- United States elections, 2010
-
The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested in this election along with 38 state and territorial governorships, 46 state legislatures (except Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey and Virginia),[1] four territorial legislatures and numerous state and local races. The election occurred in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term in office.
Approximately 82.5 million people voted.[2] The Democratic Party suffered major defeats in many national and state level elections, with many seats switching to Republican Party control. The Republican Party gained 63 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives, recapturing the majority, and making it the largest seat change since 1948 and the largest for any midterm election since the 1938 midterm elections. The Republicans gained six seats in the U.S. Senate, expanding its minority, and also gained 680 seats in state legislative races,[3][4][5] to break the previous majority record of 628 set by Democrats in the post-Watergate elections of 1974.[5] This left Republicans in control of 25 state legislatures, compared to the 15 still controlled by Democrats. After the election, Republicans took control of 29 of the 50 State Governorships.
Political analysts in October 2010 predicted sweeping Republican gains this election, but despite a reported "enthusiasm gap" between likely Republican and Democratic voters,[6] turnout increased relative to the last U.S. midterm elections without any significant shift in voters' political identification.[7] The swaying views of self-declared independent voters, however, were largely responsible for the shift from Democratic to Republican gains.[8]
Contents
Issues
Candidates and voters in 2010 focused on national economic conditions and the economic policies of the Obama Administration and Congressional Democrats. Attention was paid to public anger over the Wall Street bailout signed into law by President George W. Bush in late 2008. Voters were also motivated for and against the sweeping reforms of the health care system enacted by Democrats in 2010, as well as concerns over tax rates and record deficits.[9] At the time of the election, unemployment was over 9%, and had not declined significantly since Barack Obama had become President. Further eroding public trust in Congress were a series of scandals that saw Democratic Representatives Charlie Rangel and Maxine Waters, as well as Republican Senator John Ensign, all accused of unethical and/or illegal conduct in the months leading up to the 2010 election.
The fiscally-focused and quasi-libertarian Tea Party movement was a vocal force in mobilizing voters for Republican candidates nationwide. Their widespread exposure in the media contributed to the election's focus on economic, rather than social, issues. In the opinion of Fox News political analyst Dick Morris, a "fundamental change" occurred in which social issues did not dominate Republican activism in 2010, because "economic and fiscal issues prevail. The Tea Party has made the Republican Party safe for libertarians."[10]
Immigration reform had become an important issue in 2010, particularly following the passage of Arizona Senate Bill 1070, officially known as the Support Our Law Enforcement and Safe Neighborhoods Act. The Act greatly enhanced the power of Arizona's law enforcement agencies to investigate the immigration status of suspected illegal immigrants and to enforce state and national immigration laws. The Act also required immigrants to carry their immigration documentation on their person at all times. Its passage by a Republican-led legislature and its subsequent and very public signing by Jan Brewer, the Republican Governor of Arizona, ignited protests across the Southwest and galvanized political opinion among both pro-immigration Latino groups and Tea Party activists, many of whom supported stronger measures to stem illegal immigration.
The passage of the controversial Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act also contributed to the low approval ratings of Congress, particularly Democrats, in the months leading up to the election. Many Republicans ran on a promise to repeal the law, and successfully beat incumbent Democratic opponents who had voted in favor of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.
Federal elections
Congressional elections
Senate elections
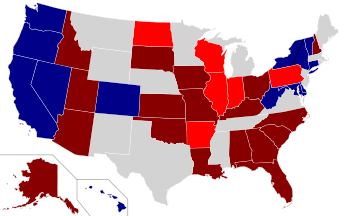
Main article: United States Senate elections, 2010The 34 seats in the United States Senate Class III were up for election. In addition, the Class II Senate seat in Delaware currently held by Ted Kaufman, the Class I Senate seat in New York currently held by Kirsten Gillibrand, and the Class I seat in West Virginia currently held by Carte Goodwin were contested in special elections resulting from Joe Biden's 2008 election as Vice President of the United States and Hillary Clinton's appointment to the Cabinet as U.S. Secretary of State and their subsequent resignations from the Senate, as well as incumbent Senator Robert C. Byrd's death and the interim appointment of Goodwin to the Senate. A special election was also held for the Class I seat in Massachusetts, as a result of the death of incumbent Senator Ted Kennedy. The election was held on January 19, 2010, resulting in Republican state senator Scott Brown winning the seat.
