensus tonight is that Vice President George Bush won last night's debate and made it all the harder for Governor Michael Dukakis to catch and pass him in the 25 days remaining. In all of the Friday morning quarterbacking, there was common agreement that Dukakis failed to seize the debate and make it his night."
Results
 Chief Justice William Rehnquist administering the oath of office to President George H. W. Bush on January 20, 1989 at the United States Capitol.
Chief Justice William Rehnquist administering the oath of office to President George H. W. Bush on January 20, 1989 at the United States Capitol.
In the November 8 election, Bush won a majority of the popular vote and a lopsided majority (40) of states in the Electoral College.
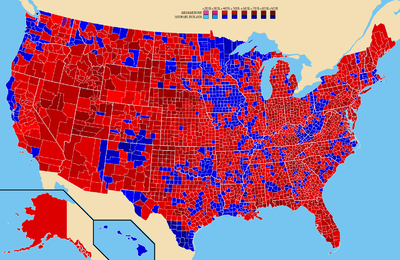
Bush performed very strongly among suburban voters, perhaps owing to his campaign themes of law and order, punctuated by his criticisms of the Massachusetts furlough program. This was a boon in several swing states. In Illinois, Bush won 69% in DuPage County and 63% out of Lake County, suburban areas which adjoin Chicago's Cook County. In Pennsylvania, Bush swept the group of suburban counties that surround Philadelphia, including Bucks, Delaware, Chester, and Montgomery. Bush also won most of the counties in Maryland, perhaps fallout from the fact that Willie Horton committed his infamous criminal acts there. New Jersey, known at the time for its many suburban voters and its moderate Republicanism, went easily for Bush. Bush also gained victory for attacking Dukakis's furlough program he had while he was Governor of Massachusetts,[45] though Dukakis still maintained popularity in Massachusetts.
In contrast to the suburbs, Bush's percentage of votes in rural counties was significantly below the support they gave Reagan in 1980 and 1984. In Illinois, Bush lost a number of downstate counties that previously went for Reagan. He lost the state of Iowa by a surprisingly wide margin, losing counties all across the state even in traditionally Republican areas. The rural state of West Virginia remained narrowly in the Democratic column. Bush also performed weaker in the northern counties of Missouri, narrowly winning the state. In three typically solid Republican states, Kansas, South Dakota, and Montana, the vote was much closer than usual. The farm states had fared poorly during the recession of the 1980s, and Dukakis was the beneficiary of these agricultural problems.
Bush's greatest area of strength was in the South, where he won most states by wide margins. He also performed very well in the northeast, winning Maine (where he had a residence), New Hampshire (at the time a Republican stronghold), Vermont (at the time a bastion of moderate Republicanism), and Connecticut (where his father had been a senator). Bush lost New York by a margin of just over 4 percent. He also won Delaware, at the time a swing state. Despite the presence of Lloyd Bentsen on the Democratic ticket (and other Texans getting prominent roles at the Democratic convention), Bush won the Lone Star State by a convincing margin. He lost the Pacific northwestern states but kept California in the Republican column for the sixth straight time, albeit very narrowly. That would be the last time a Republican candidate won California in a presidential election.
Although his victory was not a landslide in the popular vote (though it was substantial), Bush in 1988 was the last Republican to carry certain states which have since gained a reputation as "blue states" that favor the Democratic Party in presidential elections. These states were Vermont, Maine, Connecticut, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Michigan, Illinois, and California. His victory percentage — 53.4% — has not yet been surpassed in any subsequent presidential election, and he was the last candidate to get a majority of the popular vote until George W. Bush's 2004 election. This was the last election to date in which a Republican presidential nominee won a majority of Northern electoral votes.
Statistics
Presidential candidate Party Home state Popular vote Electoral
voteRunning mate Count Pct Vice-presidential candidate Home state Elect. vote George H. W. Bush Republican Texas 48,886,597 53.37% 426 James Danforth Quayle Indiana 426 Michael S. Dukakis Democratic Massachusetts 41,809,476 45.65% 111 Lloyd M. Bentsen Texas 111 Ron Paul Libertarian Texas 431,750 0.47% 0 Andre V. Marrou Alaska 0 Lenora Fulani New Alliance Pennsylvania 217,221 0.24% 0 —(b) — 0 Other 249,642 0.27% — Other — Lloyd M. Bentsen Democratic Texas —(a) —(a) 1 Michael S. Dukakis Massachusetts 1 Total 91,594,686 100% 538 538 Needed to win 270 270 Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. 1988 Presidential Election Results. Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections (August 7, 2005). Source (Electoral Vote): Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996. Official website of the National Archives. (August 7, 2005). (a) West Virginia faithless elector Margaret Leach voted for Bentsen as President and Dukakis as Vice President in order to make a statement against the U.S. Electoral College.
