- NC-4
-
- For other uses, see NC 4 (disambiguation).
NC-4 The NC-4 after her return to the U.S.A., 1919 Type Curtiss NC Manufacturer Curtiss The NC-4 was a Curtiss NC flying boat which was designed by Glenn Curtiss and his team, and manufactured by Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. In May 1919, the NC-4 became the first aircraft to fly across the Atlantic Ocean, starting in the United States and making the crossing as far as Lisbon, Portugal, in 19 days. This included time for numerous repairs and for crewmen's rest, with stops along the way in Nova Scotia, Newfoundland, and twice in the Azores Islands. Then its flight from the Azores to Lisbon completed the first transatlantic flight between North America and Europe, and two more flights from Lisbon to northeastern Spain to Plymouth, England, completed the first flight between North America and Great Britain.
The accomplishment of the naval aviators of the NC-4 was somewhat eclipsed in minds of the public by the first nonstop transatlantic flight, which took 15 hours and 57 min and was made by the British pilots John Alcock and Arthur Whitten Brown, two weeks later. [N 1]
Contents
Background
The NC-4's transatlantic capability was the result of developments that began before World War I. In 1908 Curtiss had unsuccessfully experimented with floats on the airframe of an early June Bug craft, but his first successful take off was not achieved until 1911 with an A-1 fitted with a central pontoon. In January 1912 he first flew his first hulled "hydro-aeroplane", which led to an introduction with the retired English naval officer John Cyril Porte who was looking for a partner to produce an aircraft with him in order to win the Daily Mail prize for the first transatlantic crossing. Porte improved the hull, including an innovative hull step for breaking clear of the water at takeoff. They were joined by Lt John H Towers of the US Navy as a test pilot. This "America" flying boat of 1914 was a larger craft with two pusher engines, with which they hoped to claim the transatlantic prize.[1]
Development stopped on the outbreak of war in Europe later that year. Porte, now back in the Royal Navy's flying arm the RNAS, commissioned more flying boats from Curtiss, which could be used for long-range anti-submarine and Zeppelin patrols. Porte modified these and developed them into his own range of Felixstowe flying boats with more powerful engines, longer range and better handling characteristics. The design was shared with Curtiss, who built these improved models under license, selling them to the US government.
This culminated in the NC-4, the fourth of the Navy's first series of four medium-sized Curtiss NC floatplanes made for the Navy by the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. The NC-4 made its first test flight on 30 April 1919.[2]
After the end of the war and with several of the new Curtiss NC aircraft on its hands, the officers in charge of the U.S. Navy decided to demonstrate their capability of transatlantic flight. However they allowed stops for meals and overnight sleeping, and also to refuel and carry out maintenance on the aircraft.
The Transatlantic flight
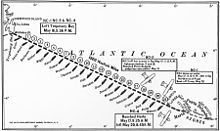
The U.S. Navy's transatlantic flight expedition began on 8 May 1919. The NC-4 started out in the company of two other Curtiss NCs, the NC-1 and the NC-3 (with the NC-2 having been cannibalized for spare parts to repair the NC-1 before this group of planes had even left New York City). The three aircraft left from the Naval Air Station Rockaway,[3] with intermediate stops at the Chatham Naval Air Station, Massachusetts and Halifax, Nova Scotia, before flying on to Trepassey, Newfoundland, on 15 May. Eight U.S. Navy warships were stationed along the east coast of North America to help the Curtiss NCs in navigation and to assist their crewmen in case of any emergency.[4]
The "base ship" or the flagship for all of the Navy ships that had been assigned to support the flight of the Curtis NCs was the large, former minelayer USS Aroostook (CM-3), which the U.S. Navy converted into an aircraft tender immediately before the flight of the Curtis NCs. With a displacement of over 3,000 tons, the Aroostook was much larger than the several squadrons of U.S. Navy destroyers of that time, that had been assigned to support the transatlantic flight attempt. Before the Curtiss NCs took off from New York, the Aroostook had been sent to Trepassey, Newfoundland, to await their arrival there, and then provide refueling, relubrication, and maintenance work on the NC-1, NC-3 and NC-4. She then steamed across the Atlantic to pick up the NC-4 in England. [5]
On 16 May, the three Curtiss NCs departed on the longest leg of their journey, from Newfoundland to the Portuguese Azores Islands in the mid-Atlantic. Twenty-two more U.S. Navy ships, mostly destroyers, were stationed at about 50-mile (80 km) spacings along this route.[6] These "station ships" were brightly illuminated during the nighttime; their sailors shone the ships' searchlights into the sky, and they also fired star shells into the sky to help the aviators to stay on their intended flight route.[7]
After flying all night and most of the next day, the NC-4 reached Horta, Faial Island, in the Azores on the following afternoon, having covered about 1,200 miles (1,920 km): It had taken 15 hours and 18 minutes to cover this leg, the aircraft having encountered thick fog banks along the route. Both the NC-1 and the NC-3 had been forced to land on the ocean due to rough flying weather.
