- Toxoplasma gondii
Taxobox | color = khaki
name = "Toxoplasma Gondii"
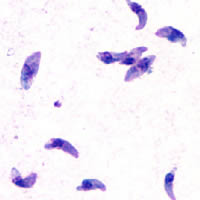
image_width = 200px
image_caption = "T. gondii"tachyzoite s
regnum =Protist a
phylum =Apicomplexa
classis =Conoidasida
subclassis =Coccidia sina
ordo =Eucoccidiorida
familia =Sarcocystidae
genus = "Toxoplasma"
species = "T. gondii"
binomial = "Toxoplasma gondii"
binomial_authority = (Nicolle & Manceaux, 1908)"Toxoplasma gondii" is a species of parasitic
protozoa in thegenus "Toxoplasma".cite book | author = Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th ed. | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | pages = 722–7 | isbn = 0838585299] The definitive host of "T. gondii" is thecat , but the parasite can be carried by the vast majority of warm-blooded animals, includinghuman s.Toxoplasmosis , the disease of which "T. gondii" is the causative agent, is usually minor and self-limiting but can have serious or even fatal effects on afetus whose mother first contracts the disease during pregnancy or on animmunocompromised human or cat.Preventing "Toxoplasma" during pregnancy involves avoiding eating undercooked or cured meat, thoroughly washing fruit and vegetables before eating, and avoiding soil contact. If gardening, wear protective rubber gloves and wash hands thoroughly afterwards. Avoidance of cats is commonly recommended to uninfected pregnant women (eg cite journal
author=AAFP American Academy of Family Physicians | title=Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy | journal=AAFP. | year=2005 | url=http://familydoctor.org/online/famdocen/home/women/pregnancy/illness/180.printerview.html ] ), but the contribution of this risk factor is controversial. Some studies have identified cat ownership or contact as a minor source of risk, while several other major studies have failed to identify exposure to cats as a significant risk factor for Toxoplasma infection [cite journal| author=Cook AJ, Gilbert RE, Buffolano W, Zufferey J, Petersen E, Jenum PA, Foulon W, Semprini AE, Dunn DT. | title=Sources of toxoplasma infection in pregnant women: European multicentre case-control study. European Research Network on Congenital Toxoplasmosis | journal=BMJ. | year=2000 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10894691| doi=10.1136/bmj.321.7254.142| volume=321| pages=142| pmid=10894691 ] [cite journal| author=Bobić B, Jevremović I, Marinković J, Sibalić D, Djurković-Djaković O.| title=Risk factors for Toxoplasma infection in a reproductive age female population in the area of Belgrade, Yugoslavia | journal=Eur J Epidemiol.. | year=1998 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9794128| doi=10.1023/A:1007461225944| volume=14| pages=605] .Life cycle
The life cycle of "T. gondii" has two phases. The sexual part of the life cycle (coccidia like) takes place only in members of the
Felidae family (domestic and wild cats), which makes these animals the parasite's primary host. The asexual part of the life cycle can take place in any warm-blooded animal, like othermammal s (including felines) andbird s.In the intermediate hosts (as well the definitive host, felines), the parasite invades cells, forming intracellular so-called parasitophorous
vacuole s containingbradyzoite s, the slowly replicating form of the parasite. [cite journal |author=Dubey JP, Lindsay DS, Speer CA |title=Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts |journal=Clin. Microbiol. Rev. |volume=11 |issue=2 |pages=267–99 |year=1998 |pmid=9564564 |url = http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/content/full/11/2/267?view=long&pmid=9564564] Vacuoles form tissuecyst s mainly within the muscles and brain. Since they are within cells, the host'simmune system does not detect these cysts. Resistance toantibiotics varies, but the cysts are very difficult to eradicate entirely. Within these vacuoles "T. gondii" propagates by a series of binary fissions until the infected cell eventually bursts andtachyzoites are released. Tachyzoites are the motile, asexually reproducing form of the parasite. Unlike the bradyzoites, the free tachyzoites are usually efficiently cleared by the host's immune response, although some manage to infect cells and form bradyzoites, thus maintaining the infection.Tissue cysts are ingested by a cat (e.g., by feeding on an infected mouse). The cysts survive passage through the stomach of the cat and the parasites infect epithelial cells of the
small intestine where they undergo sexual reproduction and oocyst formation. Oocysts are shed with the feces. Animals and humans that ingest oocysts (e.g., by eating unwashed vegetables etc.) or tissue cysts in improperly cooked meat become infected. The parasite entersmacrophage s in the intestinal lining and is distributed via the blood stream throughout the body.Acute stage toxoplasma infections can be asymptomatic, but often gives flu-like symptoms in the early acute stages, and like flu can become, in very rare cases, fatal. The acute stage fades in a few days to months, leading to the latent stage. Latent infection is normally asymptomatic; however, in the case of immunocompromised patients (such as those infected with
HIV or transplant recipients on immunosuppressive therapy),toxoplasmosis can develop. The most notable manifestation of toxoplasmosis in immunocompromised patients is toxoplasmicencephalitis , which can be deadly. If infection with "T. gondii" occurs for the first time during pregnancy, the parasite can cross the placenta, possibly leading tohydrocephalus ormicrocephaly , intracranial calcification, andchorioretinitis , with the possibility of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) or intrauterine death.Toxoplasmosis
"T. gondii" infections have the ability to change the behavior of
rat s and mice, making them drawn to rather than fearful of the scent of cats. This effect is advantageous to the parasite, which will be able to sexually reproduce if its host is eaten by a cat. [cite journal |author=Berdoy M, Webster JP, Macdonald DW |title=Fatal attraction in rats infected with Toxoplasma gondii |journal=Proc. Biol. Sci. |volume=267 |issue=1452 |pages=1591–4 |year=2000 |pmid=11007336 |doi=10.1098/rspb.2000.1182 | url = http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=11007336] The infection is almost surgical in its precision, as it does not affect a rat's other fears such as the fear of open spaces or of unfamiliar smelling food.There has been speculation that human behavior may also be affected in some ways, and correlations have been found between latent "Toxoplasma" infections and various characteristics such as decreased novelty-seeking behavior, slower reactions, feelings of insecurity, andneuroticism .Carl Zimmer, The Loom. [http://scienceblogs.com/loom/2006/08/01/a_nation_of_cowards_blame_the.php "A Nation of Neurotics? Blame the Puppet Masters?"] , 1 Aug. 2006 ]Several independent pieces of evidence point towards a possible role of "Toxoplasma" infection in some cases of
schizophrenia andparanoia , but this theory does not seem to account for many cases. [cite journal |author=Torrey EF, Yolken RH |title=Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia |journal=Emerging Infect. Dis. |volume=9 |issue=11 |pages=1375–80 |year=2003 |pmid=14725265 |url=http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol9no11/03-0143.htm] A recent study has indicated toxoplasmosis is also correlated strongly with an increase in boy births in humans, leading to an alteration of the humansex ratio . [cite journal | author = Flegr J | title = Women infected with parasite "Toxoplasma" have more sons | journal = Naturwissenschaften | year = 2006 | url = http://www.natur.cuni.cz/~flegr/pdf/toxosons.pdf | format = PDF] According to the researchers, "depending on the antibody concentration, the probability of the birth of a boy can increase up to a value of 0.72 ... which means that for every 260 boys born, 100 girls are born." The study also notes a mean rate of 0.60 to 0.65 (as opposed to the normal 0.51) for "Toxoplasma" positive mothers.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
