- Outline of domestic violence
-
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to domestic violence:
Domestic violence – pattern of abusive behaviors by one or both partners in an intimate relationship, such as marriage, dating, family, or cohabitation. It is also known as domestic abuse, spousal abuse, battering, family violence, and intimate partner violence (IPV).
Nature of domestic violence
Domestic violence can be described as all of the following:
- Violence – use of physical force to apply a state to others contrary to their wishes[1][2][3] and may include some combination of verbal, emotional, economic, physical and sexual abuse.
- Control – Braiker[4] identified the following ways that manipulators control their victims:
-
- Positive reinforcement: praise, superficial charm, superficial sympathy (crocodile tears), excessive apologizing; money, approval, gifts; attention, facial expressions such as a forced laugh or smile; public recognition.
- Negative reinforcement: removing one from a negative situation as a reward. For example: "You won't have to walk home if you allow me to do this to you."
- Intermittent or partial reinforcement: partial or intermittent negative reinforcement can create an effective climate of fear and doubt. Partial or intermittent positive reinforcement can encourage the victim to persist.
- Punishment: nagging, yelling, the silent treatment, intimidation, threats, swearing, emotional blackmail, the guilt trap, sulking, crying, and playing the victim.
- Traumatic one-trial learning: verbal abuse, explosive anger, or other intimidating behavior to establish dominance or superiority; even one incident of such behavior can condition or train victims to avoid upsetting, confronting or contradicting the manipulator.
- Oppression – exercise of authority or power in a burdensome, cruel, or unjust manner.[5] It can also be defined as an act or instance of oppressing, the state of being oppressed, and the feeling of being heavily burdened, mentally or physically, by troubles, adverse conditions, and anxiety.
Epidemiology of domestic violence – Domestic violence occurs across the world, in various cultures,[6] and affects people across society, irrespective of economic status.[7]
Types of domestic violence
The following table includes the types of violence typically defined as part of Intimate partner violence, which is domestic violence in an intimate relationship by one's spouse or lover. It also includes a column for other family members or partners.
The rate of occurrence varies considerably based upon one's country, socio-economic class, culture, religion, family history and other factors.
Type of Violence Intimate Partners / Domestic Violence Other family members or partners Specific to Women? Acid throwing – violent assault by throwing acid onto the body of a person "with the intention of injuring or disfiguring out of jealousy or revenge."[8][9] √ √ Generally Birth control sabotage – efforts to manipulate another person's use of birth control or to undermine efforts to prevent an unwanted pregnancy. Examples include replacing birth control pills with fakes, puncturing condoms and diaphragms, or threats and violence to prevent an individual's attempted use of birth control.[10] √ Yes Breast ironing – pounding and massaging of a pubescent girl's breasts using heated objects in an attempt to make them stop developing or disappear.[11][12] √ Yes Bride burning – form of domestic violence for unresolved dowry issues resulting in death. √ Yes Bride-buying – illegal industry or trade of “purchasing a bride” to become property that can be resold or repurchased for reselling.[13][14] √ Yes Child abuse – physical or psychological/emotional mistreatment of children. It is often distinguished from domestic violence as it's own form of violence. √ No Dating abuse – pattern of abusive behavior exhibited by one or both partners in a dating relationship. √ √ Generally Domestic violence and pregnancy – abusive behavior towards a pregnant woman that whether physical, verbal or emotional, produces many adverse physical and psychological effects for the mother and fetus. √ Yes Dowry death – deaths of young women who are murdered or driven to suicide by continuous harassment and torture by husbands and in-laws in an effort to extort an increased dowry. √ Yes Economic abuse – form of abuse when one intimate partner has control over the other partner's access to economic resources,[15] which diminishes the victim's earning capacity and forces financial reliance on the perpetrator.[15][16][17] √ √ Generally Elder abuse – "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person."[18] √ √ No Female genital mutilation (FGM) – "all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia, or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons."[19] √ Yes FGM: Gishiri cutting – performed commonly by the peoples of the Hausa and Fulani regions of Northern Nigeria and Southern Niger. The procedure is believed by traditional practitioners to treat a variety of gynecological ailments (difficulty in labor, infertility, dyspareunia (pain during sex), pelvic organ prolapse and urinary retention), although there is no scientific basis for this procedure, and it is considered pseudoscience.