- Pennsylvania General Assembly
-
Pennsylvania General Assembly 
Type Type Bicameral Houses Senate
House of RepresentativesLeadership President Pro Tem of the Senate Joseph B. Scarnati, (R)
since January 2, 2007Speaker of the House Sam Smith, (R)
since January 4, 2011Structure Members 253
50 Senators
203 Representatives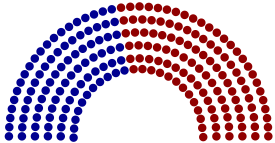
House of Representatives Political groups Democratic Party
Republican Party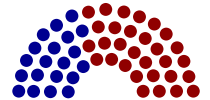
State Senate Political groups Democratic Party
Republican PartyElections House of Representatives Last election November 2, 2010 State Senate Last election November 2, 2010 Meeting place 
Pennsylvania State Capitol Website www.legis.state.pa.us The Pennsylvania General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The legislature convenes in the State Capitol building in Harrisburg. In colonial times (1682–1776), the legislature was known as the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly. Since the Constitution of 1776, written by American revolutionaries, the legislature has been known as the General Assembly. The General Assembly became a bicameral legislature in 1790.
Contents
Membership
The General Assembly has 253 members, consisting of a Senate with 50 members and a House of Representatives with 203 members, making it the second-largest state legislature in the nation (behind New Hampshire) and the largest full-time legislature. As of 2005, members' base pay was $78,314,[1] the fourth highest legislative salary in the nation[1], making it the costliest state legislature per capita in the U.S.[2] Republicans hold a 30-20 majority in the Senate[2], and a 112-90 majority in the House.
The Pennsylvania general elections are held on the Tuesday after the first Monday in November in even-numbered years. A vacant seat must be filled by special election, the date of which is set by the presiding officer of the respective house.
Senators must be at least 25 years old, and Representatives at least 21 years old. They must be citizens and residents of the state for a minimum of four years and reside in their districts for at least one year. Individuals who have been convicted of felonies, including embezzlement, bribery, and perjury, are ineligible for election; the state Constitution also adds the category of "other infamous crimes," which can be broadly interpreted by state courts. No one who has been previously expelled from the General Assembly may be elected.[3]
Legislative districts are drawn every ten years, following the U.S. Census. Districts are drawn by a five-member commission, of which four members are the majority and minority leaders of each house (or their delegates). The fifth member, who chairs the committee, is appointed by the other four and may not be an elected or appointed official. If the leadership cannot decide on a fifth member, the State Supreme Court may appoint him.
While in office, legislators may not hold civil office. Even if a member resigns, the Constitution states that he may not be appointed to civil office for the duration of the original term for which he was originally elected.
Legislative sessions
The General Assembly convenes at noon on the first Tuesday of January and then meets regularly throughout the year. Both houses adjourn on November 30 in even-numbered years, when the terms of all members of the House and half the members of the Senate expire. Neither body can adjourn for more than three days without the consent of the other.
The governor may call a special session in order to press for legislation on important issues. Most recently, a special session was called for the purpose of property tax reform.
The Assembly meets in the Pennsylvania State Capitol, which was completed in 1906. Under the Pennsylvania Constitution, the Assembly must meet in the City of Harrisburg and can move only if given the consent of both chambers.
General assembly leadership
Pennsylvania House of Representatives
Speaker of the House of Representatives: Samuel H. Smith (R) [1]
Majority Party (R) Leadership Position Minority Party (D) Mike Turzai Floor Leader Frank Dermody Stan Saylor Whip Mike Hanna Sandra Major Caucus Chair Dan Frankel Mike Vereb Caucus Secretary Jennifer Mann Bill Adolph Appropriations Committee Chairman Joe Markosek Dave L. Reed Policy Committee Chairman Mike Sturla Dick Stevenson Caucus Administrator Ron Buxton Pennsylvania State Senate
President Pro Tem of the Senate: Joseph B. Scarnati (R)
Majority Party (R) Leadership Position Minority Party (D) Dominic Pileggi Floor Leader Jay Costa Pat Browne Whip Anthony H. Williams Mike Waugh Caucus Chairman Rich Kasunic Bob D. Robbins Caucus Secretary Christine Tartaglione Jake Corman Appropriations Committee Chairman Vincent Hughes Edwin Erickson Policy Committee Chairman Lisa Boscola John Gordner Caucus Administrator Wayne Fontana See also
- 2005 Pennsylvania General Assembly pay raise controversy
- Pennsylvania House of Representatives elections, 2006
- Pennsylvania House of Representatives elections, 2008
- Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly, for the General Assembly before 1776
- Pennsylvania Legislative Black Caucus
References
- ^ a b Robert Swift (2010-04-26). "State legislature is among nation's most expensive". The Times Tribune. http://thetimes-tribune.com/news/state-legislature-is-among-nation-s-most-expensive-1.742222.
