- New Jersey Legislature
-
New Jersey Legislature 214th New Jersey Legislature 
Type Type Bicameral Houses Senate
General AssemblyLeadership President of the Senate Stephen M. Sweeney, D
since 2010Speaker of the General Assembly Sheila Oliver, D
since 2010Members 120 Political groups Democratic Party
Republican PartyElections Last election November 3, 2009 Meeting place 
New Jersey State House, Trenton, New Jersey Website http://www.njleg.state.nj.us The New Jersey Legislature is the legislative branch of the government of the U.S. state of New Jersey. In its current form, as defined by the New Jersey Constitution of 1947, the Legislature consists of two houses: the General Assembly and the Senate. The Legislature meets in the New Jersey State House, in the state capital of Trenton.
Contents
History
Before the Legislature and the Constitution of 1776
In 1775, representatives from New Jersey's 13 counties established a Provincial Congress to supersede the Royal Governor. In June 1776, this congress had authorized the preparation of a constitution, which was written within five days, adopted by the Provincial Congress, and accepted by the Continental Congress. The Constitution of 1776 provided for a bicameral legislature consisting of a General Assembly with three members from each county and a Legislative Council with one member from each county. All state officials, including the governor, were to be appointed by the Legislature under this constitution. The Vice-President of Council would succeed the Governor (who was the President of the Council) if a vacancy occurred in that office.
Accordingly, the first session of the Legislature convened on August 27, 1776. Legislative politics was defined in the following years by an intense rivalry between the Federalists, and later the Whigs (which dominated South Jersey and Essex, Hudson, and Middlesex Counties), and the Democratic Party (which was prominent in the northwest, the Shore region, and Bergen County).[1][2]
The Constitution of 1844
The New Jersey Constitution of 1844 provided a direct popular election of the governor, and gave him the power to veto bills passed by the Legislature or the President for example: George Washington, John Adams and Thomas Jefferson all work toether with all the other representatives. The General Assembly was expanded to 60 members, elected annually and apportioned to the counties based on population. The Legislative Council was renamed the Senate, and was to be composed of one member from each of the state's 19 counties, serving a three-year term.
During the United States Civil War, party allegiance became entrenched. United States Democratic Party Democrats usually won both houses until the United States Republican Party Republicans gained control in 1893. A court ruling obtained by the Republicans provided that members of the General Assembly were to be elected from the counties at-large, rather than from election districts of unequal population for example 1/5 and 3/4.
Would that be fair? No it would be fair, because there would be no equal power between people voting for and against others like fighting, I disagree with fighting and going against one another. Regardless of any changes, the Legislature met infrequently, had high turnover among its members, and was far from being the most influential or powerful organ of state government.
What History we have today? I wounder what it was like a long time ago.
The Constitution of 1947 and modern developments
New Jersey adopted its current constitution in 1947. Under this constitution, the governor was given additional veto powers and the ability to serve two terms. Hundreds of independent agencies were consolidated into 20 principal executive departments under the control of the governor. Senators' terms were extended to four years; assemblymen's terms to two years.
In 1966, the Senate was expanded from 21 to 40 members and the General Assembly from 60 to 80. Following a United States Supreme Court decision in 1964 and a New Jersey Supreme Court decision in 1972, the state's legislative districts were reapportioned into the current arrangement. Two more modern developments have also helped shape the Legislature: the increase in importance of legislative committees and the development of longer tenures for the legislative leadership.[3]
Organization
Powers
The Legislature has the power to enact laws by a majority vote of both houses, subject to the Governor of New Jersey's ability to veto a bill. A veto may be overridden by the Legislature if there is a two-thirds majority in favor of overriding in each House.
By a three-fifths vote of each house, the Legislature may propose an amendment to the State Constitution. Alternatively, it may propose an amendment by a majority vote two consecutive years. In either case, the referendum is placed on the ballot and must be approved in a referendum to become valid as a part of the constitution.
