- Cyclosporiasis
-
Cyclosporiasis Classification and external resources 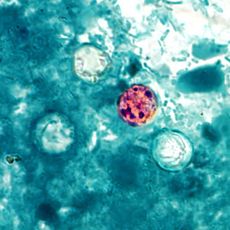
Cyclospora cayetanensisICD-10 A07.8 ICD-9 007.5 DiseasesDB 32228 eMedicine ped/527 MeSH D021866 Cyclosporiasis is an infection with the protozoan Cyclospora cayetanensis, a pathogen transmitted by feces or feces-contaminated fresh produce and water. Outbreaks have been reported due to contaminated raspberries. It is not spread from person to person. It can be a cause of diarrhea for travelers.
Contents
Mode of infection
When an oocyst of Cyclospora cayetanensis enters the small intestine and invades the mucosa it incubates for about one week. After incubation the person begins to experience severe watery diarrhea, bloating, fever, stomach cramps, and muscle aches.
Oocysts can be present due to using contaminated water or human feces as fertilizer. This infection primarily affects humans and other primates.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis can be difficult due to the lack of recognizable oocysts in the feces. Using tests like PCR-based DNA tests and acid-fast staining can help with identification. The infection is often treated with Co-trimoxazole, because traditional anti-protozoan drugs are not sufficient. To prevent transmission through food, cook food and try to avoid drinking stream water while outdoors.
References
- Talaro, Kathleen P. "Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition." New York: McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., 2005.
External links
- Cyclospora Infection at Healthocates
Infectious diseases – Parasitic disease: protozoan infection: Chromalveolate and Archaeplastida (A07, B50–B54,B58, 007, 084) Chromalveolate Coccidia: Cryptosporidium hominis/Cryptosporidium parvum (Cryptosporidiosis) · Isospora belli (Isosporiasis) · Cyclospora cayetanensis (Cyclosporiasis) · Toxoplasma gondii (Toxoplasmosis)Archaeplastida Algaemia: Prototheca wickerhamii (Protothecosis)Categories:- Disease stubs
- Protozoal diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