House of Representatives elections
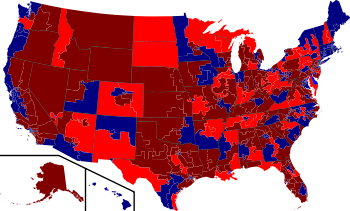
Main article: United States House of Representatives elections, 2010All 435 voting seats in the United States House of Representatives were up for election. Additionally, elections were held to select the delegates for the District of Columbia and four of the five U.S. territories. The only seat in the House not up for election was that of the Resident Commissioner of Puerto Rico, who serves a four-year term and will next face election in 2012.
State elections
Gubernatorial elections
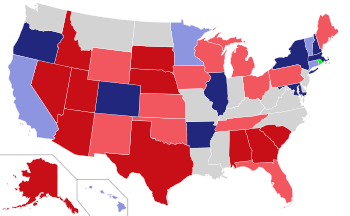
Main article: United States gubernatorial elections, 2010Thirty-six of the fifty United States governors were up for election. Elections were also held for the governorships of two U.S. territories. One state, Louisiana, had no campaign for governor but did feature a special election for lieutenant governor.[11] Jerry Brown, a longtime California politician who had been a prominent national political figure since the 1960's, was elected to a third, nonconsecutive term as Governor of California.
Other state-wide officer elections
In many states where the following positions are elected offices, voters elected state executive branch offices (including Lieutenant Governors (though some will be voted for on the same ticket as the gubernatorial nominee), Secretary of state, state Treasurer, state Auditor, state Attorney General, state Superintendent of Education, Commissioners of Insurance, Agriculture or, Labor, and etc.) and state judicial branch offices (seats on state Supreme Courts and, in some states, state appellate courts).
State legislative elections
All states except Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey and Virginia held elections for their state legislatures.[12] Republicans made substantial gains in state legislatures across the nation. Five state saw both chambers switch from Democrat to Republican majorities. Those five states switching to GOP control in both chambers were Wisconsin, Minnesota, Maine (for the first time since 1964), North Carolina, and Alabama (where the Republicans won a majority for the first time in 136 years).
In addition, Republicans picked up single chambers in several states giving them control of both houses in Indiana, Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania. They expanded majorities in both chambers in Texas, Florida, and Georgia. Republicans picked up one chamber from Democrats in Colorado, Oregon and New York to split control in those states. The massive Republican victories in legislative races would be widely expected to have a major impact on the redrawing of Congressional districts for the 2012 election cycle.
One of the few bright spots for Democrats was retaining their majorities in both the California and Illinois legislatures.
Local elections
Mayoral elections
The following major American cities held mayoral elections in 2010. (Incomplete list)
- Augusta, Georgia
- Columbia, South Carolina
- Escondido, California
- Honolulu, Hawaii (see Honolulu mayoral election, 2010 for details)
- Irvine, California
- Lexington, Kentucky
- Long Beach, California
- Louisville, Kentucky (see Louisville mayoral election, 2010 for details)
- Newark, New Jersey
- Newport News, Virginia
- New Orleans, Louisiana (see New Orleans mayoral election, 2010 for details)
- Oakland, California
- Oklahoma City, Oklahoma
- Providence, Rhode Island
- Reno, Nevada
- San Jose, California
- Santa Fe, New Mexico
- Sioux Falls, South Dakota
- Trenton, New Jersey
- Washington, D.C (see Washington, D.C. mayoral election, 2010 for details)
- Shreveport, Louisiana
See also
- Politics and sports
References
- ^ "2010 Primary Dates and Seats Up". September 23, 2009. http://www.ncsl.org/?tabid=18629. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
- ^ Tomasky, Michael (November 3, 2010). "Turnout: says a lot". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/michaeltomasky/2010/nov/03/us-midterm-elections-2010-turnout-says-a-lot. Retrieved November 3, 2010.
