- Districts of Sri Lanka
-
Sri Lanka 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
Sri LankaConstitutionJudiciaryPolitical partiesSubdivisionsForeign policyRelated issues
In Sri Lanka, districts (Sinhala: දිස්ත්රික්ක, Tamil: மாவட்ட) are the second-level administrative divisions, and are included in a province. There are 25 districts organized into 9 provinces.[1] Each district is administered under a District Secretary,[2] who is appointed by the central government.[3] The main tasks of the District Secretariat involve coordinating communications and activities of the central government and Divisional Secretariats. The District Secretariat is also responsible for implementing and monitoring development projects at the district level and assisting lower-level subdivisions in their activities,[4] as well as revenue collection and coordination of elections in the district.[5] A district is divided into a number of Divisional Secretary Divisions (commonly known as DS divisions), which are in turn subdivided into Grama Niladari Divisions.[6] There are 256 DS divisions in the country.[1]
Contents
History
The country was first divided into several administrative units during the Anuradhapura Kingdom. The kingdom was divided into three provinces; Rajarata, Ruhuna and Malaya Rata. These were further subdivided into smaller units called rata.[7] Over time, the number of provinces increased, but the second-level administrative division continued to be the rata. However, with the country eventually being divided into more than one kingdom and with foreign colonial missions landing and taking parts of the country under their control, this structure began to change. The territory of the Kotte Kingdom was organized into four disavas, which were further subdivided into forty korales. The korales had their own civil and military officials with a small militia. The Jaffna kingdom appears to have had a similar administrative structure to this with four provinces.[8]
When the Portuguese took over parts of the country after their arrival in 1505,[9] they maintained more or less the same administrative structure followed by Sri Lankan rulers.[10] During the Dutch rule in the country, the terrain under their control was divided into three administrative divisions. These were subdivided into disavas as in earlier systems.[11] The British initially continued this system,[12] but following reforms in 1796 to 1802, the country was divided according to ethnic composition.[13][14] This was abolished by the Colebrook–Cameron reforms in 1833 and a legislative council was created,[15] making the island a politically and administratively single unit. Five provinces were created, later expanded into nine, and these were subdivided into twenty-one districts. These districts were administered by officials known as Government Agents or Assistant Government Agents.[13]
In 1955, the district replaced the province as the country's main administrative unit.[16] The Ampara district was created in 1958, followed by the creation of Mullaitivu and Gampaha districts in 1978[17] through a new constitution, which also reintroduced the province as the main administrative unit.[18] The last district to be created was Kilinochchi in 1983,[19] and the current constitution (that of 1978) states that the territory of Sri Lanka consists of 25 administrative districts. These districts may be subdivided or amalgamated by a resolution of the Parliament of Sri Lanka.[20]
Districts
All population data are from the most recent census of Sri Lanka, in 2001. The districts of Jaffna, Mullaitivu and Kilinochchi were not covered in this census because of security reasons, and Batticaloa, Trincomalee, Vavuniya and Mannar were only partially covered. Therefore, the population statistics for these districts are estimates.[21] These are marked by a * symbol.
Map of Sri Lanka showing provinces and districts.
 Map of Sri Lanka showing provinces.
Map of Sri Lanka showing provinces.