[20][21] √ Yes FGM: Infibulation – removal of the labia minora (inner lips) and labia majora (outer lips). When the labial tissue heals, it forms a wall of skin and flesh across the vagina and the rest of the pubic area. By inserting a twig or similar before the wound heals, a small hole is created for the passage of urine and menstrual blood. The procedure is usually accompanied by the removal of the clitoris. √ Yes Foot binding – binding the feet of young girls painfully tight to prevent further growth. √ Yes Honor killing – homicide of a member of a family or social group by other members, due to the belief of the perpetrators that the victim has brought dishonor upon the family or community. Honor killings are directed mostly against women and girls, but have been extended to men. Also spelled "honour killing" (American and British spelling differences). √ √ Generally Marital rape – non-consensual sex in which the perpetrator is the victim's spouse, and as such, is a form of domestic violence, and sexual abuse. Although repudiated by international conventions and increasingly criminalized, in many countries, spousal rape either remains legal, or is illegal but widely tolerated and accepted as a husband's prerogative. Also known as "spousal rape". √ Generally Murder of pregnant women – type of homicide often resulting from domestic violence by a spouse or intimate partner violence (IPV).[22] √ Yes Psychological abuse – form of abuse characterized by a person subjecting or exposing another to behavior that may result in psychological trauma, including anxiety, chronic depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder. Such abuse is often associated with situations of power imbalance, such as abusive relationships, bullying, child abuse and workplace bullying.[23][24][25] Psychological abuse is also referred to as "emotional abuse" or "mental abuse". √ √ No Physical abuse – abuse involving contact intended to cause feelings of intimidation, injury, or other physical suffering or bodily harm.[26][27] √ √ No Sati – religious funeral practice among some Indian communities in which a recently widowed woman either voluntarily or by use of force and coercion would have immolated herself on her husband’s funeral pyre.[28] √ Yes Sexual violence – any sexual act, attempt to obtain a sexual act, unwanted sexual comments or advances, or acts to traffic, or otherwise directed, against a person’s sexuality using coercion, by any person regardless of their relationship to the victim, in any setting, including but not limited to home and work.[29] √ √ No Spiritual abuse – serious form of abuse which occurs when a person in religious authority or a person with a unique spiritual practice misleads and maltreats another person in the name of God or church or in the mystery of any spiritual concept. √ √ No Stalking – unwanted and obsessive attention by an individual or group to another person. Stalking behaviors are related to harassment and intimidation and may include following the victim in person and/or monitoring them via the internet. √ √ No Teen dating violence – physical, sexual, or psychological / emotional violence within a dating relationship.[30] √ Generally Verbal abuse – often used to control the victim and can lead to significant detriment to one's self-esteem, emotional well-being, and physical state. √ √ No Domestic violence against men and LGBT
- Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transsexual domestic violence – occurs in about 11% of lesbian homes, about half the rate of 20% reported by heterosexual women. Lesbians, however, often have fewer resources available for shelter and counselling.[31]
- Domestic violence against men – state that women are as violent as men and that domestic violence is sex-symmetrical.[32][33] A large study, compiled by Martin S. Fiebert, shows that women are as likely to be abusive to men, but the men are less likely to be hurt. However, he noted, men are seriously injured in 38% of the cases in which "extreme aggression" is used. Fiebert additionally noted that his work was not meant to minimize the serious effects of men who abuse women.[34][35][nb 1] Women are far more likely to use weapons, such as throwing a plate or firing a gun.[36]
- The National Institute of Justice contends that national surveys supported by NIJ, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Bureau of Justice Statistics that examine more serious assaults do not support the conclusion of similar rates of male and female spousal assaults. These surveys are conducted within a safety or crime context and clearly find more partner abuse by men against women.[37][nb 2]
Stop Abuse For Everyone (SAFE), an United States domestic violence organization, advocates for an "inclusive" model of domestic violence, focusing on groups that are "lacking in services", such as abused men, gay lesbian, and transgendered victims, and the elderly.[38]
Contributing factors
- Conflict tactics scale – research method for identifying intimate partner violence by measuring the conflict tactic behaviors.