- ^ "In Redistricting Year, GOP Gains a Big Edge". November 4, 2010. http://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2010/11/in-redistricting-year-gop-gains-a-big-edge/66128/. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ "Four More Lessons from the GOP Landslide". November 4, 2010. http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/national-affairs/blogs/NationalAffairs_May2010/231048/66235. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ a b "Devastation: GOP Picks Up 680 State Leg. Seats". November 4, 2010. http://hotlineoncall.nationaljournal.com/archives/2010/11/devastation-gop.php. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ Jonathan Weisman (October 20, 2010). "GOP in Lead in Final Lap". Wall Street Journal. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303550904575562493014465942.html?mod=WSJ_hpp_MIDDLENexttoWhatsNewsTop.
- ^ "It's the Ideology, Stupid: Midterm elections". November 4, 2010. http://www.tnr.com/blog/william-galston/78918/its-the-ideology-stupid-midterm-elections. Retrieved November 4, 2010.
- ^ "Women, Independent Voters Show Biggest Swing From 2008". Fox News. November 3, 2010. http://www.foxnews.com/politics/2010/11/03/women-independent-voters-biggest-swing/.
- ^ Jeffrey M. Jones, "Americans Give GOP Edge on Most Election Issues; Greatest Republican advantages on terrorism, immigration, federal spending", Gallup, September 1, 2010
- ^ Dick Morris, "The New Republican Right", TheHill.com October 19, 2010
- ^ See Louisiana state elections, 2010.
- ^ "2010 Primary Dates and Seats Up". September 23, 2009. http://www.ncsl.org/?tabid=18629. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
Further reading
- Paul R. Abramson et al. Change and Continuity in the 2008 and 2010 Elections (2011)
- Bullock, Charles S., et al. Key States, High Stakes: Sarah Palin, the Tea Party, and the 2010 Elections (2011)
- Sabato, Larry. Who Got in the Booth? A Look Back at the 2010 Elections (2011)
External links
- 2010 Midterm Election Debates on C-SPAN
- Wesleyan Media Project: 2010 Political Advertising Analysis at Wesleyan University
- National newspapers
- National radio
- Election 2010 at NPR
- National TV
- 2010 Election at ABC News
- Campaign 2010 on C-SPAN
- Campaign 2010 at CBS News
- Election Center at CNN
- Elections at Fox News
- Decision 2010 at MSNBC
(2009 ←) 2010 United States elections (→ 2011) U.S.
Senate
(Polling)Alabama · Alaska · Arizona · Arkansas · California · Colorado · Connecticut · Delaware (special) · Florida · Georgia · Hawaii · Idaho · Illinois · Indiana · Iowa · Kansas · Kentucky · Louisiana · Maryland · Massachusetts (special) · Missouri · Nevada · New Hampshire · New York · New York (special) · North Carolina · North Dakota · Ohio · Oklahoma · Oregon · Pennsylvania · South Carolina · South Dakota · Utah · Vermont · Washington · West Virginia (special) · Wisconsin
U.S.
House
(Complete •
Polling)Alabama · Alaska · American Samoa · Arizona · Arkansas · California · Colorado · Connecticut · Delaware · District of Columbia · Florida (19th) · Georgia (9th) · Guam · Hawaii (1st) · Idaho · Illinois · Indiana (3rd) · Iowa · Kansas · Kentucky · Louisiana · Maine · Maryland · Massachusetts · Michigan · Minnesota · Mississippi · Missouri · Montana · Nebraska · Nevada · New Hampshire · New Jersey · New Mexico · New York (29th) · North Carolina · North Dakota · Northern Mariana Islands · Ohio · Oklahoma · Oregon · Pennsylvania (12th) · Rhode Island · South Carolina · South Dakota · Tennessee · Texas · Utah · Vermont · Virginia · U.S. Virgin Islands · Washington · West Virginia · Wisconsin · Wyoming
