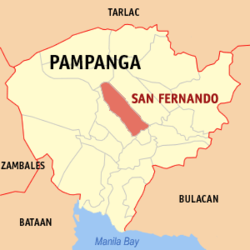
- San Fernando, Pampanga
-
- For the city in La Union, see San Fernando City, La Union. For other uses, see San Fernando.
City of San Fernando
Lakanbalen ning San Fernando
Lungsod ng San Fernando— Regional Center — The city hall of San Fernando in the province of Pampanga, on the left is the plaque of the city seal. 
Flag
SealNickname(s): Christmas Capital of the Philippines
The Nerve Center of Central LuzonMotto: Magsilbi Tamu (Let's Serve) Map of Pampanga showing the location of City of San Fernando Coordinates: 15 00 N, 120 38 E
Country  Philippines
PhilippinesRegion Central Luzon (Region III) Province Pampanga Districts Third District of Pampanga Barangays 35 Founded August 16, 1754 Cityhood February 4, 2001 Government - Representative, 3rd Congressional District Aurelio Gonzales - Governor Lilia Pineda (2010-Present Lakas Kampi CMD) - Mayor Oscar Samson Rodriguez (Liberal/Lakas-Kampi-CMD) - Vice Mayor Edwin D. Santiago (Liberal/Lakas-Kampi-CMD) Area - Total 67.74 km2 (26.2 sq mi) Population (2007) - Total 269,365 - Density 3,977/km2 (10,300.4/sq mi) Time zone PST (UTC+8) Zip code 2000 Area code(s) 45 Income Class 1st class Classification Component City; Partially Urban Website cityofsanfernando.gov.ph Population Census of the City of San Fernando Census Pop. Rate 1995 193,025 — 2000 221,857 3.03% 2007 269,365 2.71% The City of San Fernando, (Kapampangan: Lakanbalen ning San Fernando/Siudad ning San Fernando; Filipino: Lungsod ng San Fernando) is a first class, component city in the Philippine province of Pampanga. It is the capital city of Pampanga and the regional center of Central Luzon (Region III). The city is well known for its giant lanterns and is also popularly known as the "Christmas Capital of the Philippines." The annual Giant Lantern Festival is hosted by the city every December.
According to the 2000 census, it has a population of 221,857 people in 43,649 households. It is located 67 kilometers north of Manila, 50 kilometers east of Subic Bay in the Zambales province, and 16 kilometers south of Clark Field in Angeles City. The city is positioned at the crossroads of Central Luzon. The city is named after Fernando VI of Spain and placed under the patronage of Ferdinand III of Castile, King of Castile and León, whose feast is celebrated every 30 May.
Contents
History
The town of San Fernando was founded in 1754 from the towns of Bacolor and Mexico. The first church was built in 1755 with wooden walls and nipa roofing. The municipal tribunal was erected later in the year in front of the town plaza using durable materials and thatched nipa roofing. Don Vidal de Arrozal served as its first gobernadorcillo that year.
In 1796, after serving as gobernadorcillo the previous year, Don Ángel Pantaleon de Miranda retired to Barrio Saguin, from where he started setting up his hacienda in Barrio Culiat. The barrio was separated from San Fernando on the December 8, 1829 as the new town of Angeles, with the Los Santos Ángeles Custodios as titular patrons.
An expediente requesting the transfer of the provincial capital of Pampanga to San Fernando was signed on the August 6, 1852. Real Cedula 745, approving the transfer of the provincial capital of Pampanga from Bacolor to San Fernando, was signed on September 11, 1881. The said transfer would not materialize.
In 1878, moves were made to create the town of Calulut. This new town would be composed of Calulut and the neighboring barrios of Bulaun, Malpitic, Sindalan, La Paz, Lara, Saguin, Telabastagan, Balete, Malinao, Pulung Bulu, Panipuan, Macabacle and the caserio of Pau in San Fernando, and Panipuan, Acle, Suclaban and the sitio of Gandus in Mexico. This plan did not materialize due to strong opposition from the parish priest of San Fernando.
Governor-General Eulogio Despujol and Manila Archbishop Bernardino Nozaleda inaugurated the San Fernando railroad station, together with the Bagbag-Mabalacat stretch of the Manila-Dagupan Railroad, on February 23, 1892. The station was second only to Manila in revenues that year, and was thus the most important provincial station of the Manila-Dagupan Railroad. On June 27 of the same year, National Hero Dr. Jose P. Rizal made a stop-over in the town as part of his mission to recruit members to the La Liga Filipina.
On September 1, 1896 the town was declared in a state of war despite the peaceful situation. Brigadier General Diego de los Rios arrived on December 2 to calm the revolution that started in Manila on August 30. General Ruiz Serralde took over the Rios's post on June 26, 1897 to maintain the peace in San Fernando. The revolution was not yet at its height with occasional exchanges of fire in some places in Pampanga.
On June 26, 1898, representatives from all Pampanga towns, except Macabebe, gathered in San Fernando to swear allegiance to Gen. Maximino Hizon who was the provincial military governor and representative of President Emilio Aguinaldo. On October 9, Aguinaldo, together with his cabinet visited the town and was welcomed with so much applause and enthusiastic cheering from the public. He proceeded to the convento which was served as the military headquarters at that time.
On May 4, 1899, Philippine revolutionary troops led by General Antonio Luna burned the casa municipal, the town church and several houses to render them useless to the approaching American forces. On June 16, due to the strategic location of the town, Aguinaldo himself led Filipino forces in the Battle for San Fernando. The plan to retake the town proved unsuccessful. Calulut fell to the Americans on August 9.
On August 15, 1904, the Pampanga provincial government was finally transferred to San Fernando from Bacolor, by virtue of Act No. 1204 signed on July 22, 1904. This was during the term of Governor Macario Arnedo and Municipal President Juan Sengson. The town of Minalin became part of San Fernando that same year. It will later regain its political independence in 1909.
On January 2, 1905, the town of Santo Tomas was consolidated with San Fernando by virtue of Act 1208.
On August 12, 1904, US Secretary of War William H. Taft visited the town to get first hand information and gather ideas for the governance of Pampanga. Due to the short notice, a bamboo pavilion was hastily constructed for his visit where he was welcomed with a banquet for 200 people. Taft would later be elected President of the United States.
In 1921, the Pampanga Sugar Development Company (PASUDECO) sugar central began its operations. The company was formed in 1918 by large-scale planters such as José de León, Augusto Gonzaález, Francisco Liongson, Tomás Lazatin, Tomás Consunji, Francisco Hizon, José Henson, and Manuel Urquico in the San Fernando residence of Governor Honorio Ventura as part of a plan to construct a locally financed central.
In 1932, the Socialist Party of the Philippines was founded by Pedro Abad Santos. Two years later, he created and headed the Aguman Ding Madlang Talapagobra (AMT). The Abad Santos compound in Barangay San Jose became the focal point of the peasant movement.
On February 14, 1939, Philippine president Manuel L. Quezon proclaimed his social justice program before a gathering of farmers in front of the Municipal Government building.
In 1941, forces of the Japanese Imperial Army occupied the town and placed the municipal government under its supervision. The following year, thousands of Filipino and American POWs walked from Bataan to the San Fernando Train Station in what will be known as the Bataan Death March.
In 1952, the town of Santo Tomas was separated from San Fernando.
In 1986, Paterno Guevarra was sworn in as officer-in-charge of the town after the successful People Power Revolution that toppled the Marcos dictatorship that same year. He was later elected municipal mayor.
In 1990, Philippine president Corazon C. Aquino inaugurated the Paskuhan Village, the first Christmas village in Asia and the third of its kind in the world. The following year, Mount Pinatubo erupted after over 600 years of dormancy hurling a layer of ash and volcanic debris on the town.
On October 1, 1995, Typhoon Sibyl (Mameng) struck the town. It unleashed floodwaters and mudflows from Mount Pinatubo into the town. The Barangays of Sto. Nino, San Juan, San Pedro Cutud and Magliman were severely damaged by lahar. The citizens of San Fernando rallied to save the town by raising funds to build the St. Ferdinand People's Dike. The Pampanga Megadike was constructed the following year, thus preventing further damage to the town.[1]
Religions
Roman Catholicism 90%, Protestants 2%,Iglesia Ni Cristo 5%, Evangelical, 1%, Others 1.5%, Non- Religious .5%
Mayors
This is the list of the mayors of City of San Fernando.[2]
Capitanes Municipales Term Alcaldes Municipales Term Presidentes Municipales Term Vidal de Arrozal 1755 Vicente Dizon 1821 Antonio E. Consunji 1891–1892 Tiburcio Cunanan 1756 Pablo de Ocampo 1822 Juan Sengson 1893–1894 Vidal de Arrozal 1757 Maximo Dizon 1823 Teodoro Limjuco 1895 Luis Catacutan 1758 Ciriaco Dizon 1824 Saturnino Henson 1896 Juan David 1759 Celso Dayrit (accidental) 1897 Juan Yutuc 1760 Gobernadorcillos Term Domingo de Vera 1761 Vicente Dizon 1825 Republika Filipina Nicolas Capati 1762 Manuel Pasion Henson 1826 Presidente Municipal Term Tomas Aquino 1763 Anacleto del Rosario 1827 Antonio E. Consunji 1898 Miguel de los Angeles 1764 Vicente David Lising 1828 Agustin Dizon 1765 Vicente Dizon 1829 Military Government Manuel Manaloto 1766 Pablo Ocampo 1830 Alcaldes Term Francisco Bautista 1767 Doroteo Dizon 1831 Enrique Kerr 1899 Miguel David 1768 Mariano Yutuc 1832 Carlos Kerr 1900 Nicolas Dizon 1769 Manuel Pasion Henson 1833 Teodoro Limjuco 1900 Mariano Singian de Miranda 1770 Gregorio Tuason 1834 Francisco S. Hizon 1900–1901 Mateo David 1771 Blas Borja 1835 Bernardo de Anunciacion 1772 Doroteo Dizon 1836 Civil Government Francisco David 1773 Agustin Pamintuan 1837 Municipal Presidents Term Agapito Singian 1774 Agustin Cuyugan 1838 Francisco S. Hizon 1901 Vicente Concepcion 1775 Juan Dayrit 1839 Mariano J. Leon Santos 1902–1903 Eugenio Yutuc 1776 Raymundo David 1840 Juan Sengson 1904 Juan Lingat 1777 Macario Yutuc 1841 Eulalio Castro 1905–1906 Juan Lacson 1778 Matias Quiason 1842 Vicente Tiomico 1906–1907 Vicente Concepcion 1779 Pedro Lacsamana 1843 Pedro Teopaco 1908–1909 Jose de Arrozal 1780 Bernardino Singian de Miranda 1844 Clemente Ocampo 1910–1912 Nicolas Tuason 1781 Serapio Singian de Miranda 1845 Unknown 1913–1915 Carlos Catacutan 1782 Mariano Arceo 1846 Antonio B. Abad Santos 1916–1921 Vicente David 1783 Agustin Cuyugan 1847 Jose M. Valencia 1922–1927 Lucas David 1784 Guillermo Henson 1848 Antonio B. Abad Santos 1928–1931 Antonio Alonso del Rosario 1785 Bernardino Singian de Miranda 1849 Jose M. Valencia 1932–1934 Regino de Castro 1786 Agustin Pamintuan 1850 Sebastian Manarang 1787 Gregorio David 1851 Philippine Commonwealth Bernabe Pamintuan 1788 Maximo Feliciano 1852 Municipal Mayors Term Juan Dizon 1789 Paulino Paras 1853–1854 Urbano D. Dizon 1934–1937 Manuel Miranda 1790 Agustin Lacson 1854–1855 Vivencio B. Cuyugan 1938–1942 Vicente Dayrit 1791 Simon Henson 1855–1856 Vivencio B. Cuyugan 1945 Nicolas Tuason 1792 Cosme Lacson 1856–1857 Jose de los Angeles 1793 Candido Froilan Dizon 1857–1858 Japanese Occupation Vicente Quizon 1794 Florentino Dayrit 1858–1859 Municipal Mayor Term Angel Pantaleon de Miranda 1795 Manuel Pasion Henson 1859 Rodolfo P. Hizon 1942–1945 Vicente Dayrit 1796 Jose Navarro (accidental) 1859 Jose Cunanan 1797 Victor David 1860 Republic of the Philippines Juan Lacson 1798 Manuel de Ocampo 1860–1861 Municipal Mayors Term Carlos Catacutan 1799 Bernardino Singian de Miranda 1861–1862 Rodolfo P. Hizon 1946–1955 Vicente Dizon 1800 Guillermo Henson 1862–1863 Mariano P. Castro, Sr. 1955 Jose Ocson 1801 Aniceto Yusi 1863–1864 Dr. Miguel G. Baluyut 1956–1959 Agustin David Lising 1802 Simon Henson 1864–1865 Dr. Jose C. Quiwa 1960–1967 Jose Concepcion 1803 Juan Quiason 1865–1866 Levi Panlilio 1967–1969 Raymundo David 1804 Julian Buison 1867–1868 Atty. Virgilio L. Sanchez 1969–1971 Ignacio David de Miranda 1805 Benigno de Ocampo 1868–1869 Luis Gopiao 1971 Severino Henson 1806 Isidro Teopaco 1869–1870 Armando P. Biliwang 1972–1980 Juan Crisostomo Paras 1807 Domiciano Tison 1870–1871 Col. Amante S. Bueno (OIC) 1980–1982 Domingo Henson 1808 Florentino Dayrit 1871–1872 Atty. Vicente A. Macalino (OIC) 1982–1983 Leon de Vera 1809 Eustaquio Ricafort 1872–1873 Atty. Virgilio L. Sanchez 1983–1986 Vicente de Castro 1810 Pedro Paras y Castro 1873–1874 Atty. Paterno S. Guevara(Appointed) 1986–1987 Gregorio Singian 1811 Bernardino Singian de Miranda 1874–1875 Dr. Rodolfo P. Canlas (Appointed) 1987–1988 Ignacio de Miranda 1812 Julian Buison 1875–1876 Atty. Paterno S. Guevara 1988–1995 Miguel Catacutan 1813 Anacleto Hizon 1877–1879 Dr. Jesus Reynaldo B. Aquino 1995–2001 Francisco Pamintuan 1814 Catalino Henson 1879–1880 Severino Henson 1815 Mariano Custodio 1880–1881 City Mayors Term Agustin David Lising 1816 Saturnino Henson 1881–1882 Dr. Jesus Reynaldo B. Aquino 2001–2004 Bernardo David 1817 Florentino Dayrit 1882–1883 Atty. Oscar Samson Rodriguez 2004–Present Bernardo Tinio 1818 Pedro Paras 1883 Eriberto Yutuc 1819 Domiciano Tison 1884–1885 Vicente de Castro 1820 Francisco X. Panlilio 1885 Anacleto Hizon 1886–1887 Teodoro Limjuco 1887–1889 Gregorio Tioleco 1889–1890 Cityhood
On January 6, 1997, Mayor Rey B. Aquino and Senator Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo launched the campaign for cityhood. On April 27 of that same year, Rep. Oscar Rodriguez filed House Bill No. 9267 creating the City of San Fernando.
In 2000, House Speaker Arnulfo Fuentebella and Senate President Aquilino Q. Pimintel signed the approved city charter of San Fernando on December 4 and 13 respectively.
The town officially became a component city on February 4, 2001 following the ratification of Republic Act 8990 authored by Pampanga Second district Rep. Oscar Rodriguez in a plebiscite from the previous day. Dr. Rey B. Aquino was the city's first mayor. The ratification of Republic Act 8990 made the City of San Fernando the 99th city of the Republic of the Philippines.
Barangays
The City of San Fernando is politically subdivided into 35 barangays.
- Alasas
- Baliti
- Bulaon
- Calulut
- Dela Paz Norte
- Dela Paz Sur
- Del Carmen
- Del Pilar
- Del Rosario
- Dolores
- Juliana
- Lara
- Lourdes
- Maimpis
- Magliman
- Malino
- Malpitic
- Pandaras
- Panipuan
- Pulung Bulo
- Santo Rosario (Pob.)
- Quebiawan
- Saguin
- San Agustin
- San Felipe
- San Isidro
- San Jose
- San Juan
- San Nicolas
- San Pedro Cutud
- Santa Lucia
- Santa Teresita
- Santo Niño
- Sindalan
- Telabastagan
Economy
 SM City Pampanga SM City Pampanga Annex 2 (East Wing) in Mexico, Pampanga.
SM City Pampanga SM City Pampanga Annex 2 (East Wing) in Mexico, Pampanga.
 Jose Abad Santos Avenue (Olongapo-Gapan Road) and MacArthur Highway intersection in Barangay Dolores, City of San Fernando, Pampanga. The elevated road is the Olongapo-Gapan Road.
Jose Abad Santos Avenue (Olongapo-Gapan Road) and MacArthur Highway intersection in Barangay Dolores, City of San Fernando, Pampanga. The elevated road is the Olongapo-Gapan Road.
Strategically located at the heart of the province, the City of San Fernando is home to two public markets, thirty nine banks, forty eight lending institutions (investors), thirty eight pawnshops, seventeen gasoline stations, three movie houses, thirty nine public and private schools, seven hospitals, thirteen dental offices, nine hotels, twenty eight drug stores, seven disco clubs, six foreign exchange firms, fifteen garment factories, twenty four groceries, seven supermarkets, forty two insurance companies, sixteen security agencies and seventy restaurants and fast food chains such as Jollibee, McDonald's, Mr. Donut, Greenwich, Shakey's, and Chowking. In addition to being the Provincial Capital of Pampanga, almost all Philippine banking institutions, military and governmental agencies have regional offices in City of San Fernando.[3]
Manufacturing
San Fernando serves as one of the agricultural processing center of Central Luzon. It is a major rice-producing region and an important sugar-producing area. The Pampanga Sugar Development Company (PASUDECO), was once the largest private employer in Pampanga. It is a major sugar processing plant in the region. Other manufacturing companies with offices in the city include Universal Robina Corporation, Zuellig Pharma Corporation, Nestlé Philippines, Petrophil, Mondragon Industries, Asia Brewery, and Del Monte Corporation. Major bottling companies such as the San Miguel Corporation Complex, Coca-Cola, Pepsi Cola, Cosmos and Metrobottling are located within the city.
Every year during the Christmas season, the city becomes the hub of a thriving industry centered on handcrafted lanterns called parols. What distinguish the San Fernando lantern from the ordinary parol are the intricate designs and the illusion of dancing lights, which focuses on the vibrant colors of the lantern.
Infrastructure
The City of San Fernando has four TV stations - KTV Channel 12, Infomax Channel 8, CLTV 36 and ABS-CBN TV46 Pampanga. There are also two radio stations, the 5 Kilowatt RW 95.1 of the Radio World Broadcasting Corporation of the Philippines and the 2.5 kilowatt Power 92.7 of the Love Radio Network. Several local newspapers are published in the city which includes SunStar Pampanga, The Probe, Coffee Punch, Pampanga Times and the Observer.[4]
Tourism
The tourism industry of the city is fueled by two major events, the annual Good Friday Lenten Rites in San Pedro Cutud and the Giant Lantern Festival in December. Both events draw thousands of tourists from around the country and the world.
Education
Colleges and universities
- University of the Assumption, a Catholic Archdiocesan University in Pampanga. Though bearing the same name, this university in San Fernando is not, in any way, related to the Assumption College in Manila.
- East Central Colleges, formerly the Toledaño Vocational School of San Fernando, was established by the late Ciriaco Toledaño in the 1940s. The first establishment was located at the B. Mendoza Street and later, another branch was built in Mexico, Pampanga to house the high school students. As of today, East Central Colleges has two branches. One near the Iglesia ni Cristo for college students and one in Mexico, Pampanga for the high school students. The two are being managed and administered by the children of Ciriaco Toledaño.
- Metropolitan Academy Of Arts & Beauty (Met Academy) MAAB
- DATA College, formerly known as RM DATA Center
- Mother of Good Counsel Seminary
- AMA Computer College San Fernando
- Asian Institute of Computer Studies (AICS)
- STI College San Fernando
- Harvardian College
- Central Luzon College of Science and Technology, formerly known as CLIT
- New Era University
- Systems Plus College Foundation
- St. Nicolas College
- Asian College of Science and Technology
- Genetic Computer Institute - Pampanga Branch
- Tourism, Information Technology & Hotel Management School (TIHMS)
Vocational / Technical Schools
- NorthPoint Academy for Culinary Arts (http://northpointculinary.com). NorthPoint Academy is the premiere culinary school in Pampanga.
Secondary Schools
- Information and Communication Technology High School (ICTHS)
- San Vicente Pilot School for Philippine Craftsmen (SVPSPC)
- Panipuan Integrated School
- St. Scholastica's Academy, San Fernando (SSA)
- San Lorenzo Ruiz Center of Studies and Schools (SLRCSS)
- