- Florida State Road 528
-
State Road 528 Martin Andersen Beachline Expressway Route information Maintained by FTE, OOCEA and FDOT Length: 53.499 mi[1] (86.098 km) Existed: 1974 – present Major junctions West end: 
 I-4 / SR 400 near Lake Buena Vista
I-4 / SR 400 near Lake Buena VistaInternational Drive near Orlando

 Turnpike / SR 91 near Taft
Turnpike / SR 91 near Taft
 SR 417 near Lake Nona
SR 417 near Lake Nona

 I-95 / SR 9 near Cocoa
I-95 / SR 9 near Cocoa

 US 1 / SR 5 in Cocoa
US 1 / SR 5 in CocoaEast end: 
 SR A1A / SR 401near Port Canaveral
SR A1A / SR 401near Port CanaveralLocation Counties: Orange, Brevard Highway system Florida State and County Roads
Interstate • US • SR (Pre-1945) • Toll • County←  SR 527
SR 527SR 528A 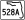 →
→State Road 528 (SR 528), the Martin Andersen Beachline Expressway (formerly known as the Martin Andersen Bee Line Expressway or simply The Bee Line), is a 53.5-mile (86.1 km) long state highway in the U.S. state of Florida. It is a mostly-tolled expressway connecting Interstate 4 in southwest Orlando with Cape Canaveral. It passes close to the tourist areas of Orlando, including SeaWorld and Universal Orlando, and serves the north entrance to Orlando International Airport. Near its east end, it passes over the Intracoastal Waterway on the Emory L. Bennett Causeway, and ends at State Road A1A and State Road 401 near Port Canaveral.
Martin Andersen, a retired publisher, used his influence to get the original stretch of road (from State Road 520 to Orlando International Airport) built in the 1960s.[2] The road is owned and maintained by Florida's Turnpike Enterprise (FTE), Orlando-Orange County Expressway Authority (OOCEA) and the Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT). The entire Beachline is compatible with the SunPass and E-Pass electronic toll collection transponders on both mainline plazas and interchange tolls.[3]
Contents
Route description
The westernmost eight miles (13 km) of the Beachline Expressway, from I-4 to State Road 482 near the airport, is known as the Beachline West Expressway and is FTE-owned. The section of the expressway is most famous for providing the link for tourists between Orlando International Airport and Orlando area attractions such as SeaWorld and Universal Orlando, and Walt Disney World via I-4. The Beachline begins at an interchange with I-4 (exit 72), and heads east, with interchanges with the tourist driven International Drive, Orangewood Blvd, John Young Parkway, and then jogs north to a massive interchange with Florida's Turnpike and Orange Blossom Trail (exit 4). The section of the Beachline Expressway from Exit 0 to Exit 4 remains a "free movement". The expressway continues east to the Beachline West barrier toll and then to SR 482 (McCoy Road/Sand Lake Road) (exit 8), ending FTE maintenance at the northwest edge of the Airport.[4]
OOCEA maintenance begins at the northwest corner of the airport, with an Airport barrier toll following a free movement section between exits 8-9 (Tradeport Drive/Conway Road), followed two airport access interchanges with SR 436 and Goldenrod Road. The last of the Beachline's free movement sections is between SR 436 and with SR 15 just east of the airport. Three miles east of the airport, it intersects with the GreeneWay, heading out of Orlando, with the road straightening out as a beeline for the rest of its journey in Orange County. From the GreeneWay to Interstate 95, the Beachline Expressway travels through mostly uninhabited marshlands. It intersects with a barrier toll just east of the GreeneWay, and has interchanges with International Corporate Park Boulevard, Dallas Boulevard and SR 520, the last interchange before the Orange County/Brevard County line, ending OOCEA maintenance and tolls.[5]
FDOT maintenance begins at the east end of the SR 520 interchange, crossing the St. Johns River into Brevard County, and just east of the Brevard County line, the road veers southeast at the interchange with SR 407. It then enters the Space Coast development area before the interchange with I-95. It continues east, with interchanges with SR 501/SR 524 and US 1 before crossing over the Intracoastal Waterway on the Emory L. Bennett Causeway, followed by interchanges with SR 3 and Banana River Drive before ending at A1A and State Road 401 near Port Canaveral.
Tolls on the east-pointing ramps at SR 520 are collected by FDOT, and 25 cents of the $1.25 OOCEA barrier toll east of the airport also goes to FDOT.[6] There are no toll roads in Brevard County so technically the 25 cents is only for use of the FDOT road section in Orange County. Nonetheless, most road maps show the Brevard County section from the Orange County line to Interstate 95 to be a toll road because it is impossible to travel over it without incurring a toll elsewhere. The TOLL 528 shield is also used on this stretch of road as well as on exit signs along I-95.
History
Pre-Bee Line
Orlando area
Prior to the construction of the Bee Line, State Road 528 was a surface road connecting Interstate 4 with the McCoy Jetport (now Orlando International Airport) and State Road 15 (Narcoossee Road). It ran along Sand Lake Road (now State Road 482) from I-4 east to Orange Blossom Trail (U.S. Highway 17/92/441 - SR 500/600 (Orange Avenue), where it turned south to reach Landstreet Road. Landstreet Road took SR 528 to State Road 527) at Taft, where SR 528 turned back north to McCoy Road. McCoy Road led east past the north entrance to the Jetport to SR 15; part of this is now SR 482, while part of McCoy Road from about one mile (1.6 km) east of SR 527 now serves as a frontage road to the Beachline.
An interchange at SR 528 and Kirkman Road (State Road 435) was built ca. 1958 to serve the new Martin Company complex (now Lockheed Martin) just to the south of that junction.[7] At that time, the area was basically empty, and the land was a part of the extensive Martin-owned Orlando Central Park.[where?]
Bennett Causeway
The Emory L. Bennett Causeway and approaches, running from State Road 520 west of Cocoa northeast and east across U.S. Highway 1, the Indian River Lagoon, Merritt Island and the Banana River, was dedicated on October 11, 1963 as a two-lane toll bridge and road.[8] It was assigned the SR 528 number over its whole length. At the same time, the present State Road 401 north of SR 528 was also built.[7] In 2003, construction was started on replacing the eastbound bridge over the Indian River Lagoon. It is now finished. The westbound bridge over the Indian River Lagoon will be replaced between 2013 and 2018. The causeway was named in honor of Emory L. Bennett, recipient of the Medal of Honor for his actions during the Korean War, and is part of the Indian River Lagoon Scenic Highway.
Construction
SR 15 to SR 520
Martin Andersen, then owner of the Orlando Sentinel, helped form the Central Florida Development Commission to ensure that Orlando would prosper, with one its goals being developing an "adequate road system". With the completion of Florida's Turnpike and Interstate 4 in 1963 and 1965, Orlando had freeway connections to the northwest, southwest, southeast and northeast, but lacked such a connection to the Kennedy Space Center to the east.
A bill creating the Orlando-Orange County Expressway Authority (OOCEA) was signed into law in 1963, which, unlike the State Road Department (SRD), could raise money for new roads using tolls. Its immediate goal was to build a road to the Kennedy Space Center, but the law was written with the intent of a larger expressway network.[9]
The OOCEA wanted to build a freeway all the way from I-4 to Cape Canaveral, but ran into several problems. It had issues with raising money for the road, with traffic projections falling short of necessary to pay for the large bond issue required. It also did not have the authority to build in Brevard County, and many Brevard residents opposed the roads, as it would draw business away from the Cape Canaveral area to Orlando.[9]
The setbacks resulted in a much shorter expressway route running from State Road 15 (Narcoosee Road) east of the McCoy Jetport east to State Road 520 in east Orange County. This was known as the Bithlo Cutoff, as it allowed traffic from southern Orlando to reach SR 520 without going north and east to Bithlo. West of SR 15, the existing SR 528 was to carry traffic to I-4. A new alignment would be built between Orange Blossom Trail and Orange Avenue, directly connecting Sand Lake Road to McCoy Road, and McCoy Road east from Daetwyler Drive (the Jetport entrance) to SR 15 would be widened as a divided surface road. Additionally, to handle traffic from downtown Orlando, SR 15 (Hoffner Avenue) between Conway Road and Goldenrod Road would be rebuilt. Concurrently, the SRD was extending Lake Barton Road (now State Road 436 - Semoran Boulevard) south to the Jetport, where it would meet the Bee Line, which opened in 1969.[9]