(b) Fulani's running mate varied from state to state.[46] Among the six vice presidential candidates were Joyce Dattner, Harold Moore,[47] and Wynonia Burke.[48]Close states
- Washington, 1.59%
- Illinois, 2.09%
- Pennsylvania, 2.31%
- Maryland, 2.91%
- Vermont, 3.52%
- California, 3.57%
- Wisconsin, 3.61%
- Missouri, 3.98%
- New York, 4.10%
- Oregon, 4.67%
- West Virginia, 4.74%
- New Mexico, 4.96%
Close states where the margin was over 5%, but less than 10%
- Connecticut, 5.11%
- Montana, 5.87%
- South Dakota, 6.34%
- Minnesota, 7.01%
- Colorado, 7.78%
- Massachusetts, 7.85%
- Michigan, 7.90%
- Hawaii, 9.52%
See also
- President of the United States
- United States Senate elections, 1988
- History of the United States (1988–present)
- Al Gore presidential campaign, 1988
References
- ^ "Dukakis announces bid for presidential nomination". The Milwaukee Sentinel. April 30, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=rI5QAAAAIBAJ&sjid=hxIEAAAAIBAJ&pg=4542,7945718&dq=dukakis+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ Mattiace, Peter (September 8, 1987). "Jesse Jackson announces plan to seek nomination". Gettysburg Times. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=LMElAAAAIBAJ&sjid=qvwFAAAAIBAJ&pg=1944,5920744&dq=jesse+jackson+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Sen. Gore announces presidential aspiration". Bangor Daily News. April 12, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=4q1JAAAAIBAJ&sjid=pQ4NAAAAIBAJ&pg=7016,1631410&dq=al+gore+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Gephardt Announces Bid For White House". The Dispatch. February 23, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=m44bAAAAIBAJ&sjid=3VEEAAAAIBAJ&pg=4320,5734439&dq=dick+gephardt+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Sen. Simon announces candidacy". The Lewiston Daily Sun. April 10, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=SjspAAAAIBAJ&sjid=cmUFAAAAIBAJ&pg=3173,1888124&dq=al+gore+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Gary Hart announces he will seek the presidency in 1988". The Fort Scott Tribune. April 13, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=ZP8fAAAAIBAJ&sjid=MAYFAAAAIBAJ&pg=4910,4333290&dq=gary+hart+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ Gailey, Phil (8 January 1987). "BABBITT OF ARIZONA FIRST DEMOCRAT TO FORM KEY PRESIDENTIAL GROUP". The New York Times: p. 24. http://www.nytimes.com/1987/01/08/us/babbitt-of-arizona-first-democrat-to-form-key-presidential-group.html. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Sen. Biden announces candidacy". The Milwaukee Journal. June 9, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=oV0aAAAAIBAJ&sjid=8yoEAAAAIBAJ&pg=5986,167224&dq=biden+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "LaRouche announces candidacy". Eugene Register-Guard. January 27, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=ZCgzAAAAIBAJ&sjid=feEDAAAAIBAJ&pg=2541,5939742&dq=larouche+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Former Klan leader announces bid". Spokane Chronicle. June 9, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=woZOAAAAIBAJ&sjid=7_oDAAAAIBAJ&pg=1841,1553457&dq=duke+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ Wilkinson, D.A. (December 4, 1987). "Traficant hat tossed into ring". The Vindicator. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=B84_AAAAIBAJ&sjid=61cMAAAAIBAJ&pg=3639,1284676&dq=traficant+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Applegate To Run As Favorite Son". Portsmouth Daily Times. November 24, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=nJA_AAAAIBAJ&sjid=r1UMAAAAIBAJ&pg=5474,1827674&dq=douglas+applegate&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Man causes Statehouse Stir". The Day. May 8, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=hiAiAAAAIBAJ&sjid=KnIFAAAAIBAJ&pg=4418,1973583&dq=anthony+martin-trigona&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Schroeder tearfully announces she won't seek presidency". Lodi News-Sentinel. September 29, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=-x0_AAAAIBAJ&sjid=fk8MAAAAIBAJ&pg=6914,3504746&dq=schroeder+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Media outlets debunk plagiary allegations to no avail.". MediaMatters for America. 2000-08-23. http://mediamatters.org/items/200808230003.
- ^ "Professional Board Clears Biden In Two Allegations of Plagiarism". The New York Times: p. 29. 1989-05-29. http://www.nytimes.com/1989/05/29/us/professional-board-clears-biden-in-two-allegations-of-plagiarism.html.