- ^ a b "Post General Election Legislative breakdown". The Council of State Governments. http://www.csg.org/pubs/Election2008/PostGELegislativeBreakdown.aspx#PA.
- ^ "CONSTITUTION OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF PENNSYLVANIA: Article II - The Legislature". Pennsylvania Constitution Web Page of the Duquesne University School of Law. Duquesne University School of Law. 2010-02-11. http://www.duq.edu/law/pa-constitution/constitutions/current.cfm#2. Retrieved 2010-02-11.
External links
Members of the Pennsylvania State Senate President of the Senate: Jim Cawley (R) • President pro tempore: Joseph Scarnati (R) • Majority Leader: Dominic Pileggi (R) • Minority Leader: Jay Costa (D)- Larry Farnese (D)
- Tina Tartaglione (D)
- Shirley Kitchen (D)
- LeAnna Washington (D)
- Mike Stack (D)
- Tommy Tomlinson (R)
- Vincent Hughes (D)
- Anthony Williams (D)
- Dominic Pileggi (R)
- Chuck McIlhinney (R)
- Judy Schwank (D)
- Stewart Greenleaf (R)
- Lloyd Smucker (R)
- John Yudichak (D)
- Jeffrey Piccola (R)
- Pat Browne (R)
- Daylin Leach (D)
- Lisa Boscola (D)
- Andy Dinniman (D)
- Lisa Baker (R)
- Mary Jo White (R)
- John Blake (D)
- Gene Yaw (R)
- Bob Mensch (R)
- Joseph Scarnati (R)
- Ted Erickson (R)
- John Gordner (R)
- Mike Waugh (R)
- Dave Argall (R)
- John Eichelberger (R)
- Pat Vance (R)
- Rich Kasunic (D)
- Rich Alloway (R)
- Jake Corman (R)
- John Wozniak (D)
- Mike Brubaker (R)
- John Pippy (R)
- Jim Ferlo (D)
- Kim Ward (R)
- Jane Orie (R)
- Don White (R)
- Wayne Fontana (D)
- Jay Costa (D)
- John Rafferty (R)
- Jim Brewster (D)
- Tim Solobay (D)
- Elder Vogel (R)
- Mike Folmer (R)
- Jane Earll (R)
- Bob Robbins (R)
Republican (30) • Democratic (20) • Pennsylvania General Assembly • Pennsylvania House of Representatives • Pennsylvania State SenateMembers of the Pennsylvania House of Representatives Speaker of the House: Sam Smith (R) • Majority Leader: Mike Turzai (R) • Minority Leader: Frank Dermody (D)- Pat Harkins (D)
- Florindo Fabrizio (D)
- John Hornaman (D)
- Curt Sonney (R)
- John R. Evans (R)
- Brad Roae (R)
- Mark Longietti (D)
- Dick Stevenson (R)
- Chris Sainato (D)
- Jaret Gibbons (D)
- Brian L. Ellis (R)
- Daryl Metcalfe (R)
- John Lawrence (R)
- Jim E. Marshall (R)
- Jim Christiana (R)
- Robert Matzie (D)
- Michele Brooks (R)
- Gene DiGirolamo (R)
- Jake Wheatley (D)
- Adam Ravenstahl (D)
- Dom Costa (D)
- Chelsa Wagner (D)
- Dan Frankel (D)
- Joseph Preston, Jr. (D)
- Joseph Markosek (D)
- Tim Hennessey (R)
- Dan Deasy (D)
- Mike Turzai (R)
- Bernie O'Neill (R)
- Randy Vulakovich (R)
- Steve Santarsiero (D)
- Anthony M. DeLuca (D)
- Frank Dermody (D)
- Paul Costa (D)
- Marc Gergely (D)
- Harry Readshaw (D)
- Thomas C. Creighton (R)
- William C. Kortz (D)
- Rick Saccone (R)
- John A. Maher (R)
- Ryan Aument (R)
- Matthew H. Smith (D)
- Scott W. Boyd (R)
- Mark Mustio (R)
- Nick Kotik (D)
- Jesse J. White (D)
- Keith J. Gillespie (R)
- Brandon Neuman (D)
- Peter Daley (D)
- Bill DeWeese (D)
- Timothy S. Mahoney (D)
- Deberah Kula (D)
- Robert Godshall (R)
- Eli Evankovich (R)
- Joseph Petrarca, Jr. (D)
- George Dunbar (R)
- Tim Krieger (R)
- Ted Harhai (D)
- Mike Reese (R)
- Jeff Pyle (R)
- Kate M. Harper (R)
