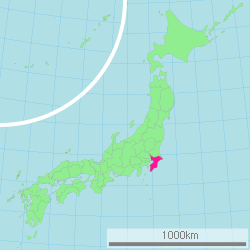
- Chiba Prefecture
-
Chiba Prefecture Japanese transcription(s) - Japanese 千葉県 - Rōmaji Chiba-ken 
Symbol of Chiba PrefectureCountry Japan Region Kantō Island Honshū Capital Chiba Government - Governor Kensaku Morita Area - Total 5,156.15 km2 (1,990.8 sq mi) Area rank 27th Population (September 1, 2010) - Total 6,201,046 - Rank 6th - Density 1,202.65/km2 (3,114.8/sq mi) ISO 3166 code JP-12 Districts 6 Municipalities 54 Flower Rape blossom Tree Kusamaki Bird Meadow Bunting Fish Seabream Website pref.chiba.lg.jp/
englishChiba Prefecture (千葉県 Chiba-ken) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kantō region and the Greater Tokyo Area.[1] Its capital is Chiba City.[2]
Contents
History
Chiba Prefecture was established on June 15, 1873 with the merger of Kisarazu Prefecture and Inba Prefecture. Historically, the prefecture constituted three provinces of Awa, Kazusa, and Shimōsa.[3]
The prefecture's name means "a thousand leaves".
Geography
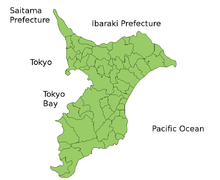
Chiba borders Ibaraki Prefecture to the north at the Tone River, Tokyo and Saitama Prefecture to the west at the Edo River, the Pacific Ocean to the east and Tokyo Bay around its southern boundary. Most of Chiba lies on the hilly Boso Peninsula, a rice farming region: the east coast, known as the Ninety-Nine League Plain, is an especially productive area. The most populous zone, in the northwest of the prefecture, is part of the Kantō region that extends into the urban agglomeration of Tokyo and Saitama. The Kuroshio Current flows near Chiba, which keeps it relatively warm in winter and cooler in summer than neighbouring Tokyo.
Cities
Thirty-six cities are located in Chiba Prefecture:
Towns and villages
These are the towns and villages in each district:
Mergers
Main article: List of mergers in Chiba PrefectureEconomy
Chiba is one of Japan's largest industrial areas, thanks to its long coastline on Tokyo Bay. After Chiba was chosen as the site for a major Kawasaki Steel factory in 1950, the prefectural government embarked on a large-scale land reclamation program that dredged up large plots of waterfront property for factories, warehouses, and docks. Chemical production, petrochemical refining, and machine production are the three main industries in Chiba today; together, they account for forty-five percent of the prefecture's exports. In recent years, the government has funded more than eighty industrial parks to bring development further inland as well.
The prefecture also boasts Japan's second-highest agricultural output. Among all the prefectures, only Hokkaidō produces more agricultural products, and Chiba leads Hokkaidō in vegetable production.[citation needed] Seaweed is harvested in large quantities from Tokyo Bay.
Demographics
Chiba's population is one of the wealthiest in Japan due to the prefecture's strong commercial and industrial sectors. Per capita GDP is ¥3.1 million, the fifth-highest in the country. 70% of the population is employed in the service sector, with 25% in industry and 5% in agriculture.[citation needed]
Education
The Chiba Prefectural Board of Education oversees municipal school districts in the prefecture. The board also directly operates the prefecture's public high schools.
University
- Chiba
- Chiba University in Inage, Chuo
- Chiba Economic University in Inage
- The Open University of Japan in Mihama
- The Meteorological College of Japan
- Heisei Teikyo University in Mihama
- Shukutoku University in Chuo
- Tokyo Information Sciences University in Wakaba
- Tokyo Dental College in Mihama
- Kanda University of International Studies in Mihama
- Tokyo University of Career Development in Chuo
- Funabashi
- Toho University - Narashino Campus
- Nihon University - Funabashi Campus
- Matsudo
- Nihon University - Matsudo Campus
- Ryutsu Keizai University
- Seitoku University
- Kashiwa
- Tokyo University - Kashiwa Campus
- Chiba University - Kashiwanoha Campus
- Nihonbashi Gakkan University
- Nishogakusha University - Kasiwa Campus
- Reitaku University
- Narashino
- Chiba Institute of Technology
- Nihon University - Narashino and Mimomi Campus
- Ichihara
- Heisei Teikyo University - Ichihara Campus
- Sakura
- Keiai University - Sakura Campus
- Noda
- Tokyo University of Science - Noda Campus
- Nagareyama
- Urayasu
- Juntendo University - Urayasu Campus
- Meikai University
- Ryotokuji University
- Abiko
- Chuo Gakuin University
- Kawamura Gakuen Woman's University
- Kisarazu
- Inzai
- Juntendo University - Sakura Campus
In popular culture
- Novels set in Chiba include: Neuromancer by William Gibson (set in Chiba city), Ningen Shikkaku by Osamu Dazai (Funabashi), and Nogiku no Haka by Sachio Itō (Matsudo).
