- Cyclospora cayetanensis
-
Cyclospora cayetanensis 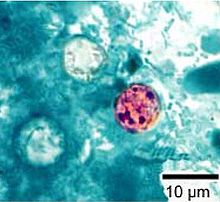
Cyclospora cayetanensis oocysts Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Chromalveolata Superphylum: Alveolata Phylum: Apicomplexa Class: Conoidasida Subclass: Coccidiasina Order: Eucoccidiorida Suborder: Eimeriorina Family: Eimeriidae Genus: Cyclospora Species: C. cayetanensis Binomial name Cyclospora cayetanensis Cyclospora cayetanensis is a protozoan that causes disease in humans, and perhaps other primates. It has been linked in the United States from fecally-contaminated imported raspberries and was virtually unknown before about 1990, but has been on the rise since. The health risk associated with the disease is usually confined to adult foreigners visiting endemic regions and acquiring the infection: this is why C. cayetanensis has been labeled as causing “traveler’s diarrhea.”
This species was placed in the Cyclospora genus because of the spherical shape of its sporocysts. The species name refers to the Cayetano Heredia University in Lima, Peru, where early epidemiological and taxonomic work was done.[1]
Contents
Characterization
Cyclospora cayentanensis is an apicomplexan, cyst-forming coccidian protozoan that causes a self-limiting diarrhea. Morphologically speaking, C. cayetanensis has spherical oocysts that are between 7.5 and 10 micrometers in diameter that also have a 50 nanometer thick wall with an outer threadlike coat that has been called a wrinkle by some researchers.
The only hosts C. cayentanensis uses are humans. The protozoan lives out its lifecycle intracellularly within the host’s epithelial cells and gastrointestinal tract. Infection is transmitted through the oral-fecal route, and begins when a person ingests oocysts in fecally contaminated food or water. Various chemicals in the host's gastrointestinal tract cause the oocysts to excyst and release sporozoites; generally, two are observed per oocyst. After these sporozoites invade the epithelial cells, they undergo merogony, a form of asexual reproduction that results in many daughter merozoites. These daughter cells may either infect new host cells and initiate yet another round of merogony, or they can take on a sexual track via gametogony: daughter merozoites become male macrogamonts — which form many microgametes — and female macrogamonts. After fertilization has occurred via male microgamete fusion with female macrogamont, the zygote matures into an oocyst and ruptures the host cell, from which point it is passed with the stool. The oocysts that are passed are not, however, immediately infectious. Sporulation can take anywhere from one to several weeks, meaning that person-to-person transmission is not a likely problem. This differentiates C. cayentanensis from Cryptosporidium parvum — a closely related organism that causes a similar disease — since C. parvum oocysts are immediately infectious upon release from the host.
Symptoms
C. cayentanensis causes gastroenteritis, with the extent of the illness varying based on age, condition of the host, and size of the infectious dose. Symptoms include "watery diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal bloating and cramping, increased flatulence, nausea, fatigue, and low-grade fever," though this can be augmented in more severe cases by vomiting, substantial weight loss, explosive diarrhea, and muscle aches. Typically, patients who come in with a persistent watery diarrhea lasting over several days may be suspected of harboring the disease, especially if they have traveled to a region where the protozoan is endemic. The incubation period in the host is typically around a week, and illness can last six weeks before self-limiting. Unless treated, illness may relapse. It is important to note here that the more severe forms of the disease can occur in immunocompromised patients such as those with AIDS.
Recognition
Due to its small size, intracellular habitat, and inability to properly uptake many histological stains, diagnosis of Cyclospora cayetanensis can be very difficult. Four methods have thus far been established for positive diagnosis of the protozoan: microscopic detection in stool samples of oocysts; recovering oocysts in intestinal fluid/small bowel biopsy specimens; demonstration of oocyst sporulation; and amplification by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of C. cayetanensis DNA. Since detection is so hard, one negative result should not discount the possibility of C. cayetanensis: tests involving fresh stool samples over the next few days should also be considered.
Except for PCR amplification, once a sample with suspected oocysts has been recovered, standard tests are followed to identify C. cayetanensis. These tests include phase contrast microscopy to check for the spherical oocysts described earlier, modified acid-fast staining to check for variable stainability (all the way from pale to red), and autofluorescence with UV lights. Obtaining these oocysts is usually the challenge, though recent studies show easier methods of obtaining them. In a recent study on different techniques used in fecal exams to identify oocysts, it was demonstrated that centrifuging a sample of feces in a sucrose solution and then transferring a small amount to a slide was remarkably effective—both in oocysts found and relative ease of labor—in detecting C. cayetanensis oocysts: indeed, the paper concluded that the total number of positive samples obtained was around 84%.
C. cayetanensis has been confused with other protozoan infections in the past, the most often of which was Cryptosporidium parvum. There are several differences that can be noted between the two, however, to ensure proper diagnosis. These differences include size difference — C. parvum is smaller; differing results from modified acid-fast staining — C. parvum has consistent red staining; and autofluorescence under UV light — C. cayetanensis does, C. parvum does not.