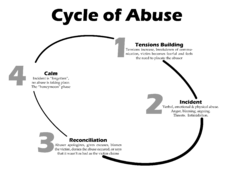
- Cycle of abuse – social cycle theory to explain patterns of behavior of a violent intimate relationship: Tension building phase, acting-out phase, reconciliation / honeymoon phase, and calm phase, which leads back to the tension building phase.[39]
- Cycle of violence
-
- Within a relationship – repeated acts of violence as a cyclical pattern, associated with high emotions and doctrines of retribution or revenge. The pattern, or cycle, repeats and can happen many times during a relationship. Each phase may last a different length of time and over time the level of violence may increase.
- Intergenerational cycle of violence – violence that is passed from father to son or daughter, parent to child, or sibling to sibling.[40]
- Misandry – the hatred or dislike of men or boys, which manifests like Misogyny.
- Misogyny – the hatred or dislike of women or girls, may be manifested in varying degrees of intensity, like pornography, jokes, teaching girls or women to feel self-contempt or violence.[41]
- Relational disorder – dysfunction within a relationship, versus being specific to a specific individual's dysfunction.[42]
Domestic violence dynamics between partners
- Situational couple violence – arises infrequently out of conflicts that escalate to arguments and then to violence, rather than a general pattern of control. It is likely the most common type of intimate partner violence. Women are as likely as men to be abusers, however, women are more likely to be physically injured, require police intervention and become fearful of their mates.[43]
- Intimate terrorism (IT) – pattern of ongoing control using emotional, physical and other forms of domestic violence. It is what was traditionally the definition of domestic violence depicted in the "Power and Control Wheel"[44] which illustrates the different and inter-related forms of abuse.[45]
- Violent resistance (VR), or "self-defense" – violence perpetrated by victims against their abusive partners.[46] It is generally used infrequently because, men are often better able to physically overpower women.[43]
- Common couple violence (CCV) – domestic violence "in which conflict occasionally gets ‘out of hand,’ leading usually to ‘minor’ forms of violence, and rarely escalates into serious or life-threatening forms of violence.”[47]
- Mutual violent control (MVC) – rare type of intimate partner violence that occurs when both partners act in a violent manner, battling for control.[48]
Impacts
The incidence of abuse may result in the following:
- Effects of domestic violence on children – dysfunctions in the physical, behavioral, emotional, and social areas of life which affect their well-being, child development, teen dating experiences, future domestic situations and mortality.
- Mental illness [49][50] – psychological or behavioral pattern generally associated with subjective distress or disability that occurs in an individual, and which is not a part of normal development or culture. Such a disorder may consist of a combination of affective, behavioral, cognitive and perceptual components.
-
- Battered person syndrome – physical and psychological condition victims of domestic abuse, which may be manifested as a type of Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), from an ongoing Cycle of abuse.
- Self-harm – intentional, direct injuring of body tissue most often done without suicidal intentions.[49]
- Suicide,[49][50] – act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse.[51]
-
- Self-immolation – setting oneself on fire, often as a form of protest or for the purposes of martyrdom or suicide.
Legal
Remedies
- Evidence-based prosecution of domestic violence – prosecutors aggressively trying domestic violence cases, basing their cases on evidence rather than victim cooperation, resulting in higher conviction rates.[52]
- Injunction – equitable remedy in the form of a court order that requires a party to do or refrain from doing certain acts. A party that fails to comply with an injunction faces criminal or civil penalties and may have to pay damages or accept sanctions. In some cases, breaches of injunctions are considered serious criminal offenses that merit arrest and possible prison sentences.
