- Dual oxidase 2
-
Dual oxidase 2, also known as DUOX2 or ThOX2 (for thyroid oxidase) is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DUOX2 gene.[1][2] Dual oxidase is an enzyme that was first identified in the mammalian thyroid gland. In humans, two isoforms are found; hDUOX1 and hDUOX2 (this enzyme). The protein location is not exclusive to thyroid tissue; hDUOX1 is prominent in airway epithelial cells[3] and hDUOX2 in the salivary glands and gastrointestinal tract.[4][5][6]
Function
Investigations into reactive oxygen species (ROS) in biological systems have, until recently, focused on characterization of phagocytic cell processes. It is now well accepted that production of such species is not restricted to phagocytic cells and can occur in eukaryotic non-phagocytic cell types via NADPH oxidase (NOX) or dual oxidase (DUOX). This new family of proteins, termed the NOX/DUOX family or NOX family of NADPH oxidases, consists of homologs to the catalytic moiety of phagocytic NADPH-oxidase, gp91phox. Members of the NOX/DUOX family have been found throughout eukaryotic species, including invertebrates, insects, nematodes, fungi, amoeba, alga, and plants (not found in prokaryotes). These enzymes clearly demonstrate regulated production of ROS as their sole function. Genetic analyses have implicated NOX/DUOX derived ROS in biological roles and pathological conditions including hypertension (NOX1) , innate immunity (NOX2/DUOX), otoconia formation in the inner ear (NOX3) and thyroid hormone biosynthesis (DUOX1/2). It has been suggested that DUOX2 is the isoform to generate H2O2 utilized by thyroid peroxidase (TPO) for the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones, supported by the discovery of congenital hypothyroidism resultant from an inactivating mutation in the DUOX2 gene.[1][7]
The family currently has seven members including NOX1, NOX2 (formerly known as gp91phox), NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2.
This protein is known as a dual oxidase because it has both a peroxidase homology domain and a gp91phox domain.[8]
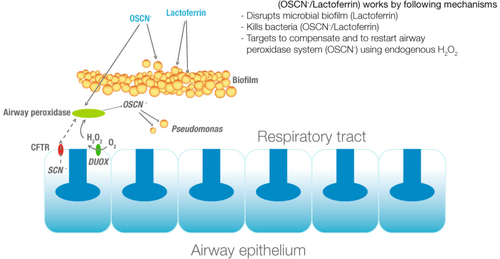
Duox are also implicated in lung defence system[9] and especially in cystic fibrosis.[10][11][12]
Schema of duox implication in human lung defence system
References
- ^ a b Dupuy C, Ohayon R, Valent A, Noël-Hudson MS, Dème D, Virion A (December 1999). "Purification of a novel flavoprotein involved in the thyroid NADPH oxidase. Cloning of the porcine and human cdnas". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (52): 37265–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.52.37265. PMID 10601291.
- ^ De Deken X, Wang D, Many MC, Costagliola S, Libert F, Vassart G, Dumont JE, Miot F (July 2000). "Cloning of two human thyroid cDNAs encoding new members of the NADPH oxidase family". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30): 23227–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000916200. PMID 10806195.
- ^ Harper RW, Xu C, Eiserich JP, Chen Y, Kao CY, Thai P, Setiadi H, Wu R (August 2005). "Differential regulation of dual NADPH oxidases/peroxidases, Duox1 and Duox2, by Th1 and Th2 cytokines in respiratory tract epithelium". FEBS Lett. 579 (21): 4911–7. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.002. PMID 16111680.
- ^ Geiszt M, Witta J, Baffi J, Lekstrom K, Leto TL (August 2003). "Dual oxidases represent novel hydrogen peroxide sources supporting mucosal surface host defense". FASEB J. 17 (11): 1502–4. doi:10.1096/fj.02-1104fje. PMID 12824283.
- ^ El Hassani RA, Benfares N, Caillou B, Talbot M, Sabourin JC, Belotte V, Morand S, Gnidehou S, Agnandji D, Ohayon R, Kaniewski J, Noël-Hudson MS, Bidart JM, Schlumberger M, Virion A, Dupuy C (May 2005). "Dual oxidase2 is expressed all along the digestive tract". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 288 (5): G933–42. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00198.2004. PMID 15591162.
- ^ Rokutan K, Kawahara T, Kuwano Y, Tominaga K, Nishida K, Teshima-Kondo S (July 2008). "Nox enzymes and oxidative stress in the immunopathology of the gastrointestinal tract". Semin Immunopathol 30 (3): 315–27. doi:10.1007/s00281-008-0124-5. PMID 18521607.
- ^ Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, van Trotsenburg AS, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ, Vulsma T, Ris-Stalpers C (July 2002). "Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism". N. Engl. J. Med. 347 (2): 95–102. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012752. PMID 12110737.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DUOX2 dual oxidase 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=50506.
- ^ Fischer H (October 2009). "Mechanisms and function of DUOX in epithelia of the lung". Antioxid. Redox Signal. 11 (10): 2453–65. doi:10.1089/ARS.2009.2558. PMC 2823369. PMID 19358684. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2823369.
- ^ Rada B, Lekstrom K, Damian S, Dupuy C, Leto TL (October 2008). "The Pseudomonas toxin pyocyanin inhibits the dual oxidase-based antimicrobial system as it imposes oxidative stress on airway epithelial cells". J. Immunol. 181 (7): 4883–93. PMC 2776642. PMID 18802092. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2776642.