Name Area map Province District
capitalLand area Inland water
areaTotal area Population Population
density[N 1]Ampara 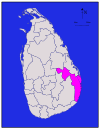
Eastern Ampara 4,222 km2 (1,630 sq mi) 193 km2 (75 sq mi) 4,415 km2 (1,705 sq mi) 592,997 140 /km2 (363 /sq mi) Anuradhapura 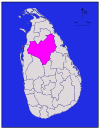
North Central Anuradhapura 6,664 km2 (2,573 sq mi) 515 km2 (199 sq mi) 7,179 km2 (2,772 sq mi) 745,693 112 /km2 (290 /sq mi) Badulla 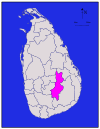
Uva Badulla 2,827 km2 (1,092 sq mi) 34 km2 (13 sq mi) 2,861 km2 (1,105 sq mi) 779,983 276 /km2 (715 /sq mi) Batticaloa 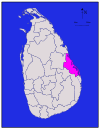
Eastern Batticaloa 2,610 km2 (1,010 sq mi) 244 km2 (94 sq mi) 2,854 km2 (1,102 sq mi) 486,447 * 186 /km2 (482 /sq mi) Colombo 
Western Colombo 676 km2 (261 sq mi) 23 km2 (8.9 sq mi) 699 km2 (270 sq mi) 2,251,274 3,330 /km2 (8,625 /sq mi) Galle 
Southern Galle 1,617 km2 (624 sq mi) 35 km2 (14 sq mi) 1,652 km2 (638 sq mi) 990,487 613 /km2 (1,588 /sq mi) Gampaha 
Western Gampaha 1,341 km2 (518 sq mi) 46 km2 (18 sq mi) 1,387 km2 (536 sq mi) 2,063,684 1,539 /km2 (3,986 /sq mi) Hambantota 
Southern Hambantota 2,496 km2 (964 sq mi) 113 km2 (44 sq mi) 2,609 km2 (1,007 sq mi) 526,414 211 /km2 (546 /sq mi) Jaffna 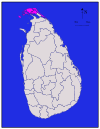
Northern Jaffna 929 km2 (359 sq mi) 96 km2 (37 sq mi) 1,025 km2 (396 sq mi) 490,621 * 528 /km2 (1,368 /sq mi) Kalutara 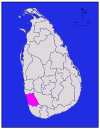
Western Kalutara 1,576 km2 (608 sq mi) 22 km2 (8.5 sq mi) 1,598 km2 (617 sq mi) 1,066,239 677 /km2 (1,753 /sq mi) Kandy 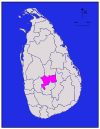
Central Kandy 1,917 km2 (740 sq mi) 23 km2 (8.9 sq mi) 1,940 km2 (750 sq mi) 1,279,028 667 /km2 (1,728 /sq mi) Kegalle 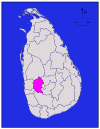
Sabaragamuwa Kegalle 1,685 km2 (651 sq mi) 8 km2 (3.1 sq mi) 1,693 km2 (654 sq mi) 785,524 466 /km2 (1,207 /sq mi) Kilinochchi 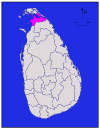
Northern Kilinochchi 1,205 km2 (465 sq mi) 74 km2 (29 sq mi) 1,279 km2 (494 sq mi) 127,263 * 106 /km2 (275 /sq mi) Kurunegala 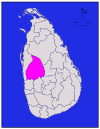
North Western Kurunegala 4,624 km2 (1,785 sq mi) 192 km2 (74 sq mi) 4,816 km2 (1,859 sq mi) 1,460,215 316 /km2 (818 /sq mi) Mannar 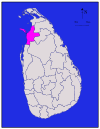
Northern Mannar 1,880 km2 (730 sq mi) 116 km2 (45 sq mi) 1,996 km2 (771 sq mi) 151,577 * 81/km2
(208/sq mi)Matale 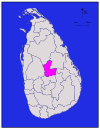
Central Matale 1,952 km2 (754 sq mi) 41 km2 (16 sq mi) 1,993 km2 (770 sq mi) 441,328 226 /km2 (585 /sq mi) Matara 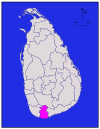
Southern Matara 1,270 km2 (490 sq mi) 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) 1,283 km2 (495 sq mi) 761,370 600 /km2 (1,554 /sq mi) Moneragala 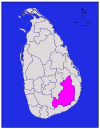
Uva Moneragala 5,508 km2 (2,127 sq mi) 131 km2 (51 sq mi) 5,639 km2 (2,177 sq mi) 397,375 72 /km2 (186 /sq mi) Mullaitivu 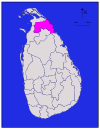
Northern Mullaitivu 2,415 km2 (932 sq mi) 202 km2 (78 sq mi) 2,617 km2 (1,010 sq mi) 121,667 * 50 /km2 (129 /sq mi) Nuwara Eliya 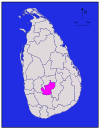
Central Nuwara Eliya 1,706 km2 (659 sq mi) 35 km2 (14 sq mi) 1,741 km2 (672 sq mi) 703,610 412 /km2 (1,067 /sq mi) Polonnaruwa 
North Central Polonnaruwa 3,077 km2 (1,188 sq mi) 216 km2 (83 sq mi) 3,293 km2 (1,271 sq mi) 358,984 117 /km2 (303 /sq mi) Puttalam 
North Western Puttalam 2,882 km2 (1,113 sq mi) 190 km2 (73 sq mi) 3,072 km2 (1,186 sq mi) 709,677 246 /km2 (637 /sq mi) Ratnapura 
Sabaragamuwa Ratnapura 3,236 km2 (1,249 sq mi) 39 km2 (15 sq mi) 3,275 km2 (1,264 sq mi) 1,015,807 314 /km2 (813 /sq mi) Trincomalee 
Eastern Trincomalee 2,529 km2 (976 sq mi) 198 km2 (76 sq mi) 2,727 km2 (1,053 sq mi) 340,158 * 135/km2
(349/sq mi)Vavuniya 
Northern Vavuniya 1,861 km2 (719 sq mi) 106 km2 (41 sq mi) 1,967 km2 (759 sq mi) 149,835 * 81/km2
(208/sq mi)Total 62,705 km2 (24,211 sq mi) 2,905 km2 (1,122 sq mi) 65,610 km2 (25,330 sq mi) 18,797,257 300 /km2 (777 /sq mi) See also
- Provinces of Sri Lanka
- ISO 3166-2:LK
Notes
- ^ Population density has been calculated using the land area rather than the total area.