In November 1964, the OOCEA and SRD signed an agreement where the OOCEA would build the road, and then turn it over to the SRD, which would operate and maintain it, giving toll revenue to the OOCEA. Construction of the $6.8 million project began in early 1966, with groundbreaking at the location of the present Dallas Boulevard interchange (exit 24). The 17.4-mile (28.0 km) road was dedicated on July 14, 1967 at the 35-cent toll plaza, just east of SR 15 (28°27′00″N 81°15′09″W / 28.4500°N 81.2525°W), and the remaining section (Orange Blossom Trail to Orange Avenue) opened 9 days later. The OOCEA board had voted to name it after Martin Andersen in December 1966, and in 1967 the Florida Legislature passed this designation into law.[9]
I-4 to McCoy Jetport and SR 520 to the Bennett Causeway
In early 1967, the Florida State Turnpike Authority (FTA) announced plans for an expansion of the Turnpike system, including taking over the existing Bee Line and Bennett Causeway and forming a continuous route from the Turnpike to the Atlantic Ocean, with a spur (now State Road 407) to the Orsino Causeway. Enabling legislation was signed into law in July 1967. However, inflation caused problems with that plan. In December 1968, bonds were sold for a joint project - FTA would build from McCoy Jetport west to the Turnpike (at the existing Orlando-South interchange with Orange Blossom Trail), and Orange and Brevard Counties would fund the extension from SR 520 east to the Bennett and Orsino Causeways, in addition to a four-laning on the Bennett Causeway.[9]
An interchange at State Road 15 replaced an at-grade crossing ca. 1971.[7]
The FTA planned to build from the Turnpike east past the Jetport to SR 15, upgrading the existing SR 528 (McCoy Road) with frontage roads from west of the Jetport to SR 15. An interchange would be provided with the new State Road 436, planned to open in 1969. However, Governor Claude Kirk insisted that the new road continue west past the Turnpike to Interstate 4, and so the FTA did not have enough money to upgrade the road past the Jetport. (The FTA merged into the new Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) in 1969.) The piece from west of the Jetport to the Turnpike opened in late July 1973, and the rest of the road to I-4 opened in December. The road had one 15-cent toll booth (28°26′41″N 81°22′54″W / 28.4448°N 81.3818°W), lying between the Turnpike and Jetport. The rest of the road to I-4 was free; initially there were no interchanges except at International Drive, just east of I-4, but overpasses were built at roughly one-mile intervals which would eventually provide exits for Orangewood Blvd. and John Young Parkway.[9]
At the same time, construction had begun on the eastern section, originally known as the Central Florida Expressway,[6] by December 1971. The road ran east from SR 520 past a 20-cent toll booth (28°27′11″N 80°57′36″W / 28.453°N 80.960°W) to the St. Johns River, where it crossed into Brevard County. Shortly after crossing, it split, with a two-lane spur (State Road 407) heading northeast, interchanging with Interstate 95, and ending at State Road 405 west of the Orsino Causeway for access to the central part of the Kennedy Space Center. The main line headed southeast from the split and then east across I-95 to join the Bennett Causeway approach just west of U.S. Highway 1. The Causeway was widened, with a new eastbound side added, ca. 1970-71,[7] and the extension of the Bee Line to connect with the two causeways opened February 16, 1974.[9] The former Bennett Causeway approach west of the new road became State Road 524.
At the Orlando International Airport
While the sections west and east of the Jetport were freeways, the piece along McCoy Road, from west of the Jetport to SR 15, was a four-lane divided surface road. It had two major intersections - Daetwyler Drive (the Jetport entrance) and Semoran Boulevard (State Road 436), and a number of minor access points. Adding to the need for an upgrade was the Greater Orlando Aviation Authority's plans for expanding the Jetport (which became Orlando International Airport once the expansion was complete in September 1981).[9]
To help pay for the upgrade, the OOCEA raised tolls at the Bee Line toll plaza (east of SR 15) from 35 cents to 50 cents effective May 1, 1980. Bonds were sold in January 1981, and the finished SR 436/Airport interchange was dedicated on January 21, 1983. The 25-cent toll plaza (28°27′05″N 81°19′12″W / 28.4514°N 81.3201°W) just west of the Airport interchange opened July 2, 1983.[9]
Later changes
The spaces left for interchanges on the section west of the Turnpike have since been used by junctions with Orangewood Boulevard and Universal Boulevard, John Young Parkway, and Consulate Drive (for access between the west and Orange Blossom Trail and the Turnpike). East of SR 15, similar connections have been built with International Corporate Park Boulevard and Dallas Boulevard.