- ^ Brummert, John (July 22, 1988). "I just fell on my sword". Arkansas Democrat-Gazette.
- ^ "Bush Announces Quest for Presidency". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. October 13, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=3_McAAAAIBAJ&sjid=rnIEAAAAIBAJ&pg=6869,4085135&dq=george+bush+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Dole announces presidential hopes in hometown talk". Star-News. November 10, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=K5s0AAAAIBAJ&sjid=CxQEAAAAIBAJ&pg=5835,4017707&dq=bob+dole+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Robertson announces". Ellensburg Daily Record. October 2, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=-otUAAAAIBAJ&sjid=XI8DAAAAIBAJ&pg=4675,159477&dq=pat+robertson+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Kemp announces bid for nomination". The Bryan Times. April 6, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=GbFPAAAAIBAJ&sjid=U1IDAAAAIBAJ&pg=3541,486109&dq=jack+kemp+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Dionne Jr., E. J. (17 September 1986). "DU PONT ENTERS THE G.O.P. RACE FOR PRESIDENT". The New York Times: p. 1. http://www.nytimes.com/1986/09/17/us/du-pont-enters-the-gop-race-for-president.html. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Haig announces his bid for presidency". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. March 24, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=BtU0AAAAIBAJ&sjid=6G0DAAAAIBAJ&pg=2317,6652737&dq=haig+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Wallace, David (August 6, 1987). "GOP PRESIDENTIAL CANDIDATE MAKES STOP IN SOUTH FLORIDA". Sun Sentinel. http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/sun_sentinel/access/88010221.html?dids=88010221:88010221&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&type=current&date=Aug+06%2C+1987&author=DAVID+WALLACE%2C+Staff+Writer&pub=South+Florida+Sun+-+Sentinel&desc=GOP+PRESIDENTIAL+CANDIDATE+MAKES+STOP+IN+SOUTH+FLORIDA&pqatl=google. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Witt, Evans (April 29, 1987). "Laxalt announces bid for presidency, says 'there is unfinished work to do'". Gettysburg Times. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=7MUlAAAAIBAJ&sjid=iPwFAAAAIBAJ&pg=1271,170287&dq=laxalt+announces&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Rumsfeld enters race". The Telegraph-Herald. January 20, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=VpddAAAAIBAJ&sjid=tFwNAAAAIBAJ&pg=6853,3241160&dq=rumsfeld+president&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "Stassen announces his candidacy". The Milwaukee Journal. September 22, 1987. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=iG0aAAAAIBAJ&sjid=pCoEAAAAIBAJ&pg=4462,5711800&dq=stassen&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ "'Super Tuesday' Ballots Ready; Some Unfamiliar Names Explained". The Durant Daily Democrat. March 6, 1988. http://news.google.com/newspapers?id=y_ZDAAAAIBAJ&sjid=L7AMAAAAIBAJ&pg=1553,418010&dq=isabell-masters&hl=en. Retrieved 12 July 2011.
- ^ Dillin, John (February 18, 1988). "Even with win, Bush seen to be vulnerable". Christian Science Monitor: p. 1.
- ^ Webster G. Tarpley and Anton Chaitkin. "George Bush: The Unauthorized Biography: Chapter XXII Bush Takes The Presidency". Webster G. Tarpley. http://www.tarpley.net/bush22.htm. Retrieved 2006-12-17.
- ^ Dowd, Maureen (June 11, 1988). "Bush Traces How Yale Differs From Harvard". The New York Times: p. 10. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/06/11/us/bush-traces-how-yale-differs-from-harvard.html
- ^ Baker, Russell (June 15, 1988). "The Ivy Hayseed". The New York Times: p. A31. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/06/15/opinion/observer-the-ivy-hayseed.html
- ^ Bradlee, Ben, Jr.; Fred Kaplan (September 14, 1988). "Dukakis spells out Soviet policy". The Boston Globe.
- ^ Safire, William (September 15, 1988). "Rat-Tat-Tatting". The New York Times: p. A35. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/09/15/opinion/essay-rat-tat-tatting.html.
- ^ Dowd, Maureen (September 17, 1988). "Bush Talks of Lasers and Bombers". The New York Times: p. 8. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/09/17/us/bush-talks-of-lasers-and-bombers.html.
- ^ Mapes, Jeff (August 17, 1988). "Bush taps Quayle for VP". The Oregonian: p. A01.
- ^ Toner, Robin (October 7, 1988). "Quayle Reflects Badly on Bush, Dukakis Asserts". The New York Times: p. B6. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/10/07/us/quayle-reflects-badly-on-bush-dukakis-asserts.html.