The crewmen of the NC-1 were rescued by the Greek freighter SS Ionia; the NC-1 was taken in tow but sank three days later.[7][8] The pilots of the "NC-3" "taxied" their aircraft on its floats the rest of the way to the Azores, where it was taken in tow by a U.S. Navy ship.[7]
Three days later on 20 May, the NC-4 took off bound for Lisbon, but it was forced by mechanical problems to land again at Ponta Delgada, São Miguel Island, in the Azores, having covered only about 150 miles (240 km). After days of delays for repairs, the NC-4 took off again on 27 May, again aided by the station ships of the U.S. Navy: 13 ships distributed between the Azores and Lisbon.[6] The NC-4 had no further serious problems, and it landed at Lisbon harbor after a flight of nine hours and 43 minutes, becoming the first aircraft of any kind to fly across the Atlantic Ocean - or any other ocean.
The part of this flight just from the Island of Newfoundland to Lisbon on the European mainland had taken a total time 10 days and 22 hours, but with the actual flight time being just 26 hours and 46 minutes.
The "NC-4" later flew on to England, arriving in Plymouth on 31 May to great fanfare,[9] having taken 23 days for the flight from Newfoundland to Great Britain. For the final legs (from Lisbon to Ferrol, Spain, and then from Ferrol to Plymouth), 10 more U.S. Navy ships were stationed along the route. In total of 53 U.S. Navy warships had been stationed along the route from New York City to Plymouth.[6]
Most of the flight route taken by the NC-4 was indicated on the map of the North Atlantic published by Flight magazine on 29 May 1919, while the NC-4 was still at the mainland of Portugal.[10]
The feat of making the first transatlantic flight was somewhat eclipsed shortly afterwards by the first nonstop transatlantic flight by John Alcock and Arthur Whitten Brown in a faster Vickers Vimy biplane, when they flew from Newfoundland to Ireland nonstop on 14–15 June 1919, in 16 hours and 27 minutes. Consequently, Alcock and Brown won a prize of £10,000 pounds sterling offered by the Daily Mail newspaper, which had been first announced in 1913, and then renewed in 1918, to "the aviator who shall first cross the Atlantic in an aeroplane in flight from any point in the United States, Canada, or Newfoundland to any point in Great Britain or Ireland, in 72 consecutive hours."[11][12] The conditions also stipulated that "only one aircraft may be used for each attempt."
Alcock and Brown also made their flight nonstop, even though this was not specified in the rules given by the Daily Mail. Conceivably, Alcock and Brown (or someone else) could have made stops on Iceland and/or Greenland along the way for refueling, as long as they completed the entire flight within 72 hours. The rule that "only one aircraft may be used" eliminated the possibility of having fresh aircraft, with their fuel tanks already topped off, and new oil in their crankcase(s), waiting for pilots to change from one exhausted airplane to a fresh one.
The Curtiss NCs had not been entered into the above competition - because the U.S. Navy never planned for their flight to be completed in fewer than 72 hours, because this was completely impractical. For example, flying for 15 hours, 18 minutes, from Newfoundland to the Azones was an exhausting experience, requiring meals and sleep afterward. Also, as we have seen, after taking off from the Azores the first time, the "NC-4" experienced mechanical problems and hence had to land again at another of those islands for several days of repairs. Hence, just making a reasonable allowance beforehand for the probable requirement of a lot of repair work on the Curtis NCs, plus the flight time, plus the rest time required, plus the additional time that it took to fly from Lisbon to England, ruled out the possibility of any of the Curtis NCs making the flight from Newfoundland to southern England in under 72 hours.
A 1945 newsreel covering various firsts in human flight, including footage of the flight across the AtlanticThe Crewmen on the NC-4
The crewmen of the NC-4 were Albert Cushing Read, the commander and navigator; Walter Hinton and Elmer Fowler Stone, the two pilots; James L. Breese and Eugene T. "Smokey" Rhoads, the two flight engineers; and Herbert C Rodd, the radio operator. Earlier, E.H. Howard had been chosen go as one of the flight engineers, but Howard had one of his hands cut off by an aircraft propeller in a bad accident in New York, consequently, he was replaced by Smokey Rhoads in the crew.
After the crossing
 An engine, one of the floats, and one wing of the NC-4 in the National Museum of Naval Aviation, Pensacola, in 1997.
An engine, one of the floats, and one wing of the NC-4 in the National Museum of Naval Aviation, Pensacola, in 1997.
After arriving at Plymouth, England, the crewmen of the NC-4, who had been reunited with the crewmen of the less-successful NC-1 and NC-3, went by train to London, and there they received a tumultuous welcome. Next, they visited Paris, France, for more acclaim.
