- Outline of geophysics
-
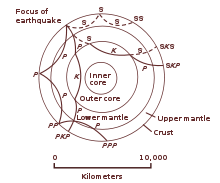 Seismic velocities and boundaries in the interior of the Earth sampled by seismic waves.
Seismic velocities and boundaries in the interior of the Earth sampled by seismic waves.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geophysics:
Geophysics – the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations have a broader definition that includes the hydrological cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.
Contents
- 1 Nature of geophysics
- 2 Branches of geophysics
- 3 History of geophysics
- 4 General geophysics concepts
- 5 Closely allied sciences
- 6 Society
- 7 Geophysics lists
- 8 See also
- 9 External links
Nature of geophysics
Geophysics can be described as all of the following:
- An academic discipline: one with academic departments, curricula and degrees; national and international societies; and specialized journals.
- A scientific field (a branch of science) – widely-recognized category of specialized expertise within science, and typically embodies its own terminology and nomenclature. Such a field will usually be represented by one or more scientific journals, where peer reviewed research is published. There are several geophysics-related scientific journals.
- A natural science – one that seeks to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world using empirical and scientific methods.
- A physical science – one that studies non-living systems.
- An earth science – one that studies the plant Earth and its surroundings.
- A physical science – one that studies non-living systems.
- A biological science – one that studies the effect of organisms on their physical environment.
- A natural science – one that seeks to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world using empirical and scientific methods.
- An interdisciplinary field – one that overlaps atmospheric sciences, geology, glaciology, hydrology, oceanography and physics.
Branches of geophysics
- Biogeophysics – the study of how plants, microbial activity and other organisms alter geologic materials and affect geophysical signatures.
- Exploration geophysics – the use of surface methods to detect concentrations of ore minerals and hydrocarbons.
- Geophysical fluid dynamics – the study of naturally occurring, large-scale flows on Earth and other planets.
- Geodesy – the measurement and representation of the Earth, including its gravitational field.
- Geodynamics – the study of modes of transport deformation within the Earth: rock deformation, mantle convection, heat flow, and lithosphere dynamics.
- Geomagnetism – the study of the Earth's magnetic field, including its origin, telluric currents driven by the magnetic field, the Van Allen belts, and the interaction between the magnetosphere and the solar wind.
- Mathematical geophysics – the development and applications of mathematical methods and techniques for the solution of geophysical problems.
- Mineral physics – the science of materials that compose the interior of planets, particularly the Earth.
- Near-surface geophysics – the use of geophysical methods to investigate small-scale features in the shallow (tens of meters) subsurface.
- Paleomagnetism – the measurement of the orientation of the Earth's magnetic field over the geologic past.
- Seismology – the study of the structure and composition of the Earth through seismic waves, and of surface deformations during earthquakes and seismic hazards.
- Tectonophysics – the study of the physical processes that cause and result from plate tectonics.
History of geophysics
Main article: History of geophysics- History of geomagnetism
- Timeline of the development of tectonophysics
- Vine-Matthews-Morley hypothesis
General geophysics concepts
Gravity
Main article: Gravity of EarthHeat flow
Main article: Geothermal gradient- Internal heating
Electricity
Atmospheric electricity
Main article: Atmospheric electricity- Lightning
- Sprite (lightning)
Electricity in Earth
- Electrical resistivity tomography
- Induced polarization
- Seismoelectrical method
- Spectral induced polarisation
- Spontaneous potential
- Telluric current
Electromagnetic waves
- Alfvén wave
- Dawn chorus (electromagnetic)
- Hiss (electromagnetic)
- Magnetotellurics
- Seismo-electromagnetics
- Transient electromagnetics
- Whistler (radio)
Fluid dynamics
Main article: Geophysical fluid dynamics- Isostasy
- Post-glacial rebound
- Mantle convection
- Geodynamo
Magnetism
Geomagnetism subfields
- Environmental magnetism
- Magnetostratigraphy
- Paleomagnetism
- Rock magnetism
Earth's magnetic field
Main article: Earth's magnetic fieldDescription
- Geomagnetic pole
- Magnetic declination
- Magnetic inclination
- North Magnetic Pole
- South Magnetic Pole
Sources
- Geodynamo
- Magnetic anomaly
- Magnetosphere
Short-term changes
- Secular variation
- Geomagnetic secular variation
- Geomagnetic jerk
Long term behavior
- Apparent polar wander
- Geomagnetic excursion
- Geomagnetic pole
- Geomagnetic reversal
- Geomagnetic secular variation
- Polar wander
- True polar wander
Magnetostratigraphy
- Archaeomagnetic dating
- Chron
- Magnetostratigraphy
- Superchron (currently redirected to Geomagnetic reversal#Moyero Reversed Superchron)
Rock magnetism
Main article: Rock magnetism- Magnetic mineralogy
- Natural remanent magnetization
- Saturation isothermal remanence
- Thermoremanent magnetization
- Viscous remanent magnetization
Tectonic applications
- Plate reconstruction
Magnetic survey
Radioactivity
Mineral physics
Main article: Mineral physicsVibration
Main article: Seismology- Deep focus earthquake
- Earthquake
- Intraplate earthquake
- Seismic waves
- Reflection seismology
- Seismic refraction
- Seismic tomography
- Structure of the Earth
Closely allied sciences
Atmospheric sciences
Main article: Atmospheric sciences- Aeronomy – the study of the physical structure and chemistry of the atmosphere.
- Meteorology – the study of weather processes and forecasting.
- Climatology – the study of weather conditions averaged over a period of time.
Geology
Main article: Geology- Mineralogy – the study of chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals.
- Petrophysics – The study of the origin, structure, and composition of rocks.
- Volcanology – the study of volcanoes, volcanic features (hot springs, geysers, fumaroles), volcanic rock, and heat flow related to volcanoes.
Engineering
- Geological and geophysical engineering – the application of geophysics to the engineering design of facilities including roads, tunnels, and mines.
Water on the Earth
- Glaciology – the study of ice and natural phenomena that involve ice, particularly glaciers.
- Hydrology – the study of the movement, distribution, and quality of water on Earth and other planets.
- Physical oceanography – the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.
Society
Influential persons
Main article: List of geophysicistsOrganizations
- American Geophysical Union · Canadian Geophysical Union · Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society · European Geosciences Union · International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics · Royal Astronomical Society · Society of Exploration Geophysicists · Seismological Society of America
Publications
- Geophysics journals
- Important publications in geophysics (geology)
- Important publications in geophysics (physics)
Geophysics lists
Main category: Geophysics lists- Free geophysics software
See also
External links
Outlines - General reference
- Culture and the arts
- Geography and places
- Health and fitness
- History and events
- Mathematics and logic
- Natural and physical sciences
- People and self
- Philosophy and thinking
- Religion and belief systems
- Society and social sciences
- Technology and applied sciences
Geophysics Overview Outline · GeophysicistsSubfields Geophysical fluid dynamics · Geodesy · Geodynamics · Geomagnetism · Mathematical geophysics · Mineral physics · Near-surface geophysics · Paleomagnetism · Seismology · TectonophysicsPhysical Phenomena Coriolis effect · Earth's magnetic field · Geodynamo · Geothermal gradient · Gravity of Earth · Mantle convection · Seismic waveOrganizations American Geophysical Union · Canadian Geophysical Union · Environmental and Engineering Geophysical Society · European Geosciences Union · International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics · Royal Astronomical Society · Society of Exploration Geophysicists · Seismological Society of AmericaCategories:- Geophysics
- Geophysics lists
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