- ^ "Dan Quayle in the Vice Presidential Debate". The History Channel: Video and Speeches. A&E Television Networks. http://www.historychannel.com/broadband/clipview/index.jsp?id=0906. Retrieved March 17, 2004.[dead link]
- ^ Sanders, Joshunda (July 4, 2004). "State's Dems still hope for a bit of suspense / A contested primary is viewed as a plus for party". The San Francisco Chronicle. http://articles.sfgate.com/2004-07-04/living/17434097_1_pots-in-american-politics-campaign-manager-john-kerry.
- ^ Conason, Joe (July/August 1992). "Reason No. 1 Not To Vote For George Bush: He Cheats on His Wife." Spy magazine.
- ^ Kurtz, Howard (August 12, 1992). "Bush Angrily Denounces Report of Extramarital Affair as 'a Lie'". Washington Post
- ^ "Story on Mrs. Dukakis Is Denied by Campaign". New York Times. August 26, 1988. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/08/26/us/story-on-mrs-dukakis-is-denied-by-campaign.html
- ^ "Bush Edge Is Holding In Survey". The New York Times: p. 24. October 23, 1988. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/10/23/us/bush-edge-is-holding-in-survey.html.
- ^ Hirshson, Paul (October 19, 1988). "Editors on Dukakis: Down, but not out". The Boston Globe: p. 29.
- ^ http://www.multied.com/elections/1988.html
- ^ Athitakis, Mark (1999-08-11). "Booty Call". SF Weekly (Village Voice Media). http://www.sfweekly.com/issues/1999-08-11/music4_2.html. Retrieved 2006-03-21.
- ^ Fulani, Lenora (1992). The Making of a Fringe Candidate. pp. 127. ISBN 0962862134.
- ^ "Political Party History in Alaska". Internet Archive copy of official website of Alaska Division of Elections. 2003. Archived from the original on July 1, 2004. http://web.archive.org/web/20040701172615/http://www.gov.state.ak.us/ltgov/elections/partysta.htm. Retrieved March 24, 2006.
Further reading
- Germond, Jack W., and Jules Witcover. Whose Broad Stripes and Bright Stars? (1989), narrative by two famous reporters
- Gopoian, J. David. "Images and issues in the 1988 presidential election," Journal of Politics, Feb 1993, Vol. 55 Issue 1, pp 151–66
- Lemert, James B.; Elliott, William R.; Bernstein, James M.; Rosenberg, William L.; Nestvold, Karl J. (1991). News Verdicts, the Debates, and Presidential Campaigns. New York: Praeger. ISBN 0275937585
- Moreland, Laurence W.; Steed, Robert P.; Baker, Tod A. (1991). The 1988 Presidential Election in the South: Continuity Amidst Change in Southern Party Politics. New York: Praeger. ISBN 0275931455
- Runkel, David R. (1989). Campaign for President: The Managers Look at '88. Dover: Auburn House. ISBN 0865691940
- Stempel, Guido H. III; Windhauser, John W. (1991). The Media in the 1984 and 1988 Presidential Campaigns. New York: Greenwood Press. ISBN 0313265275
External links
- The Election Wall's 1988 Election Video Page
- 1988 popular vote by counties
- 1988 popular vote by state
- 1988 popular vote by states (with bar graphs)
- Campaign commercials from the 1988 election
- How close was the 1988 election? — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Senator Paul Simon Papers at Southern Illinois University Carbondale
 United States presidential elections
United States presidential elections1788 · 1792 · 1796 · 1800 · 1804 · 1808 · 1812 · 1816 · 1820 · 1824 · 1828 · 1832 · 1836 · 1840 · 1844 · 1848 · 1852 · 1856 · 1860 · 1864 · 1868 · 1872 · 1876 · 1880 · 1884 · 1888 · 1892 · 1896 · 1900 · 1904 · 1908 · 1912 · 1916 · 1920 · 1924 · 1928 · 1932 · 1936 · 1940 · 1944 · 1948 · 1952 · 1956 · 1960 · 1964 · 1968 · 1972 · 1976 · 1980 · 1984 · 1988 · 1992 · 1996 · 2000 · 2004 · 2008 · 2012
Electoral College · Electoral vote changes · Electoral votes by state · Results by Electoral College margin · Results by popular vote margin · Results by state · Voter turnout · Presidential primaries · Presidential nominating conventionsSee also: House elections · Senate elections · Gubernatorial electionsCategories:- United States presidential election, 1988
- History of the United States (1980–1991)
- 1988 elections in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.