- Manga (comics) representations include: Be Free!, Chameleon, Kyō Kara Ore Wa!!, Makuhari (set in Chiba city), Makuhari Saboten Campus (Chiba city), Susume!! Pirates, and Urayasu Tekkin Kazoku (Urayasu).
- Anime (animation) representations include: Chikyū Bōei Kazoku (set in Funabashi), Battle Programmer Shirase (Narashino), and Zegapain (Urayasu).
- TV series representations include: Kisarazu Cat's Eye (set in Kisarazu), Mio Tsukushi (Chōshi), Beach Boys (filmed in Tateyama and Shirahama (now Minamiboso) and Yappari Neko ga Suki (Chiba city).
Notable residents
- Various rock bands have roots that stem from Chiba prefecture, including the popular X Japan, Plastic Tree, girugamesh and punk bands like Nicotine and Ellegarden.
- Aiba Masaki of Arashi, Yamashita Tomohisa of NEWS, Tanaka Koki and Akanishi Jin of KAT-TUN, Ryo, Satoshi, Ni and ShuU Girugamesh, Keiko Terada and Miki Nakamura of Show-Ya, Tsugunaga Momoko and Natsuyaki Miyabi of Berryz Kobo, Suzuki Airi of C-ute, Arioka Daiki of Hey! Say! JUMP and Shinya Sano of An Cafe are all from the Chiba Prefecture.
Sports
The prefecture plays host to two major events in the Japanese athletics calendar: the International Chiba Ekiden and the Chiba International Cross Country.
The following sports teams are based in Chiba.
Football
Baseball
Rugby
Basketball
- JBL: Hitachi Sunrockers(Kashiwa)
- BJ: Chiba Expansion Franchise
Futsal
- Bardral Urayasu
Transportation
Most Tokyo-bound visitors arriving on international flights land in Narita International Airport, which is situated in Narita in the north of the prefecture, and connected to Tokyo by the East Japan Railway's Narita Express and the Keisei Electric Railway's Skyliner.
Railway
- East Japan Railway Company
- Sōbu Main Line
- Jōban Line
- Jōban Line (Local)
- Jōban Line (Rapid)
- Narita Line
- Uchibō Line
- Sotobō Line
- Keiyō Line
- Musashino Line
- Tōgane Line
- Kashima Line
- Kururi Line
- Keisei
- Main Line
- Narita Sky Access
- Chiba Line
- Chihara Line
- Higashi Narita Line
- Hokuso Line
- Shibayama Railway
- Tokyo Metro Tozai Line
- Choshi Electric Railway
- Kominato Railway
- Isumi Railway
People Movers
Road
Expressway
- Joban Expressway
- Narita Airport Expressway
- Higashi Kanto Expressway
- Tokyo Gaikan Expressway
- Tateyama Expressway
- Shuto Expressway
- Keiyo Road
- Togane Road
- Tokyo Bay Aqua Line
National Highway
- Route 6
- Route 14
- Route 16
- Route 51
- Route 124
- Route 126
- Route 127
- Route 128
- Route 294
- Route 295
- Route 296
- Route 297
- Route 298
- Route 356
- Route 357
- Route 408
- Route 409
- Route 410
- Route 464
- Route 465
Airport
- Narita International Airport - Most of International flight and part of Domestic Flight
Tourism
The Tokyo Disney Resort is located in Urayasu near the western border of the prefecture.
There are also a number of tourist sites on the Chiba peninsula, such as Nokogiriyama; Kujūkuri Beach; and Onjuku beach.
Chiba is linked to Tokyo by several railway lines; the main trunk lines are the Keiyo Line and Sobu Line. The Musashino Line connects Chiba to Saitama and northern Tokyo. Southern Chiba is connected to Kanagawa Prefecture by the Tokyo Bay Aqua-Line bridge-tunnel.
Prefectural symbols
Chiba is famous for peanuts. Most of Japan's peanuts are harvested in this prefecture and are also processed into peanut oil.[citation needed]
Notes
References
- Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric and Käthe Roth. (2005). Japan encyclopedia. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. 10-ISBN 0-674-01753-6; 13-ISBN 978-0-674-01753-5; OCLC 58053128
External links
 Media related to Chiba prefecture at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Chiba prefecture at Wikimedia Commons- Official Chiba Prefecture website (English)
- Chiba Information Guide (English)
- Japan Statistical yearbook (English)
 Chiba Prefecture
Chiba PrefectureChiba (capital city) 
Other cities Chōshi | Ichikawa | Funabashi | Tateyama | Kisarazu | Matsudo | Noda | Mobara | Narita | Sakura | Tōgane | Asahi | Narashino | Kashiwa | Katsuura | Ichihara | Nagareyama | Yachiyo | Abiko | Kamogawa | Kamagaya | Kimitsu | Futtsu | Urayasu | Yotsukaidō | Sodegaura | Yachimata | Inzai | Shiroi | Tomisato | Minamibōsō | Sōsa | Katori | Sanmu | IsumiInba District Katori District Sanbu District Chōsei District Isumi District Awa District Regions and administrative divisions of  Japan
JapanRegions 
Prefectures Hokkaido Tōhoku Kantō Chūbu Kansai Chūgoku Shikoku Kyushu Coordinates: 35°36′18″N 140°07′24″E / 35.605°N 140.12333°E
Categories: - Chiba
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.