- Dave L. Reed (R)
- Donna Oberlander (R)
- Scott Hutchinson (R)
- Kathy Rapp (R)
- Sam Smith (R)
- Martin Causer (R)
- Matt E. Baker (R)
- Carl Walker Metzgar (R)
- Matthew Bradford (D)
- Bryan Barbin (D)
- Frank Burns (D)
- Gary Haluska (D)
- Bud George (D)
- Matt Gabler (R)
- Mike Hanna (D)
- H. Scott Conklin (D)
- Dick Hess (R)
- Richard Geist (R)
- Jerry Stern (R)
- Mike Fleck (R)
- Adam Harris (R)
- Richard Mirabito (D)
- Garth Everett (R)
- Fred Keller (R)
- Mark Keller (R)
- Glen Grell (R)
- Sheryl M. Delozier (R)
- Rob Kauffman (R)
- Todd Rock (R)
- Dan Moul (R)
- Scott Perry (R)
- Ron E. Miller (R)
- Stan Saylor (R)
- Eugene DePasquale (D)
- Mike Sturla (D)
- John C. Bear (R)
- David Hickernell (R)
- Gordon Denlinger (R)
- Bryan Cutler (R)
- Mauree Gingrich (R)
- RoseMarie Swanger (R)
- Ron Buxton (D)
- Sue Helm (R)
- Ron Marsico (R)
- John D. Payne (R)
- Kurt A. Masser (R)
- Lynda Schlegel-Culver (R)
- David R. Millard (R)
- Tina Pickett (R)
- Sandra Major (R)
- Kenneth J. Smith (D)
- Kevin P. Murphy (D)
- Sid Michaels Kavulich (D)
- Edward Staback (D)
- Tarah Toohil (R)
- Karen Boback (R)
- Michael B. Carroll (D)
- Gerald R. Mullery (D)
- Phyllis Mundy (D)
- Eddie Day Pashinski (D)
- Doyle Heffley (R)
- Neal Goodman (D)
- Jerry Knowles (R)
- Mike Tobash (R)
- Dante Santoni (D)
- Thomas Caltagirone (D)
- Mark M. Gillen (R)
- Jim A. Cox (R)
- David M. Maloney (R)
- Justin Simmons (R)
- Jennifer Mann (D)
- Joseph F. Brennan (D)
- Doug Reichley (R)
- Steve Samuelson (D)
- Robert L. Freeman (D)
- Joe Emrick (R)
- Marcia Hahn (R)
- Michael Peifer (R)
- John Galloway (D)
- Tina M. Davis (D)
- Frank Farry (R)
- Marguerite Quinn (R)
- Kathy Watson (R)
- Paul Clymer (R)
- Tom Quigley (R)
- Marcy Toepel (R)
- Michael F. Gerber (D)
- Tim Briggs (D)
- Mike Vereb (R)
- Todd Stephens (R)
- Tom Murt (R)
- Josh Shapiro (D)
- Lawrence Curry (D)
- Curt Schroder (R)
- Dan Truitt (R)
- Warren Kampf (R)
- L. Chris Ross (R)
- Thaddeus Kirkland (D)
- Stephen Barrar (R)
- Joe Hackett (R)
- Nicholas Miccarelli III (R)
- Nicholas Micozzie (R)
- Margo L. Davidson (D)
- Bill Adolph (R)
- Greg Vitali (D)
- Duane Milne (R)
- Tom Killion (R)
- Dennis M. O'Brien (R)
- Brendan F. Boyle (D)
- Kerry Benninghoff (R)
- Kevin J. Boyle (D)
- Michael McGeehan (D)
- John Sabatina, Jr. (D)
- Michael H. O'Brien (D)
- Mario Scavello (R)
- John J. Taylor (R)
- Scott Petri (R)
- Tony Payton (D)
- Angel Cruz (D)
- Curtis Thomas (D)
- Babette Josephs (D)
- Julie Harhart (R)
- William F. Keller (D)
- Maria Donatucci (D)
- Kenyatta Johnson (D)
- Gary Day (R)
- James R. Roebuck, Jr. (D)
- Rosemary M. Brown (R)
- Vanessa L. Brown (D)
- Ronald Waters (D)
- Louise Bishop (D)
- Will Tallman (R)
- Pamela A. Delissio (D)
- Michelle F. Brownlee (D)
- Seth Grove (R)
- Jewell Williams (D)
- Rosita Youngblood (D)
- Stephen Bloom (R)
- Cherelle Parker (D)
- John L. Myers (D)
- Mark B. Cohen (D)
- Dwight E. Evans (D)
Republican (112) • Democratic (91) • Pennsylvania General Assembly • Pennsylvania House of Representatives • Pennsylvania State SenateCategories:- Pennsylvania General Assembly
- Pennsylvania State Capitol Complex
- Bicameral legislatures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



