- Dagum distribution
-
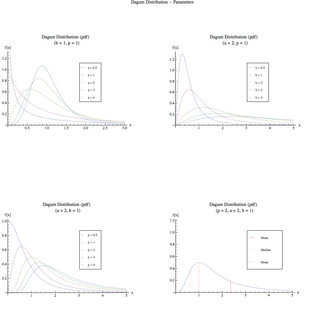
Dagum Distribution Probability density function
Cumulative distribution function
No image availableparameters: p > 0 shape
a > 0 shape
b > 0 scalesupport: x > 0 pdf: 
cdf: 
mean: 
median: 
mode: 
variance: 
mgf: UNIQ21c15a213ff61bcc-math-0000000A-QINU cf: UNIQ21c15a213ff61bcc-math-0000000B-QINU The Dagum distribution is a continuous probability distribution defined over all positive real numbers. It is named after Camilo Dagum, who proposed it in a series of papers in the 1970s.[1][2] The Dagum distribution arose from several variants of a new model on the size distribution of personal income and is mostly associated with the study of income distribution. There is both a three-parameter specification (Type I) and a four-parameter specification (Type II) of the Dagum distribution; a summary of the genesis of this distribution can be found in.[3] A general source on statistical size distributions often cited in work using the Dagum distribution is.[4]
Definition
The cumulative distribution function of the Dagum distribution (Type I) is given by
 for x > 0 and where a,b,p > 0.
for x > 0 and where a,b,p > 0.
The corresponding probability density function is given by
The Dagum distribution can be derived as a special case of the generalized Beta II (GB2) distribution. There is also an intimate relationship between the Dagum and Singh-Maddala distribution.
The cumulative distribution function of the Dagum (Type II) distribution adds a point mass at the origin and then follows a Dagum (Type I) distribution over the rest of the support (i.e. over the positive halfline)
References
- ^ Dagum, Camilo (1975); A model of income distribution and the conditions of existence of moments of finite order; Bulletin of the International Statistical Institute, 46 (Proceeding of the 40th Session of the ISI, Contributed Paper), 199-205.
- ^ Dagum, Camilo (1977); A new model of personal income distribution: Specification and estimation; Economie Appliquée, 30, 413-437.
- ^ Kleiber, Christian (2008) "A Guide to the Dagum Distributions" in Chotikapanich, Duangkamon (ed.) Modeling Income Distributions and Lorenz Curves (Economic Studies in Inequality, Social Exclusion and Well-Being), Chapter 6, Springer
- ^ Kleiber, Christian and Samuel Kotz (2003) Statistical Size Distributions in Economics and Actuarial Sciences, Wiley
External links
- Camilo Dagum (1925 - 2005) : obituary
Categories:- Continuous distributions
- Income distribution
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