The interchange with State Road 417 (the Eastern Beltway) opened June 26, 1990, resulting in the toll booth east of SR 15 being moved several miles east.[9]
With the startup of the Disney Cruise Line from Port Canaveral in 1998, Disney started running buses along the Bee Line for tourists going between Walt Disney World and the port.
SR 528 east of State Road 436 was designated the Kennedy Space Center Highway in 1998 by the Florida Legislature.[10]
The 20-cent FDOT toll booth east of SR 520 was rounded up to 25 cents in July 1996 to improve efficiency. After an agreement signed May 8, 1998 by the OOCEA and FDOT, it was removed May 11, and replaced with an additional 25 cents at the $1 (originally 35-cent) OOCEA toll east of SR 417. The extra 25 cents goes to FDOT, as traffic that exits at State Road 520 now has to pay an extra quarter—the 25-cent ramp tolls pointing eastward at the SR 520 interchange were added August 19, 1999.[6] [11]
The last at-grade interchange on the original Bee Line alignment, a connection on the westbound side to a derelict portion of the McCoy Road frontage, was finally eliminated in 2002 as part of the Goldenrod Road extension project. The break in the frontage allowing eastbound traffic to cross over to McCoy Road at that point had been closed about a decade before during a resurfacing project. At that point, the Bee Line became completely limited-access from Interstate 4 to State Road 401.
In 2003, a new interchange was completed at George J. King Blvd at Port Canaveral, extending the freeway beyond SR 401. While SR 528 officially ends at SR 401,[1] signage continues it along State Road A1A to the new interchange at the city limits of Cape Canaveral.
 A billboard for the Space Coast, calling it "Orlando's closest beach", and labeling SR 528 the BeachLine
A billboard for the Space Coast, calling it "Orlando's closest beach", and labeling SR 528 the BeachLine
The name of the entire road, except between U.S. Highway 1 and State Road 3 (where it is the Emory L. Bennett Causeway), was officially designated as the Martin Andersen Beachline Expressway by the 2005 Florida Legislature.[12] This was done after lobbying by Brevard County, which wanted the shortest route to the Atlantic Ocean from the Orlando area designated as such. An organization representing businesses on the Space Coast has put up billboards calling it "Orlando's closest beach".
During 2006 construction began on a redesigned interchange with State Road 436 at the entrance to Orlando International Airport. It was completed in early 2008. A new flyover ramp was built from the Beachline westbound into the airport, eliminating the weaving of cars entering and leaving the airport from/to the Beachline. The mainline toll plazas east and west of the airport remain subject to traffic congestion because of the high percentage of tourists at those plazas who must pay with cash since they don't have access to SunPass, E-Pass or other acceptable electronic toll collection transponders.
The interchange at Exit 13 (Florida State Road 15) was reconstructed between September 2007 and July 2009, which expanded the interchange ramps and replaced the old bridges with wider ones, and did not eliminate free movement that exists between that exit and Exit 11 (Florida State Road 436).[13]
In May 2007, Florida's Turnpike Enterprise began Phase I of a project to widen the Beachline West. It encompasses the reconstruction of the mainline toll plaza located near Milepost 5, which is now complete. The new mainline toll plaza features two electronic (E-pass/SunPass) at-speed express lanes in each direction in the middle of the roadway (with capability to add another when the roadway proper is widened), and four staffed lanes in each direction to accommodate cash customers.[citation needed] The OOCEA had a similar reconstruction of the Beachline main toll plaza just east of the Greeneway between January 2008 and July 2009.[13]
In 2011, an accident involving an exploding fuel truck destroyed the overpass at Florida State Road 3. Traffic was forced to exit the highway around the damage. The overpass was replaced, high priority, within 30 days, for $2.2 million.[14]
Sightseers wishing to view the final launch of the Space Shuttle Discovery in 2011, caused a 40-mile (64 km) backup from Cape Canaveral.[15]
Expansion
East of the GreeneWay, a new interchange just west of ICP Blvd (Avalon Park Blvd.) and a Beachline East toll plaza that would be constructed between Dallas Blvd. and SR 520 that would end the free movement section, are in the five year work plan.[16]
In June 2008, a $49 million project to widen the Beachline from the Turnpike to McCoy Road to four lanes in each direction begun. Improvements include widening the existing bridge structures at US 441, Landstreet Road, CSX Transportation, CSX Taft Yard, Orange Avenue and McCoy Road, with a new bridge being constructed for the access ramp over CSX.[17]
Exit list
All tolls are assumed paying cash in a two-axle vehicle, such as a car.
