- Northrop X-4 Bantam
-
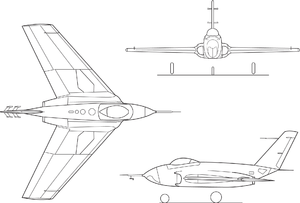
X-4 Bantam X-4 Bantam Role Tailless aircraft prototype Manufacturer Northrop First flight 15 December 1948 Number built 2 The Northrop X-4 Bantam was a prototype small twin-jet aircraft manufactured by Northrop Corporation in 1948. It had no horizontal tail surfaces, depending instead on combined elevator and aileron control surfaces (called elevons) for control in pitch and roll attitudes, almost exactly in the manner of the similar-format, rocket-powered Messerschmitt Me 163 of Nazi Germany's Luftwaffe. Some aerodynamicists had proposed that eliminating the horizontal tail would also do away with stability problems at fast speeds resulting from the interaction of supersonic shock waves from the wings and the horizontal stabilizers. The idea had merit, but the flight control systems of that time prevented the X-4 from any success.
Contents
Development
Two X-4s were built by the Northrop Corporation, but the first was found to be mechanically unsound and after 10 flights it was grounded and used to provide parts for the second. While being tested from 1950 to 1953 at the NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station (now Edwards Air Force Base), the X-4's semi-tailless configuration exhibited inherent longitudinal stability problems (porpoising) as it approached the speed of sound. It was concluded that (with the control technology available at the time) tailless craft were not suited for transonic flight.
It was believed in the 1940s that a design without horizontal stabilizers would avoid the interaction of shock waves between the wing and stabilizers. These were believed to be the source of the stability problems at transonic speeds up to Mach 0.9. Two aircraft had already been built using a semi-tailless design—the rocket-powered Me-163 Komet flown by Germany in World War II, and the British de Havilland DH.108 Swallow built after the war. The United States Army Air Forces signed a contract with the Northrop Aircraft Company on 11 June 1946, to build two X-4s. Northrop was selected because of its experience with flying wing designs, such as the N-9M, XB-35 and YB-49 aircraft.
The resulting aircraft was very compact, only large enough to hold two Westinghouse J30 jet engines, a pilot, instrumentation, and a 45-minute fuel supply. Nearly all maintenance work on the aircraft could be done without using a ladder or footstool. A person standing on the ground could easily look into the cockpit. The aircraft also had split flaps, which doubled as speed brakes.
Operational history
The first X-4 (serial number 46-676) was delivered to Muroc Air Force Base, California, in November 1948. It underwent taxi tests and made its first flight on December 15, 1948, with Northrop test pilot Charles Tucker at the controls. Winter rains flooded Rogers Dry Lake soon after, preventing additional X-4 flights until April 1949. The first X-4 proved mechanically unreliable, and made only 10 flights. Walt Williams, the head of the NACA Muroc Flight Test Unit (now Dryden Flight Research Center) called the aircraft a "lemon". The second X-4 (serial number 46-677) was delivered during the halt of flights, and soon proved far more reliable. It made a total of 20 contractor flights. Despite this, the contractor flight program dragged on until February 1950, before both aircraft were turned over to the Air Force and the NACA. The first X-4 never flew again, used as spare parts for the second aircraft.
The NACA instrumented the second X-4 to conduct a short series of flights with Air Force pilots. These included Chuck Yeager, Frank Kendall Everest, Jr., Al Boyd, Richard Johnson, Fred Ascani, Arthur Murray and Jack Ridley. The flights were made in August and September 1950. The first flight by a NACA pilot was made by John H. Griffith on September 28, 1950.
The initial NACA X-4 flights, which continued from late 1950 through May of 1951, focused on the aircraft's sensitivity in pitch. NACA pilots Griffith and Scott Crossfield noted that as the X-4's speed approached Mach 0.88, it began a pitch oscillation of increasing severity, which was likened to driving on a washboard road. Increasing speeds also caused a tucking phenomena, in which the nose pitched down, a phenomenon also experienced by the Me 163A Anton prototypes in 1941. More seriously, the aircraft also showed a tendency to "hunt" about all three axes. This combined yaw, pitch and roll, which grew more severe as the speed increased, was a precursor to the inertial coupling which would become a major challenge in the years to come.
To correct the poor stability, project engineers decided to increase the flap/speed brake trailing edge thickness. Balsa wood strips were added between the flap/speed brake halves, causing them to remain open at a 5° angle. The first test of the blunt trailing edge was flown on 20 August 1951, by NACA pilot Walter Jones. A second test was made by Crossfield in October. The results were positive, with Jones commenting that the X-4's flight qualities had been greatly improved, and the aircraft did not have pitch control problems up to a speed of Mach 0.92.
