- Noctilucales
-
Noctilucales 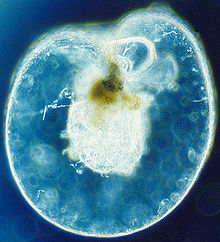
Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Chromalveolata Superphylum: Alveolata Phylum: Dinoflagellata Class: Noctiluciphyceae Order: Noctilucales
Haeckel, 1894Families Kofodiniaceae
Leptodiscaceae
NoctilucaceaeThe Noctilucales are a peculiar order of marine dinoflagellates.
Contents
Characteristics
They differ from most others in that the mature cell is diploid and its nucleus does not show a dinokaryotic organization; also they show gametic meiosis. These cells are very large, from 1 to 2 millimetres in diameter, and are filled with large buoyant vacuoles. Some may contain symbiotic green algae, but there are no chloroplasts. Instead, they feed on other plankton, and there is usually a special tentacle involved in ingestion.
Noctilucales reproduce mainly by fission, but sexual reproduction also occurs. Each cell produces numerous gametes, which resemble more typical athecate dinoflagellates and have the dinokaryotic nuclei. Evidence suggests that they diverged from most other dinoflagellates early on, and they are generally placed in their own class.
Examples
The most common species is Noctiluca scintillans, also called N. miliaris. It can be bioluminescent when disturbed,[1] as are various other dinoflagellates, and large blooms can sometimes be seen as flickering lights on the ocean.
Another example is Spatulodinium pseudonoctiluca.[2]
References
- ^ Eckert R, Reynolds GT (May 1967). "The subcellular origin of bioluminescence in Noctiluca miliaris". Journal of General Physiology 50 (5): 1429–58. doi:10.1085/jgp.50.5.1429. PMC 2225713. PMID 5340466. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2225713.
- ^ Gómez F, Souissi S (March 2007). "The distribution and life cycle of the dinoflagellate Spatulodinium pseudonoctiluca (Dinophyceae, Noctilucales) in the northeastern English Channel". Comptes Rendus Biologies 330 (3): 231–6. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2007.02.002. PMID 17434117.
External links
- Noctiluca scintillans - Guide to the Marine Zooplankton of south eastern Australia, Tasmanian Aquaculture & Fisheries Institute
- A dense Noctiluca red tide
Ciliophora Spirotrichea (Stylonychia) · Litostomatea (Didinium, Balantidium) · Phyllopharyngea (Tokophrya) · Nassophorea (Nassula) · Colpodea (Colpoda) · Oligohymenophorea (Tetrahymena, Ichthyophthirius, Vorticella, Paramecium) · Plagiopylea (Plagiopyla) · Prostomatea (Coleps)OtherMyzozoa Plasmodiidae/Haemosporida (Plasmodium, Haemoproteus, Leucocytozoon)
Piroplasmida (Babesia, Theileria)Adele-Eimeri-Cryptosporidiidae (Cryptosporidium)
Eimeriidae (Isospora, Cyclospora, Eimeria)
Sarcocystidae (Toxoplasma, Sarcocystis, Besnoitia, Neospora)Agamo-Rhytidocystidae (Rhytidocystis)GregariniaGregarinasina (Gregarina)ColpodellidaeChromeridaWith a theca: Peridiniales (Pfiesteria, Peridinium) · Gonyaulacales (Ceratium, Gonyaulax) · Prorocentrales (Prorocentrum) · Dinophysiales (Dinophysis, Histioneis, Ornithocercus, Oxyphysis)
Without theca: Gymnodiniales (Gymnodinium, Karenia, Karlodinium, Amphidinium) · Suessiales (Polarella, Symbiodinium)
Noctilucales (Noctiluca)Syndiniales: Amoebophryaceae (Amoebophyra) · Duboscquellaceae (Duboscquella) · Syndiniaceae (Hematodinium, Syndinium)OtherRelatedCategories:- Dinoflagellates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