Citations
- ^ a b "Sri Lanka in Brief". The Government of Sri Lanka. http://www.priu.gov.lk/TourCountry/Indextc.html. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ "District Secretariats". District and Divisional Secretariats Portal—Ministry of Public Administration and Home Affairs. http://www.ds.gov.lk/dis_sec/dis_eng/District_Secretariats.php. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ "Kilinochchi a brief look". Daily News. 2009-04-27. http://www.dailynews.lk/2009/04/27/Visit.asp?id=s02. Retrieved 2009-08-01.
- ^ "District Secretariat—Vavuniya". District and Divisional Secretariats Portal—Ministry of Public Administration and Home Affairs. http://www.ds.gov.lk/dist_vavuniya/english/about_us.html. Retrieved 2009-07-29.
- ^ "Performs Report and Accounts—2008" (PDF). District and Divisional Secretariats Portal—Ministry of Public Administration and Home Affairs. http://www.ds.gov.lk/uploads/karayasadana_english_.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-29.
- ^ "Identification of DS Divisions of Sri Lanka Vulnerable for food insecurity" (PDF). World Food Program. http://documents.wfp.org/stellent/groups/public/documents/vam/wfp173167.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ Siriweera (2004), p. 91
- ^ Yogasundaram (2006), p. 170
- ^ Hewavissenti, Panchamee (2008-02-03). "Episodes of colonised history". Sunday Observer. http://www.sundayobserver.lk/2008/02/03/imp02.asp. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ Yogasundaram (2006), p. 168
- ^ Yogasundaram (2006), p. 195
- ^ Yogasundaram (2006), p. 214
- ^ a b Yogasundaram (2006), p. 258
- ^ Peebles (2006), p. 48
- ^ Peebles (2006), p. 52
- ^ Peebles (2006), p. 110
- ^ "Population by sex and district, census years" (PDF). Department of Census and Statistics—Sri Lanka. http://www.statistics.gov.lk/Abstract_2008_PDF/abstract2008/table%202008/Chap%202/AB2-1.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-06.[dead link]
- ^ Schmiegelow, Michèle (1997). Democracy in Asia. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 425. ISBN 0312164955.
- ^ "Amendments to the 1978 constitution". The Government of Sri Lanka. http://www.priu.gov.lk/Cons/1978Constitution/AMENDMENTS.html#Seventh%20Amendment. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ "The Constitution of Sri Lanka—Chapter 1". The Government of Sri Lanka. http://www.priu.gov.lk/Cons/1978Constitution/Chapter_01_Amd.html#1. Retrieved 2009-07-21.
- ^ Europa Publications Staff, ed (2002). Far East and Australasia 2003. Routledge. p. 1524. ISBN 1857431332. http://books.google.com/books?id=LclscNCTz9oC&pg=PA1524&dq=%22Sri+Lanka%22%2B%2225+Districts%22.
References
- "Population by District, Sex, Sex Ratio and Population Density" (PDF). Census of Population and Housing 2001. Department of Census and Statistics—Sri Lanka. http://www.statistics.gov.lk/PopHouSat/PDF/Population/p9p2%20Population%20by%20district%20,%20sex,%20sex%20ratio%20and%20population%20density.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- "Area of Sri Lanka by province and district" (PDF). Survey Department of Sri Lanka. Department of Census and Statistics—Sri Lanka. http://www.statistics.gov.lk/Abstract_2008_PDF/abstract2008/table%202008/Chap%201/ab1-1.pdf. Retrieved 2009-09-23.[dead link]
- "Administrative Districts and Main Towns of Sri Lanka". International Centre for Ethnic Studies. http://www.ices.lk/sl_database/maps/towns.shtml. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- Siriweera, W. I. (2004). History of Sri Lanka. Dayawansa Jayakodi & Company. ISBN 955-551-257-4.