Treatment
Though the diarrhea caused by C. cayetanensis is self-limiting, relapses can and do occur. To date, the most effective drug for the treatment of the protozoan is a seven-day course of oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). Effects of the drug include significant decrease in the duration of oocyst excretion and cessation of diarrhea and stool samples negative for oocysts between two and three days. Relapse patients respond promptly to the therapy, and there has been talk of using TMP-SMX as a prophylaxis for HIV/AIDS patients.
Prevention
Since infection occurs via fecally contaminated food and water in endemic environments, there are several simple solutions to suggest for the prevention of C. cayetanensis infections. The simplest one is to warn travelers not to visit regions where the protozoan is endemic (generally tropical and sub-tropical regions such as Peru, Brazil, and Haiti), especially when the disease is in its best season for spreading: such was the reason behind the first reported case of cyclosporiasis in Korea. This is not to say that natives of a region are completely free from possible infection: a middle-aged Turkish lawyer living in an urban area with water sanitized by the local government and with no travel history recently became Turkey’s first [en.wiktionary.org/wiki/autochthon autochthonous] case. This woman most likely received the infection from consuming some infected foodstuffs (possibly raspberries) that were not thoroughly washed before consumption. Thus, better health practices in the originating agricultural setting—such as ensuring produce is fully washed and kept away from human feces—and in the individual’s environment—taking an extra few seconds to wash that produce as well—would lead to a lower incidence of infection.
References
- ^ "Cyclospora cayetanensis". http://www.k-state.edu/parasitology/cyclospora/cyclospora.html. Retrieved 2009-01-21.
- Türk M, Türker M, Ak M, Karaayak B, Kaya T (March 2004). "Cyclosporiasis associated with diarrhoea in an immunocompetent patient in Turkey". J. Med. Microbiol. 53 (Pt 3): 255–7. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.45531-0. PMID 14970253. http://jmm.sgmjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14970253.
- Kimura K, Kumar Rai S, Takemasa K, et al. (September 2004). "Comparison of three microscopic techniques for diagnosis of Cyclospora cayentanensis". FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 238 (1): 263–6. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2004.07.045. PMID 15336431.
- Mansfield LS, Gajadhar AA (December 2004). "Cyclospora cayentanensis, a food- and waterborne coccidian parasite". Vet. Parasitol. 126 (1-2): 73–90. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.09.011. PMID 15567580. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304-4017(04)00419-4.
- Yu JR, Sohn WM (October 2003). "A case of human cyclosporiasis causing traveler's diarrhea after visiting Indonesia". J. Korean Med. Sci. 18 (5): 738–41. PMID 14555830.
Ciliophora Spirotrichea (Stylonychia) · Litostomatea (Didinium, Balantidium) · Phyllopharyngea (Tokophrya) · Nassophorea (Nassula) · Colpodea (Colpoda) · Oligohymenophorea (Tetrahymena, Ichthyophthirius, Vorticella, Paramecium) · Plagiopylea (Plagiopyla) · Prostomatea (Coleps)OtherMyzozoa Plasmodiidae/Haemosporida (Plasmodium, Haemoproteus, Leucocytozoon)
Piroplasmida (Babesia, Theileria)Adele-Haemogregarina, Hepatozoon, KaryolysusEimeri-Cryptosporidiidae (Cryptosporidium)
Eimeriidae (Isospora, Cyclospora, Eimeria)
Sarcocystidae (Toxoplasma, Sarcocystis, Besnoitia, Neospora)Agamo-Rhytidocystidae (Rhytidocystis)GregariniaGregarinasina (Gregarina)ColpodellidaeChromeridaChromera velia, Vitrella brassicaformisWith a theca: Peridiniales (Pfiesteria, Peridinium) · Gonyaulacales (Ceratium, Gonyaulax) · Prorocentrales (Prorocentrum) · Dinophysiales (Dinophysis, Histioneis, Ornithocercus, Oxyphysis)
Without theca: Gymnodiniales (Gymnodinium, Karenia, Karlodinium, Amphidinium) · Suessiales (Polarella, Symbiodinium)
Noctilucales (Noctiluca)Syndiniales: Amoebophryaceae (Amoebophyra) · Duboscquellaceae (Duboscquella) · Syndiniaceae (Hematodinium, Syndinium)OtherRelatedInfectious diseases – Parasitic disease: protozoan infection: Chromalveolate and Archaeplastida (A07, B50–B54,B58, 007, 084) Chromalveolate Coccidia: Cryptosporidium hominis/Cryptosporidium parvum (Cryptosporidiosis) · Isospora belli (Isosporiasis) · Cyclospora cayetanensis (Cyclosporiasis) · Toxoplasma gondii (Toxoplasmosis)Archaeplastida Algaemia: Prototheca wickerhamii (Protothecosis)Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