-
- Restraining order – requires a party to do, or to refrain from doing, certain acts. A party that refuses to comply with an order faces criminal or civil penalties and may have to pay damages or accept sanctions. Breaches of restraining orders can be considered serious criminal offences that merit arrest and possible prison sentences. The term is most commonly used in reference to domestic violence, harassment, stalking or sexual assault.
Topics
- Battered woman defense – a self-defense measure used in court that the person accused of an assault / murder was suffering from battered person syndrome.
- Domestic violence court – specialized courts designed to improve victim safety and enhance defendant accountability, created in response to frustration among victim advocates, judges and attorneys who saw the same litigants cycling through the justice system repeatedly.
Religion and domestic violence
-
- AHA Foundation – Muslim women's rights in western countries
- Peaceful Families Project – Muslim organization
Domestic violence by region
- Domestic violence in Afghanistan
- Family Response Unit – office of the Afghan National Police which deals with domestic violence, female and child victims of crime, and female suspects. The unit is staffed by policewomen trained by the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA).[53]
- Domestic violence in Argentina
- Domestic violence in Armenia
- Domestic violence in Australia
- Act as 1 Campaign – Domestic Violence and Family Violence Prevention campaign [54] led by the Queensland Government.
- Humbug (Aboriginal) – forms of begging and domestic violence in rural and remote Aboriginal communities in the Northern Territory, Australia.
- Domestic violence in Bolivia
- Domestic violence in Brazil
- Human rights in Brazil and domestic violence
- Lei Maria da Penha – Brazil's federal law against domestic violence
- Domestic violence in Chile
- Domestic violence in Colombia
- Lissette Ochoa domestic violence case – one of the best known cases of spousal abuse in Colombia because of the couple's elite social status and for the brutality of the battering perpetrated on Lissette Ochoa by her husband Rafael Dangond.
- Domestic violence in Ecuador
- Domestic violence in Guyana
- Domestic violence in India
- Bell Bajao – campaign of the Breakthrough (human rights) organization
- Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act 2005 – India federal law
- Save Indian Family (India) – men's rights movement that asserts misuse of India's laws related to dowry harassment and domestic violence[55] and provides moral and legal support for men and their families who have suffered or have been accused of intimate partner violence.[56]
- Domestic violence in Iran
- Domestic violence in Malaysia
- Women's Aid Organisation – non-governmental organization that fights for women's rights and specifically against violence against women.
- Domestic violence in Panama
- Domestic violence in Paraguay
- Domestic violence in Peru
- Domestic violence in Russia
- Domestic violence in Samoa
- Domestic violence in South Korea
- Korea Women's Hot Line – non-profit women's rights activist group, protecting women's rights from all kinds of violence and advancing women's social position as well as establishing gender equality in the spheres of family, work, and society.
- Domestic violence in Spain
- Shows red card to abuser – a public awareness campaign and symbol to say "no" to domestic violence
- Domestic violence in Tajikistan
- Domestic violence in the United Kingdom
- Organizations
- Broken Rainbow (organization) – deals with same sex domestic violence
- Campaign Against Domestic Violence – organization with multi-pronged approach towards eliminating domestic violence
- Mankind Initiative – domestic violence charity
- Refuge (United Kingdom charity) – charity for female victims
- Scottish Women's Aid – charity to prevent domestic violence against women an children
- Women's Aid Federation of England – United Kingdom charity to prevent domestic violence against women an children
- What's it going to take? – campaign of the WAFOE
- Organizations
- Domestic violence in the United States
- Laws \ legal issues
- Address confidentiality program – some states in the United States
- Domestic Violence, Crime and Victims Act 2004 –
- Domestic Violence Offender Gun Ban – addresses Gun violence in the United States
- Violence Against Women Act – United States federal law
- Family Violence Prevention and Services Act –
- Models to reduce domestic violence
- Duluth model (United States) –
- Initiatives to prevent sexual violence (United States) –
- Organizations
- Laws \ legal issues
-
- Declaration on the Elimination of Violence Against Women –
- United Nations Development Fund for Women –
- United Nations Entity for Gender Equality and the Empowerment of Women (UN Women) –
-
- AHA Foundation – concerned with Muslim women's rights in western countries
- Peaceful Families Project – (Muslim organization)
Conventions on domestic violence
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women –
- Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence –
Publications
- Contemporary Family Therapy – journal with articles about "the latest developments in theory, research and practice pertaining to family therapy, with an emphasis on examining families within their broader socio-economic and ethnic matrices."[57]
- Family Process – non-profit journal with current articles about family system issues, focusing on research, policy, and applied practice.[58]
- Family Relations – international journal, published on behalf of the National Council on Family Relations, regarding family studies.[59]
- International Journal of Interdisciplinary Social Sciences
- Journal of Adult Protection
- Journal of Child and Family Studies[60]
- Journal of Family Issues – peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes papers in the field of Family Studies.