- Yogasundaram, Nath (2006). A Comprehensive History of Sri Lanka. Vijitha Yapa Publishers. ISBN 978-955-665-002-0.
- Peebles, Patrick (2006). The History of Sri Lanka. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 0313332053. http://books.google.lk/books?id=6ERtz5mld8AC&pg=PA53&lpg=PA53&dq=%22Thomas+Maitland%22%2B1805%2Bethnic+composition&source=bl&ots=C6yuDqwbeY&sig=X64Uvl9oDQ3xfBP_FpDKZ-PgQFI&hl=en&ei=LCplStvPFoy4NaXq7acB&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6.
External links
Districts of Sri Lanka Central (Kandy • Matale • Nuwara Eliya) · Eastern (Ampara • Batticaloa • Trincomalee) · North Central (Anuradhapura • Polonnaruwa) · Northern (Jaffna • Kilinochchi • Mannar • Mullaitivu • Vavuniya) · North Western (Kurunegala • Puttalam) · Sabaragamuwa (Kegalle • Ratnapura) · Southern (Galle • Hambantota • Matara) · Uva (Badulla • Moneragala) · Western (Colombo • Gampaha • Kalutara)
Articles on second-level administrative divisions of Asian countries Afghanistan · Armenia2 · Bangladesh · Bhutan · Brunei · Burma · Cambodia · People's Republic of China · Cyprus1 · Egypt1 · Georgia1 · India · Indonesia · Iran · Iraq · Israel · Japan · Jordan · Kazakhstan1 · North Korea · South Korea · Kuwait · Kyrgyzstan · Laos · Lebanon · Malaysia · Mongolia · Nepal · Oman · Pakistan · Philippines · Russia1 · Saudi Arabia · Sri Lanka · Syria · Taiwan · Tajikistan · Thailand · Timor-Leste (East Timor) · Turkey1 · Turkmenistan · Uzbekistan · Vietnam · Yemen
1 Country spanning more than one continent (transcontinental country).
Sri Lanka topics History TimelinePrehistory · Dipavamsa · Mahavamsa · Culavamsa · Vijaya · Portuguese Ceylon · Dutch Ceylon · British Ceylon · Kandyan Wars · Uva Rebellion · Matale Rebellion · Independence movement · Dominion of Ceylon · Civil WarkingdomsKingdom of Tambapanni · Kingdom of Upatissa Nuwara · Anuradhapura Kingdom · Kingdom of Polonnaruwa (Kingdom of Jaffna · Kingdom of Ruhuna) · Kingdom of Dambadeniya · Kingdom of Gampola · Kingdom of Raigama · Kingdom of Kotte · Kingdom of Sitawaka · Kingdom of KandyTopicsGovernment Politics Elections · Parliament · President of Sri Lanka (current) · Prime Minister (current) · Foreign relations · Elections · Political parties · Supreme Court · PoliceGeography LandformsExtreme points · Mountains · Islands · Rivers · Waterfalls
EnvironmentEconomy Central Bank of Sri Lanka · Sri Lankan rupee · Colombo Stock Exchange · Agriculture · Ceylon tea · Gems · Communications · Power stations · Companies · Banking · Insurance · Standard of living · Tourism · Buildings · Transportation (Airports · A-Grade Highways · Passenger vehicles · Railroads)Society Crime · Demographics (Ethnic groups in Sri Lanka) · Education (schools · universities) · Health care · Languages (Sri Lankan English) · Media · People (List of Sri Lankans) · Public holidays · Religion (Buddhism · Hinduism · Islam) · Social class · Sports (Cricket · Rugby) · BirthCulture Architecture (Ancient architecture / constructions (stupas)) · Television / Cinema · Cuisine · Dance · Folklore · Fashion · Literature · Music · Scouting · World Heritage Sites · Poetry · Radio · Visual artsSymbols Other topics Human rights · ResearchCategories:- Districts of Sri Lanka
- Lists of country subdivisions
- Country subdivisions of Asia
- Second-level administrative country subdivisions
- Lists of places in Sri Lanka
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