- ^ Conner GE, Salathe M, Forteza R (December 2002). "Lactoperoxidase and hydrogen peroxide metabolism in the airway". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 166 (12 Pt 2): S57–61. doi:10.1164/rccm.2206018. PMID 12471090.
- ^ Rada B, Leto TL (2008). "Oxidative innate immune defenses by Nox/Duox family NADPH oxidases". Contrib Microbiol 15: 164–87. doi:10.1159/000136357. PMC 2776633. PMID 18511861. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2776633.
Further reading
- Lambeth JD (2002). "Nox/Duox family of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) oxidases.". Curr. Opin. Hematol. 9 (1): 11–7. doi:10.1097/00062752-200201000-00003. PMID 11753072.
- Moreno JC, Visser TJ (2007). "New phenotypes in thyroid dyshormonogenesis: hypothyroidism due to DUOX2 mutations.". Endocrine development 10: 99–117. doi:10.1159/0000106822. PMID 17684392.
- Dupuy C, Ohayon R, Valent A, et al. (2000). "Purification of a novel flavoprotein involved in the thyroid NADPH oxidase. Cloning of the porcine and human cdnas.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (52): 37265–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.52.37265. PMID 10601291.
- Dias Neto E, Correa RG, Verjovski-Almeida S, et al. (2000). "Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (7): 3491–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3491. PMC 16267. PMID 10737800. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=16267.
- De Deken X, Wang D, Many MC, et al. (2000). "Cloning of two human thyroid cDNAs encoding new members of the NADPH oxidase family.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (30): 23227–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000916200. PMID 10806195.
- Dupuy C, Pomerance M, Ohayon R, et al. (2000). "Thyroid oxidase (THOX2) gene expression in the rat thyroid cell line FRTL-5.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277 (2): 287–92. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3671. PMID 11032719.
- Caillou B, Dupuy C, Lacroix L, et al. (2001). "Expression of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (ThoX, LNOX, Duox) genes and proteins in human thyroid tissues.". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86 (7): 3351–8. doi:10.1210/jc.86.7.3351. PMID 11443211.
- Edens WA, Sharling L, Cheng G, et al. (2001). "Tyrosine cross-linking of extracellular matrix is catalyzed by Duox, a multidomain oxidase/peroxidase with homology to the phagocyte oxidase subunit gp91phox.". J. Cell Biol. 154 (4): 879–91. doi:10.1083/jcb.200103132. PMC 2196470. PMID 11514595. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2196470.
- Lacroix L, Nocera M, Mian C, et al. (2002). "Expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase flavoprotein DUOX genes and proteins in human papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas.". Thyroid 11 (11): 1017–23. doi:10.1089/105072501753271699. PMID 11762710.
- De Deken X, Wang D, Dumont JE, Miot F (2002). "Characterization of ThOX proteins as components of the thyroid H(2)O(2)-generating system.". Exp. Cell Res. 273 (2): 187–96. doi:10.1006/excr.2001.5444. PMID 11822874.
- Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, et al. (2002). "Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism.". N. Engl. J. Med. 347 (2): 95–102. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012752. PMID 12110737.
- Geiszt M, Witta J, Baffi J, et al. (2003). "Dual oxidases represent novel hydrogen peroxide sources supporting mucosal surface host defense.". FASEB J. 17 (11): 1502–4. doi:10.1096/fj.02-1104fje. PMID 12824283.
- Pachucki J, Wang D, Christophe D, Miot F (2004). "Structural and functional characterization of the two human ThOX/Duox genes and their 5'-flanking regions.". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 214 (1-2): 53–62. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.11.026. PMID 15062544.
- Morand S, Agnandji D, Noel-Hudson MS, et al. (2004). "Targeting of the dual oxidase 2 N-terminal region to the plasma membrane.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (29): 30244–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405406200. PMID 15150274.
- Schwarzer C, Machen TE, Illek B, Fischer H (2004). "NADPH oxidase-dependent acid production in airway epithelial cells.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (35): 36454–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404983200. PMID 15210697.
- Wang D, De Deken X, Milenkovic M, et al. (2005). "Identification of a novel partner of duox: EFP1, a thioredoxin-related protein.". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (4): 3096–103. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407709200. PMID 15561711.
- El Hassani RA, Benfares N, Caillou B, et al. (2005). "Dual oxidase2 is expressed all along the digestive tract.". Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 288 (5): G933–42. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00198.2004. PMID 15591162.
- Forteza R, Salathe M, Miot F, et al. (2005). "Regulated hydrogen peroxide production by Duox in human airway epithelial cells.". Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 32 (5): 462–9. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2004-0302OC. PMID 15677770.
- Ameziane-El-Hassani R, Morand S, Boucher JL, et al. (2005). "Dual oxidase-2 has an intrinsic Ca2+-dependent H2O2-generating activity.". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (34): 30046–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500516200. PMID 15972824.
Oxidoreductases: NADH or NADPH (EC 1.6) 1.6.1: NAD/NADP 1.6.2: Heme 1.6.3: Oxygen NADPH oxidase (P91-PHOX, Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1, Neutrophil cytosolic factor 2, Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4) · dual oxidase (Dual oxidase 1, Dual oxidase 2)1.6.5: Quinone or similar 1.6.6: Nitrogenous group 1.6.99: other Enzymes Thyroid peroxidase · Iodotyrosine deiodinase · Dual oxidase 1/Dual oxidase 2 · Iodothyronine deiodinase · Diiodotyrosine transaminaseTransporters Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 15 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.