- Journal of Family Psychology[61]
- Journal of Family Violence
- Journal of Interdisciplinary Social Sciences
- Journal of Interpersonal Violence – publishes current "information on domestic violence, rape, child sexual abuse and other violent crimes."[62]
- Journal of Marital and Family Therapy[63]
- Journal of Marriage and the Family
- Signs: Journal of Women in Culture and Society – academic journal covering a wide range of disciplines covering issues like gender, race, culture, class, sexuality, and/or nation.
- Trauma, Violence, & Abuse – publishes original research for practioners.[64]
- Violence Against Women – peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes papers in the field of Women’s Studies.[65]
Documentaries
- The Conspiracy of Silence
- Defending Our Lives
- Power and Control: Domestic Violence in America
- Silent Voices
- Sin by Silence
Films
- American Tragedy
- Black and Blue
- Blinded
- Bordertown
- The Burning Bed
- Daughters
- Enough
- Looking for Angelina
- Once Were Warriors
- One Minute to Nine
- Provoked
- Submission
- What's Love Got to Do with It
Gallery
See also
- Abuse
- Domestic violence (women's) shelter
- Feminist dominance in domestic violence discussions
- Gender studies
- Interpersonal relationships
- Men's rights
- Sociology of the family
- Victimization
- Violence
References
- Notes
- ^ Martin S. Fiebert of the Department of Psychology at California State University, Long Beach, has compiled an annotated bibliography of research relating to spousal abuse by women on men. This bibliography examines 275 scholarly investigations: 214 empirical studies and 61 reviews and/or analyses appear to demonstrate that women are as physically aggressive, or more aggressive, than men in their relationships with their spouses or male partners. The aggregate sample size in the reviewed studies exceeds 365,000.[34] In a Los Angeles Times article about male victims of domestic violence, Fiebert suggests that "...consensus in the field is that women are as likely as men to strike their partner but that—as expected—women are more likely to be injured than men."[35]
- ^ The National Institute of Justice states that studies finding equal or greater frequency of abuse by women against men are based on data compiled through the Conflict Tactics Scale. This survey tool was developed in the 1970s and may not be appropriate for intimate partner violence research because it does not measure control, coercion, or the motives for conflict tactics; it also leaves out sexual assault and violence by ex-spouses or partners and does not determine who initiated the violence.[37]
- Citations
- ^ Violence., Merriam-Webster Dictionary Retrieved January 8, 2009.
- ^ Violence., Oxford English Dictionary Retrieved January 8, 2009.
- ^ Violence., American Heritage Dictionary, Violence, Retrieved January 8, 2009.
- ^ Braiker, Harriet B. (2004) Who's Pulling Your Strings? How to Break The Cycle of Manipulation ISBN 0071446729.
- ^ Oppression. Merriam Webster Online.
- ^ Watts C.; Zimmerman C. (April 2002) "Violence against women: global scope and magnitude." Lancet. 359(9313):1232–7. PMID 11955557. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08221-1.
- ^ Waits, Kathleen. (1984-1985). "The Criminal Justice System's Response to Battering: Understanding the Problem, Forging the Solutions." Washington Law Review. 60:267–330.