Governors
(Polling)Alabama · Alaska · Arizona · Arkansas · California · Colorado · Connecticut · Florida · Georgia · Guam · Hawaii · Idaho · Illinois · Iowa · Kansas · Maine · Maryland · Massachusetts · Michigan · Minnesota · Nebraska · Nevada · New Hampshire · New Mexico · New York · Ohio · Oklahoma · Oregon · Pennsylvania · Rhode Island · South Carolina · South Dakota · Tennessee · Texas · U.S. Virgin Islands · Utah · Vermont · Wisconsin · Wyoming
Mayors District of Columbia · Honolulu · Louisville · New Orleans
States Alabama · Alaska · American Samoa · Arizona · Arkansas · California · Colorado · Connecticut · Delaware · Florida · Georgia · Guam · Hawaii · Idaho · Illinois · Indiana · Iowa · Kansas · Kentucky · Louisiana · Maine · Maryland · Massachusetts · Michigan · Minnesota · Mississippi · Missouri · Montana · Nebraska · Nevada · New Hampshire · New Jersey · New Mexico · New York · North Carolina · North Dakota · Ohio · Oklahoma · Oregon · Pennsylvania · Puerto Rico · Rhode Island · South Carolina · South Dakota · Tennessee · Texas · Utah · Vermont · Virginia · U.S. Virgin Islands · Washington · West Virginia · Wisconsin · Wyoming
 United States elections1789 · 1790 · 1792 · 1794 · 1796 · 1798 · 1800 · 1802 · 1804 · 1806 · 1808 · 1810 · 1812 · 1814 · 1816 · 1818 · 1820 · 1822 · 1824 · 1826 · 1828 · 1830 · 1832 · 1834 · 1836 · 1838 · 1840 · 1842 · 1844 · 1846 · 1848 · 1850 · 1852 · 1854 · 1856 · 1858 · 1860 · 1862 · 1864 · 1866 · 1868 · 1870 · 1872 · 1874 · 1876 · 1878 · 1880 · 1882 · 1884 · 1886 · 1888 · 1890 · 1892 · 1894 · 1896 · 1898 · 1900 · 1902 · 1904 · 1906 · 1908 · 1910 · 1912 · 1914 · 1916 · 1918 · 1920 · 1922 · 1924 · 1926 · 1928 · 1930 · 1932 · 1934 · 1936 · 1938 · 1940 · 1942 · 1944 · 1946 · 1948 · 1950 · 1952 · 1954 · 1956 · 1958 · 1960 · 1962 · 1964 · 1966 · 1968 · 1970 · 1972 · 1974 · 1976 · 1978 · 1980 · 1982 · 1984 · 1986 · 1988 · 1990 · 1992 · 1994 · 1996 · 1998 · 2000 · 2001 · 2002 · 2003 · 2004 · 2005 · 2006 · 2007 · 2008 · 2009 · 2010 · 2011 · 2012 · 2013 · 2014See also: House of Representatives elections · Senate elections · Presidential elections · Gubernatorial electionsCategories:
United States elections1789 · 1790 · 1792 · 1794 · 1796 · 1798 · 1800 · 1802 · 1804 · 1806 · 1808 · 1810 · 1812 · 1814 · 1816 · 1818 · 1820 · 1822 · 1824 · 1826 · 1828 · 1830 · 1832 · 1834 · 1836 · 1838 · 1840 · 1842 · 1844 · 1846 · 1848 · 1850 · 1852 · 1854 · 1856 · 1858 · 1860 · 1862 · 1864 · 1866 · 1868 · 1870 · 1872 · 1874 · 1876 · 1878 · 1880 · 1882 · 1884 · 1886 · 1888 · 1890 · 1892 · 1894 · 1896 · 1898 · 1900 · 1902 · 1904 · 1906 · 1908 · 1910 · 1912 · 1914 · 1916 · 1918 · 1920 · 1922 · 1924 · 1926 · 1928 · 1930 · 1932 · 1934 · 1936 · 1938 · 1940 · 1942 · 1944 · 1946 · 1948 · 1950 · 1952 · 1954 · 1956 · 1958 · 1960 · 1962 · 1964 · 1966 · 1968 · 1970 · 1972 · 1974 · 1976 · 1978 · 1980 · 1982 · 1984 · 1986 · 1988 · 1990 · 1992 · 1994 · 1996 · 1998 · 2000 · 2001 · 2002 · 2003 · 2004 · 2005 · 2006 · 2007 · 2008 · 2009 · 2010 · 2011 · 2012 · 2013 · 2014See also: House of Representatives elections · Senate elections · Presidential elections · Gubernatorial electionsCategories:- 2010 elections in the United States
- United States general elections
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.