County Location Mile[1][18] # Destination Notes Orange Orlando 0.000 
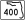 I-4 / SR 400 – Downtown Orlando, Tampa
I-4 / SR 400 – Downtown Orlando, Tampa0.855 1 International Drive 1.904 2 Orangewood Boulevard; Universal Boulevard 3.122 3  CR 423 (John Young Parkway)
CR 423 (John Young Parkway)split into 3A and 3B eastbound 4.443 4 


 Turnpike / US 17 / US 92 / US 441 (Orange Blossom Trail); Consulate Drive (State Road 91; State Road 500; State Road 600)
Turnpike / US 17 / US 92 / US 441 (Orange Blossom Trail); Consulate Drive (State Road 91; State Road 500; State Road 600)Beachline West barrier toll ($0.75) 8.163 8 
 SR 482 (McCoy Road to Sand Lake Road) to SR 527 (Orange Avenue)
SR 482 (McCoy Road to Sand Lake Road) to SR 527 (Orange Avenue)9.225 9 Tradeport Drive; Conway Road Airport barrier toll ($1.00) 10.734 11 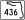 SR 436 north (Semoran Boulevard) - International Airport
SR 436 north (Semoran Boulevard) - International Airportsplit into 11A (SR 436) and 11B (Airport) westbound 12.085 12 Goldenrod Road; Heintzelman Boulevard 13.448 13  SR 15 (Narcoossee Road)
SR 15 (Narcoossee Road)15.536 16  SR 417 (Central Florida GreeneWay) – Tampa, Orlando, Sanford, Disney World
SR 417 (Central Florida GreeneWay) – Tampa, Orlando, Sanford, Disney WorldBeachline Main barrier toll ($1.50) 19.759 20 International Corporate Park Boulevard $1.25 westbound exit and eastbound entrance 23.783 24 Dallas Boulevard eastbound exit and westbound entrance 30.844 31 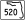 SR 520
SR 520$0.25 westbound exit and eastbound entrance Brevard 36.975 37 

 SR 407 to I-95 / SR 9 north – Kennedy Space Center, Titusville
SR 407 to I-95 / SR 9 north – Kennedy Space Center, Titusvilleeastbound exit and westbound entrance 41.728 42 
 I-95 / SR 9 – West Palm Beach, Daytona Beach
I-95 / SR 9 – West Palm Beach, Daytona Beachsplit into 42A and 42B 45.280 45 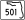
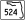 SR 501 (Clearlake Road) / SR 524 (Industry Road)
SR 501 (Clearlake Road) / SR 524 (Industry Road)split into 45A and 45B westbound Cocoa 45.956 46 
 US 1 / SR A1A / SR 5 – Cocoa, Titusville
US 1 / SR A1A / SR 5 – Cocoa, TitusvilleWestern end of SR A1A concurrency/Emory L. Bennett Causeway begins 48.842 49  SR 3 – Merritt Island, Kennedy Space Center
SR 3 – Merritt Island, Kennedy Space Center37,500 vehicles daily east of SR 3, 51,000 vehicles daily west of SR 3[19] 51.405 52 Banana River Drive 53.323 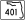 SR 401 north - Cape Canaveral Air Force Station; Port Canaveral A cruise terminals; north cargo piers
SR 401 north - Cape Canaveral Air Force Station; Port Canaveral A cruise terminals; north cargo piersEastern terminus, eastern end of SR A1A cocurrency 53.499 George J. King Boulevard References
- ^ a b c FDOT GIS data
- ^ This Day in Central Florida History - July 15
- ^ System Description - Beachline Expressway Retrieved 14 April 2010
- ^ FTE Map
- ^ OOCEA Map
- ^ a b c Florida Department of Transportation 2005 annual report, Department-owned Facilities (PDF)
- ^ a b c d National Bridge Inventory data
- ^ Interesting Dates in the history of the City of Cocoa
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Dr. Jerrell H. Shofner, Building a Community: The History of the Orlando-Orange County Expressway Authority (PDF), ISBN 0-9714713-0-4
- ^ Committee Substitute for Senate Bill No. 1014 (PDF)
- ^ Minutes of Orlando-Orange County Expressway Authority Special Board Meeting
- ^ House Bill No. 385 (PDF)
- ^ a b OOCEA: SR 528 Construction Retrieved 14 April 2010
- ^ Moody, R. Norman (15 February 2011). "Motorists praise overpass repairs". Florida Today (Melbourne, Florida): pp. 1A. http://www.floridatoday.com/article/20110215/NEWS01/102150331/Motorists-praise-overpass-repairs-State-Road-528-Merritt-Island?odyssey=tab.