The balsa strips were removed, and the X-4 then undertook a long series of flights to test landing characteristics. By opening the speed brakes, the lift-to-drag ratio of the aircraft could be reduced to less than 3:1. This was for data on future rocket-powered aircraft. The tests continued through October 1951, until wing tank fuel leaks forced the aircraft to be grounded until March 1952, when the landing tests resumed. NACA pilots Joe Walker, Stanley Butchard, and George Cooper were also checked out in the aircraft.
The thickened flap/speed brake tests had been encouraging, so balsa wood strips were reinstalled on both the flap/speed brake and the elevons. The first flight was made by Jones on 19 May 1952, but one of the engines was damaged during the flight, and it was August before a replacement J30 could be found. When the flights resumed, they showed that the modifications had improved stability in both pitch and yaw, and delayed the nosedown trim changes from Mach 0.74 to Mach 0.91. Above Mach 0.91, however, the X-4 still oscillated.
In May 1953, the balsa wood strips were again removed, and the X-4's dynamic stability was studied in the original flap/speed brake and elevon configuration. These flights were made by Crossfield and John B. McKay. This was the final project for the X-4, which made its 81st and final NACA flight on September 29, 1953. Both aircraft survived the test program. The first X-4 was transferred to the United States Air Force Academy, Colorado Springs, Colorado, before being returned to Edwards Air Force Base. The second X-4 went to the National Museum of the United States Air Force at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base near Dayton, Ohio, where it remains on display.
The X-4's primary importance involved proving a negative, in that a swept-wing semi-tailless design was not suitable for speeds near Mach 1, although the F7U Cutlass proved to be something of a counterexample—the developed version was the first aircraft to demonstrate stores separation above Mach 1. Aircraft designers were thus able to avoid this dead end. It was not until the development of computer fly-by-wire systems that such designs could be practical. Semi-tailless designs appeared on the X-36, Have Blue, F-117, and Bird of Prey, although these aircraft all differed significantly in shape from the X-4. The trend during its test program was already toward delta and modified delta aircraft such as the Douglas F4D, the Convair F-102A derived from the XF-92A, and the Avro Vulcan.
Specifications (X-4)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 22 ft 3 in (7.1 m)
- Wingspan: 26 ft 10 in (8.2 m)
- Height: 14 ft 10 in (4.5 m)
- Wing area: ft² (m²)
- Empty weight: 5,600 lb (2,540 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 7,820 lb (3,550 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Westinghouse J30 turbojet, 1,600 lbf (7.1 kN) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 640 mph (1,035 km/h)
- Service ceiling: 44,000 ft (13,400 m)
See also
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- DH.108 Swallow
- Messerschmitt Me 163
- Lippisch P.15
- Related lists
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.External links
Northrop aircraft Manufacturer
designations'Greek' series'N' seriesNote: Northrop company designations include a wide variety of technologies. Only aircraft, aero engines, and missiles are linked here.
N-1 · N-2 · N-3 · N-4 · N-5 · N-6 · N-7 · N-8 · N-9 · N-10 · N-12 · N-14 · N-15 · N-16 · N-18 · N-19 · N-20 · N-21 · N-23 · N-24 · N-25 · N-26 · N-29 · N-31 · N-32 · N-34 · N-35 · N-36 · N-37 · N-38 · N-39 · N-40 · N-41 · N-46 · N-47 · N-48 · N-49 · N-50 · N-51 · N-52 · N-54 · N-55 · N-59 · N-60 · N-63 · N-65 · N-67 · N-68 · N-69 · N-71 · N-72 · N-73 · N-74 · N-77 · N-81 · N-82 · N-94 · N-96 · N-102 · N-103 · N-105 · N-110 · N-111 · N-112 · N-117 · N-124 · N-132 · N-133 · N-134 · N-135 · N-138 · N-141 · N-144 · N-149 · N-150 · N-151 · N-155 · N-156 · N-205 · N-267 · N-285 · N-300'P' seriesP530 · P600 · P610
By role AttackBombersDronesFightersReconnaissanceTrainersTransportsExperimentalNames Bantam · Black Bullet · Black Widow · Chukar · Nomad · Pioneer · Raider · Reporter · Scorpion · Snark · Talon · Tigershark
See also: TR-3USAF/Joint Service experimental aircraft designations 1941– (X-planes) 1–25 26–50 50- X-51 · (X-52 not assigned) · X-53 · X-54 · X-55
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Edwards Air Force Base
- United States experimental aircraft 1940–1949
- Northrop aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.