The NC-4 was dismantled in Plymouth, and then loaded onto the aircraft tender USS Aroostook, the base ship for the Curtis NC's transatlantic flight, [13] for the return journey to the United States. The Aroostook arriving in New York Harbor on 2 July 1919.[14]
Following the return of the three aircrews on board the USS Zeppelin, a goodwill tour of the East Coast of the United States and the Gulf Coast was carried out by the crewmen. [4]
In 1929, to honor the men of this first transatlantic flight, the U.S. Navy created a special military decoration known as the NC-4 Medal.[15]
The NC-4 is property of the Smithsonian Institution, since it was given to that institution by the U.S. Navy after its return to the United States. However, the aircraft was too large to be housed in either the older Smithsonian Arts & Industries Building in Washington, D.C., or in its successor, the National Air and Space Museum, also in Washington. A model of the NC-4 is kept in the Milestones of Flight Gallery in the National Air and Space Museum, a place of honor, along with the original Wright Flyer of 1903; Charles Lindbergh's Spirit of St. Louis of 1927; and Chuck Yeager's Glamorous Glennis X-1 rocket aircraft of 1947. The fully reassembled NC-4 is on loan from the Smithsonian to the National Museum of Naval Aviation in Pensacola, Florida.
Operators
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: six
- Length: 68 ft 5½ in (20.8 m)
- Wingspan: (38.40 m)
- Height: 24 ft 5⅛ in (7.40 meter)
- Wing area: 2,380 square feet (221 square meters)
- Empty weight: 15,874 lb (7,260 kg)
- Loaded weight: 28,000 lb[16] (12,700 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 27,386 lb (12,422 kg)
- Powerplant: × Four Liberty L-12 400 hp water-cooled V-12 engines, 400 hp (300 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 84 knots
- Stall speed: 54 knots (62 mph, 100 km/h)
- Range: 1,278 nautical miles (1,470 miles, 2,352 km)
- Service ceiling: 4,500 feet (1,370 meters)
- Wing loading: 11.5 lb/ft² (56.3 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.06 hp/lb (0.01 kW/kg)
Armament
machine guns in front and rear cockpits; provision for depth charges in wartime
References
- Notes
- ^ Alcock and Brown's flight was between Newfoundland and Ireland (both of which are islands), whereas the NC-4 traveled from Long Island via Nova Scotia, Newfoundland and the Azores to the mainland of Europe (in Portugal), assisted by 21 US warships spaced on average about 57 nautical miles (106 km) apart along the whole route over the open ocean.
- Citations
- ^ "The Felixstowe Flying-boats." Flight Magazine archive, 2 December 1955.
- ^ "Chapter II: A Boat With Wings, p. 27." The Flight Across the Atlantic. Hammondsport, New York: Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Corporation, 1919. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ The Rockawy Naval Air Station was later abandoned by the Navy and made a part of the Gateway National Recreation Area
- ^ a b Turnbull and Lord 1949, p. 125.
- ^ Vance 2002, p. 75.
- ^ a b c "First across the Atlantic." bluejacket.com. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ a b c "... the Atlantic fleet, strung out like pearls, with its brightly-illuminated ships posted fifty miles apart along the Nancys' flight path... clearly marked by Navy destroyers' search lights and star-burst shells." patspalace.com. Retrieved" 13 May 2011.
- ^ "NC-4." Aviation History website. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ Nevin 1980, p. 23.
- ^ "Map of the North Atlantic." flightglobal.com. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ "50,000 for Flight across Atlantic." The New York Times, 1 April 1913. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ "₤10,000 for first transatlantic flight (in 72 consecutive hours)." Flight magazine, 21 November 1918, p. 1316. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ "Aroostook." Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships, Department of the Navy - Naval Historical Center. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ "Mine layer brings NC-4." The New York Times, 3 July 1919. Retrieved: 12 September 2010.
- ^ "The United States of America: NC-4 Medal." medals.org. Retrieved: 13 May 2011.
- ^ Smith 1973
- Bibliography
- Nevin, David. The Pathfinders (The Epic of Flight series). Alexandria, Virginia: Time Life Books, 1980. ISBN 0-80943-526-0.
- Smith, Richard K. First Across: The U.S. Navy's Transatlantic Fight of 1919. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1973.
- Turnbull, Archibald D., Captain, USNR and Clifford L. Lord, Lt. Commander, USNR. History of United States Naval Aviation. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press, 1949.
- Vance, Jonathan. High Flight. Toronto, Ontario: Penguin of Canada, 2002. ISBN 978-0143013457.
External links
- First flight across the Atlantic
- Forgotten Flyers of 1919
- NC-4 on Naval Aviation Museum site
- Albert C. Read and the NC-4 on Early Aviators site, with good photographs
- Navy-Curtiss NC-4 Flying Boat on aviation-history.com
- History Detectives . Investigations - NC-4: First Across the Atlantic - PBS
Related content
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Seaplanes and flying boats
- Congressional Gold Medal recipients
- Rockaway, Queens
- United States Coast Guard Aviation
- Individual aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.