- ^ Karmakar, R.N. (2003). Forensic Medicine and Toxicology. Academic Publishers. ISBN 8187504692.
- ^ Vij, Krishan. (2003) Textbook of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology: Principles and Practice, 5th Edition. Elsevier India. p. 462. ISBN 9788131226841.
- ^ Miller, Dr Elizabeth, et al. "Male Partner Pregnancy-Promoting Behaviors and Adolescent Partner Violence: Findings from a Qualitative Study with Adolescent Females." UC Davis School of Medicine, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston University School of Public Health. March 2, 2007.
- ^ Sa'ah, Randy Joe. Cameroon girls battle 'breast ironing' BBC News. June 23, 2006. Retrieved January 2, 2008.
- ^ Gidley, Ruth; Rowling, Megan. [Millions of Cameroon girls suffer "breast ironing". AlertNet, Reuters July 7, 2006. Reproduced at the Child Rights Information Network. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ Marshall, Samantha, Joanne Lee-Young, and Matt Forney, Vietnamese Women Are Kidnapped and Later Sold in China as Brides. The Wall Street Journal. August 3, 1999.
- ^ Rose, Winifred Hodge. The Purchase of a Bride: Bargain, Gift, Hamingja, Frigga's Web.
- ^ a b Adams, Adrienne; Sullivan, Bybee, Greeson. (May 2008) "Development of the Scale of Economic Abuse." Violence Against Women 14(5):563–588. Retrieved September 19, 2011.
- ^ Brewster, M. P. (2003) "Power and Control Dynamics in Pre-stalking and Stalking Situations." Journal of Family Violence. 18(4):207–217.
- ^ Sanders, Cynthia. Organizing for Economic Empowerment of Battered Women: Women’s Savings Accounts. Center for Social Development, George Warren Brown School of Social Work, Washington University. Retrieved September 19 2011.
- ^ Action on Elder Abuse. Retrieved October 12, 2007.
- ^ Female genital mutilation, World Health Organization. February 2010.
- ^ Romanzi, Lauri. (2010) “Yankan Gishiri” cutting, a home remedy, cause fistula in Niger and Nigeria. Urogynics. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Fistula Forward. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Campbell, JC, Glass, N, Sharps, PW, Laughon, K, and Bloom, T (2007) Intimate Partner Homicide: Review and Implications of Research and Policy. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse. (8), 246-269.
- ^ Dutton, D. G. (1994). Patriarchy and wife assault: The ecological fallacy. Violence and Victims, 9, 125-140.
- ^ Maiuro, Roland D.; O'Leary, K. Daniel. (2000). Psychological Abuse in Violent Domestic Relations. New York: Springer Publishing Company. p. 197. ISBN 0-8261-1374-5.
- ^ Child Sexual Abuse. National Clearinghouse on Family Violence, Health Canada. 1997. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Haugan, Grethemor Skagseth; Nøttestad, Jim Aage.Norway : Treatment Program For Men Who Batter Norwegian University of Science and Technology. Trondheim, Norway.
- ^ Giardino, Angelo P.; Giardino, Eileen R. Child Abuse & Neglect: Physical Abuse December 12, 2008. eMedicine. WebMD.
- ^ Sati. SOS Sexisme. Retrieved July 26, 2010.
- ^ World report on violence and health. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2002. p. 149.
- ^ "Teen dating violence" Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- ^ Ten Things Lesbians Should Discuss with their Health Care Providers. Gay and Lesbian Medical Association. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ^ Dragiewicz, Molly. (April 12 2011). Equality with a Vengeance: Men's Rights Groups, Battered Women, and Antifeminist Backlash. UPNE. p. 84–5. Retrieved October 22, 2011. ISNB 978-1-55553-739-5.
- ^ Loseke, Donileen R.; Gelles, Richard J.; Cavanaugh, Mary M. (2005). Current controversies on family violence. SAGE. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-7619-2106-6. Retrieved October 22, 2011.