- ^ Knapp, Andrew (25 February 2011). "Long after liftoff, traffic tie-ups linger". Florida Today (Melbourne, Florida): pp. 1A. http://www.floridatoday.com/article/20110225/NEWS01/102250316/Long-after-liftoff-traffic-tie-ups-linger?odyssey=tab.
- ^ OOCEA 2010-2014 Five-Year Work Plan Retrieved 14 April 2010
- ^ http://www.floridasturnpike.com/downloads/TurnPOrangeWidenBeachlineEastern.pdf
- ^ "Florida Department of Transportation Interchange Report" (PDF). Florida Department of Transportation. 2008-11-24. p. 19. http://www.dot.state.fl.us/planning/statistics/hwydata/interchange.pdf. Retrieved 2009-07-27.
- ^ Moody, R. Norman (25 January 2011). "Overpass repair on tight timeline". Florida Today (Melbourne, Florida): pp. 1B. http://www.floridatoday.com/article/20110125/NEWS01/101250320/Overpass-repair-tight-timeline.
- Expressway Map 1972
- STATE ROAD 528 (MARTIN B. ANDERSEN BEACHLINE EXPRESSWAY) OOCEA
- Florida @ SouthEastRoads - Florida 528
Florida's Turnpike Enterprise Florida's Turnpike
systemFDOT-owned  I-75 (Alligator Alley) •
I-75 (Alligator Alley) •  SR 528 (Beachline East Exp) •
SR 528 (Beachline East Exp) • 
 SR 679 / SR 682 (Pinellas Bayway) •
SR 679 / SR 682 (Pinellas Bayway) • 
 I-275 / US 19 (Sunshine Skyway Bridge)
I-275 / US 19 (Sunshine Skyway Bridge)FDOT-operated  SR 618 (Selmon Crosstown Expwy) •
SR 618 (Selmon Crosstown Expwy) •  SR 281 (Garcon Point Bridge) •
SR 281 (Garcon Point Bridge) •  SR 293 (Mid-Bay Bridge)
SR 293 (Mid-Bay Bridge)Expressways in Greater Orlando Orlando-Orange County Expressway Authority
SR 408 · SR 414 · SR 417 · SR 429 · SR 451 · SR 528 · Goldenrod Road Extension · SR 529† · Xpress 400†
† = planned, never builtFlorida's Turnpike Enterprise
Florida's Turnpike · SR 417 · SR 429 · SR 528Other agencies
Interstate 4 · Osceola Parkway · SR 407Notable bridges and tunnels in Florida Panhandle Escambia Bay · Garcon Point · John Gorrie · Mid-Bay · Pensacola Bay · St. George Island · Trammell · Victory
North Acosta · Bridge of Lions · Buckman · Dames Point · Fuller Warren · Hart · Mathews · Memorial · Strauss Trunnion
West Central East Central A. Max Brewer · Bennett Causeway · Bert Dosh · Broadway · Eau Gallie Causeway · Granada · Melbourne Causeway · Merritt Island Causeway · NASA Causeway · Pineda Causeway · Port Orange Causeway · Roosevelt · Wabasso
South Broad Causeway · Cape Coral · Coral Springs† · Julia Tuttle Causeway · John F. Kennedy Causeway · John Ringling Causeway · Lehman Causeway · MacArthur Causeway · Matanzas Pass · Midpoint · Rickenbacker Causeway · Sanibel Causeway · Snow-Reed‡ · Venetian Causeway
Keys Bahia Honda · Card Sound · Jewfish Creek · Overseas Highway · Seven Mile
Tunnels † – Covered bridge‡ - Swing bridge
See also: List of bridges in FloridaCategories:- Toll roads in Florida
- State highways in Florida
- State Roads in Orange County, Florida
- State Roads in Orlando, Florida
- Expressways in Orlando, Florida
- Expressways in Orange County, Florida
- State Roads in Brevard County, Florida
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.