- Martin Marietta X-24B
-
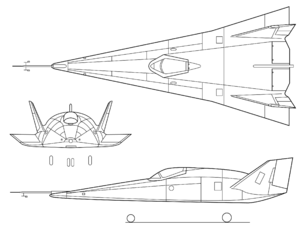
X-24B The X-24B in flight Role Lifting body Manufacturer Martin Marietta First flight 1 August 1973 Retired 26 November 1975 Status Out of service Primary users United States Air Force
NASANumber built 1 (rebuilt X-24A) Developed from Martin Marietta X-24A The Martin Marietta X-24B was an experimental US aircraft developed from a joint USAF-NASA program named PILOT (1963–1975). It was designed and built to test lifting body concepts, experimenting with the concept of unpowered reentry and landing, later used by the Space Shuttle.[1]
Contents
Design and development
The X-24 was one of a group of lifting bodies flown by the NASA Flight Research Center (now Dryden Flight Research Center) in a joint program with the U.S. Air Force at Edwards Air Force Base in California from 1963 to 1975. The lifting bodies were used to demonstrate the ability of pilots to maneuver and safely land wingless vehicles designed to fly back to Earth from space and be landed like an airplane at a predetermined site.
The X-24B's design evolved from a family of potential reentry shapes, each with higher lift-to-drag ratios, proposed by the Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory. To reduce the costs of constructing a research vehicle, the Air Force returned the X-24A to the Martin Marietta Corporation (as Martin Aircraft Company became after a merger) for modifications that converted its bulbous shape into one resembling a "flying flatiron" -- rounded top, flat bottom, and a double delta planform that ended in a pointed nose.
First to fly the X-24B was John Manke, a glide flight on 1 August 1973. He was also the pilot on the first powered mission 15 November 1973.
X-24C
There were a variety of "X-24C" proposals floated between 1972 and 1978. Perhaps the most notable was a Lockheed Skunk Works design, the L-301, which was to use scramjets to reach a top speed of Mach 8.[2]
Operational history
The X-24B demonstrated that accurate unpowered reentry vehicle landings were operationally feasible. Top speed achieved by the X-24B was 1,164 mph (1873 km/h) and the highest altitude it reached was 74,130 feet (22.59 km). The pilot on the last powered flight of the X-24B was Bill Dana, who also flew the last X-15 flight about seven years earlier.
Among the final flights with the X-24B were two precise landings on the main concrete runway at Edwards which showed that accurate unpowered reentry vehicle landings were operationally feasible. These missions were flown by Manke and Air Force Maj. Mike Love, and represented the final milestone in a program that helped write the flight plan for the NASA Space Shuttle program.
The X-24B was the last aircraft to fly in Dryden's Lifting Body program. The X-24B was flown 36 times.
The X-24B is on public display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio.
- X-24B pilots
- John A. Manke - 16 flights
- Michael V. Love - 12 flights
- William H. Dana - 2 flights
- Einar K. Enevoldson - 2 flights
- Thomas C. McMurtry - 2 flights
- Francis Scobee - 2 flights
Specifications (X-24B)
General characteristics
- Crew: one pilot
- Length: 37 ft 6 in (11.43 m)
- Wingspan: 19 ft 0 in (5.79 m)
- Height: 9 ft 7 in (2.92 m)
- Wing area: 330 ft² (30.7 m²)
- Empty weight: 8,500 lb (3,855 kg)
- Loaded weight: 11,800 lb (5,350 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 13,800 lb (6,260 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × XLR-11-RM-13 four-chamber rocket engine, 8,480 lbf (37.7 KN)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,164 mph (1,873 km/h)
- Range: 45 miles (72 km)
- Service ceiling: 74,130 ft (22.59 km)
- Wing loading: 205 kg/m² ()
- Thrust/weight: 0.71
See also
- Related development
- Martin Marietta X-24A
- Lockheed L-301
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
- ^ Reed, R. Dale; Darlene Lister (2002). Wingless Flight: The Lifting Body Story. University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 0813190266. also available as a PDF file.
- ^ Jenkins, Dennis R. (2001). Space Shuttle: The History of the National Space Transportation System (3rd edition ed.). Voyageur Press. ISBN 0-9633974-5-1.
Miller, Jay. The X-Planes: X-1 to X-45. Hinckley, UK: Midland, 2001.
Rose, Bill, 2008. Secret Projects: Military Space Technology. Hinckley, England: Midland Publishing.
External links
- NASA Dryden X-24 Photo Collection
- X-24B at Encyclopedia Astronautica
Glenn L. Martin Company and Martin Marietta aircraft Model numbers Airliners Attack aircraft Bombers Maritime patrol Military transports Military trainers Scout/Torpedo bombers Martin Marietta USAF/Joint Service experimental aircraft designations 1941– (X-planes) 1–25 26–50 50- X-51 · (X-52 not assigned) · X-53 · X-54 · X-55
See also: Douglas Skystreak · Douglas Skyrocket · List of X-planes • List of experimental aircraft Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Lifting body aircraft
- Parasite aircraft
- United States experimental aircraft 1960–1969
- Gliding in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.