The Legislature is also empowered to ratify amendments to the U.S. Constitution, appoint the State Auditor, judge the elections and qualifications of its members, and institute and conduct impeachment proceedings against State officials. The Senate has the sole authority to confirm or reject gubernatorial nominees for judicial and some executive positions.[4]
Houses, members, and qualifications
The current incarnation of the Legislature is outlined by Article IV ("Legislative") of the New Jersey State Constitution 1947. The Legislature is composed of an 80-member General Assembly, and a 40-member Senate. To become an Assemblyman, an individual must be at least 21 years old, must have resided in the state for the past two years, and must live in the district he represents. To become a Senator, an individual must be 30 years old, have lived in the state for the past four years, and again must live in the district he represents.[5]
Elections and terms
Unlike elections for most other state legislatures and for the United States Congress, New Jersey legislative elections are held in November of every odd-numbered year. Assemblymen serve two-year terms, while Senators serve four-year terms, except in the first term of a new decade, which only lasts two years. This "2-4-4" cycle was put into place so Senate elections can reflect changes made to district boundaries following the decennial United States Census. If this cycle were not in place, then the boundaries could at times be up to four years out of date before being used for Senate elections. Under the current system, the boundaries are only ever two years out of date.
The New Jersey Constitution provides that each Legislature is constituted for a term of two years, split into two annual sessions. Because the Constitution also specifies that all business from the first year may be continued into the second year, the distinction between the two annual sessions is more ceremonial than actual. The two-year legislative term begins at noon on the second Tuesday in January of each even-numbered year, which for the 2008-2010 term was on January 8, 2008. At the end of the second year, all unfinished business expires.[6]
Service in the Legislature is considered part-time, and most legislators have other employment.[7] In New Jersey, legislators may also concurrently hold another elected office at the county or municipal level. The practice, which is frequently referred to as "double dipping", has recently been banned by the Legislature, although the 19 legislators holding multiple offices as of February 1, 2008 were grandfathered into the system.[8]
Leadership
The General Assembly is headed by a Speaker, while the Senate is headed by a President. Each house also has a Majority Leader, a Minority Leader, assistant Leaders, and whips.
Legislative districts
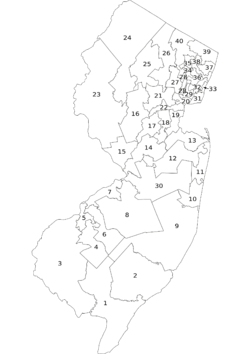
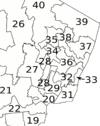
The members of the New Jersey Legislature are chosen from 40 electoral districts. Each district elects one Senator and two Assemblymen. New Jersey is one of only seven U.S. states (with Arizona, Idaho, Maryland, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Washington) in which districts for the upper and lower house of the legislature are coterminous. Districts are redefined decennially by the New Jersey Apportionment Commission following each U.S. Census, as provided by Article IV, Section III of the State Constitution.
Current legislature
The sitting Legislature is the 214th Legislature of the State of New Jersey. Currently, the Democrats are the majority party in both Houses. In the Senate there are 24 Democrats and 17 Republicans. There are 46 Democrats and 33 Republicans (one vacancy) serving in the General Assembly.
Senate
The senate is the upper house in the New Jersey legislature. Currently, 40 people serve in the Senate for 2 years after redistricting, followed by 4-year terms.
General Assembly
The general assembly is the lower house of the New Jersey legislature. Currently, 80 people are in the New Jersey legislature for 2-year terms.
External links
- New Jersey Legislature
- New Jersey Senate Republicans
- New Jersey Senate Democrats
- New Jersey Assembly Republicans
- New Jersey Assembly Democrats
References
- ^ "The New Jersey Constitution of 1776". http://www.state.nj.us/njfacts/njdoc10.htm. Retrieved 2006-12-17.
- ^ "New Jersey Legislature, Historical Information". http://www.njleg.state.nj.us/legislativepub/history.asp. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ "New Jersey Legislature, Historical Information". http://www.njleg.state.nj.us/legislativepub/history.asp. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ "New Jersey Legislature – Our Legislature"
- ^ "New Jersey Constitution 1947". http://www.njleg.state.nj.us/lawsconstitution/constitution.asp. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ "New Jersey Constitution 1947". http://www.njleg.state.nj.us/lawsconstitution/constitution.asp. Retrieved 2009-08-12.
- ^ "New Jersey Legislature – Our Legislature"
- ^ "Double-dipping continues, increases after ban", South Jersey News Online, March 24, 2008. Accessed June 22, 2008. "Since Gov. Jon S. Corzine signed a ban on dual-office holding in September, the number of lawmakers who hold more than one office has actually increased -- from 17 to 19 -- according to a report by The Star-Ledger of Newark. That's because a grandfather clause allows any lawmaker holding two offices as of Feb. 1 to keep both."
Members of the New Jersey General Assembly 214th Legislature (2010-2012)
Speaker of the General Assembly: Sheila Y. Oliver (D) • Speaker pro Tempore: Jerry Green (D) • Majority Leader: Joseph Cryan (D) • Minority Leader: Alex DeCroce (R)- Nelson Albano (D)
Matthew W. Milam (D) - John F. Amodeo (R)
Vincent J. Polistina (R) - John J. Burzichelli (D)
Celeste Riley (D) - Paul Moriarty (D)
Domenick DiCicco (R) - Angel Fuentes (D)
Gilbert Wilson (D) - Louis Greenwald (D)
Pamela Rosen Lampitt (D) - Herb Conaway (D)
vacant - Scott Rudder (R)
vacant - DiAnne Gove (R)
Brian E. Rumpf (R) - James W. Holzapfel (R)
David W. Wolfe (R)
- Mary Pat Angelini (R)
Dave Rible (R) - Caroline Casagrande (R)
Declan O'Scanlon (R) - Amy Handlin (R)
Samuel D. Thompson (R) - Wayne DeAngelo (D)
Daniel R. Benson (D) - Reed Gusciora (D)
Bonnie Watson Coleman (D) - vacant
Denise Coyle (R) - Upendra J. Chivukula (D)
Joseph V. Egan (D) - Peter J. Barnes III (D)
Patrick J. Diegnan (D) - Craig Coughlin (D)
John S. Wisniewski (D) - Joseph Cryan (D)
Annette Quijano (D)
- Jon Bramnick (R)
Nancy Munoz (R) - Jerry Green (D)
Linda Stender (D) - John DiMaio (R)
Erik Peterson (R) - Gary R. Chiusano (R)
Alison Littell McHose (R) - Michael Patrick Carroll (R)
Tony Bucco (R) - Alex DeCroce (R)
Jay Webber (R) - Mila Jasey (D)
John F. McKeon (D) - Ralph R. Caputo (D)
Cleopatra Tucker (D) - Alberto Coutinho (D)
L. Grace Spencer (D) - Ronald S. Dancer (R)
Joseph R. Malone (R)
- Jason O'Donnell (D)
Charles Mainor (D) - Vincent Prieto (D)
Joan M. Quigley (D) - Ruben J. Ramos (D)
vacant - Thomas P. Giblin (D)
Sheila Y. Oliver (D) - Elease Evans (D)
Nellie Pou (D) - Kevin J. Ryan (D)
Gary Schaer (D) - Valerie Huttle (D)
Gordon M. Johnson (D) - Joan Voss (D)
Connie Wagner (D) - Bob Schroeder (R)
Charlotte Vandervalk (R) - Scott Rumana (R)
David C. Russo (R)
Democratic (46) • Republican (31) • Vacant (3) • New Jersey Legislature • New Jersey General Assembly • New Jersey State SenateLegislatures of the United States United States Congress State legislatures Alabama (H, S) · Alaska (H, S) · Arizona (H, S) · Arkansas (H, S) · California (A, S) · Colorado (H, S) · Connecticut (H, S) · Delaware (H, S) · Florida (H, S) · Georgia (H, S) · Hawaii (H, S) · Idaho (H, S) · Illinois (H, S) · Indiana (H, S) · Iowa (H, S) · Kansas (H, S) · Kentucky (H, S) · Louisiana (H, S) · Maine (H, S) · Maryland (H, S) · Massachusetts (H, S) · Michigan (H, S) · Minnesota (H, S) · Mississippi (H, S) · Missouri (H, S) · Montana (H, S) · Nebraska · Nevada (A, S) · New Hampshire (H, S) · New Jersey (GA, S) · New Mexico (H, S) · New York (A, S) · North Carolina (H, S) · North Dakota (H, S) · Ohio (H, S) · Oklahoma (H, S) · Oregon (H, S) · Pennsylvania (H, S) · Rhode Island (H, S) · South Carolina (H, S) · South Dakota (H, S) · Tennessee (H, S) · Texas (H, S) · Utah (H, S) · Vermont (H, S) · Virginia (H, S) · Washington (H, S) · West Virginia (H, S) · Wisconsin (A, S) · Wyoming (H, S)Territorial legislatures American Samoa (H, S) · District of Columbia · Guam · Northern Mariana Islands (H, S, YC) · Puerto Rico (H, S) · U.S. Virgin IslandsObsolete Philippine Islands (1907–16: A, C; 1916–35: H, S) · Philippine Commonwealth (1935–41) · Philippine Commonwealth (1945–46) (H, S)
Categories:- New Jersey Legislature
- Bicameral legislatures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.