- ^ a b Fiebert, Martin S. References examining assaults by women on their spouses or male partners: an annotated bibliography
- ^ a b Academic website of Martin S. Feibert, Ph. D.
- ^ Violence by Intimates Analysis of Data on Crimes by Current or Former Spouses, Boyfriends, and Girlfriends. US Department of Justice. Retrieved September 10, 2010.
- ^ a b Measuring Intimate Partner (Domestic) Violence National Institute of Justice. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Main page Stop Abuse For Everyone. 2010. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Walker, Lenore E. (1979) The Battered Woman. New York: Harper and Row.
- ^ Intergenerational Cycle Of Abuse AbusiveLove.com. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Johnson, Allan G. (2000). The Blackwell dictionary of sociology: A user's guide to sociological language. p. 197. ISBN 9780631216810.
- ^ Michael B. First, MD. A Research Agenda for DSM-V: Summary of the DSM-V Preplanning White Papers. Published in May 2002.
- ^ a b A Sociologist’s Perspective on Domestic Violence, A Conversation with Michael Johnson, Ph.D. Theodora Ooms, interviewer. Center for Law and Social Policy (CLASP). p. 3. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
- ^ Power and Control Wheel, National Center on Domestic and Sexual Violence. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
- ^ A Sociologist’s Perspective on Domestic Violence, A Conversation with Michael Johnson, Ph.D. Theodora Ooms, interviewer following May 2006 conference. Center for Law and Social Policy (CLASP). pp. 2-4. Retrieved November 20, 2011.
- ^ Bachman, R.; D. Carmody. (1994) "Fighting Fire with Fire: The Effects of Victim Resistance in Intimate Versus Stranger Perpetrated Assaults Against Females." Journal of Family Violence. 9(4):317–31. doi:10.1007/BF01531942.
- ^ Johnson, M. P., (1995). Patriarchal terrorism and common couple violence: Two forms of violence against women. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 57, 283–294.
- ^ Saunders D.G. (1998). "Wife Abuse, Husband Abuse, or Mutual Combat? A Feminist Perspective on the Empirical Findings." Feminist perspectives on wife abuse. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. pp. 90–113. ISBN 0-8039-3053-4.
- ^ a b c Shipway, Lynn. (2004). Domestic violence: a handbook for health professionals. New York: Routledge. ISBN 9780415282208.
- ^ a b Mayhew, P.; Mirlees-Black, C.; Percy, A. (1996) The 1996 British Crime Survey England & Wales. Home Office.
- ^ Hawton K.; van Heeringen, K. (April 2009). "Suicide." Lancet. 373(9672):1372–81. PMID 19376453. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60372-X.
- ^ Fagan, Jeffrey. (1996).The Criminalization of Domestic Violence: Promises and Limits National Institute of Justice. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ UNFPA. Afghanistan's First Family Response Unit Open for Business. January 24, 2006.
- ^ Act As One Queensland Government. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ "Wife harassing you? Call for help." IBN. November 29, 2006. Retrieved December 31, 2008.
- ^ Book Review: Who Stole Feminism? How Women have Betrayed Women? Save Indian Family. Retrieved November 21, 2011.
- ^ Contemporary Family Therapy. Springer Science+Business Media. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Family Process
- ^ Family Relations. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Journal of Child and Family Studies, ISSN: 1062-1024 (Print) 1573-2843 (Online), Springer.
- ^ Journal of Family Psychology
- ^ Journal of Interpersonal Violence. Sage Publications. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Journal of Marital and Family Therapy
- ^ Trauma, Violence, & Abuse. Sage Publications. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
- ^ Violence Against Women. Sage Publications. Retrieved November 22, 2011.
External links
Outlines - General reference
- Culture and the arts
- Geography and places
- Health and fitness
- History and events
- Mathematics and logic
- Natural and physical sciences
- People and self
- Philosophy and thinking
- Religion and belief systems
- Society and social sciences
- Technology and applied sciences
Categories:- Outlines
- Violence against women
- Crime-related lists
- Domestic violence
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.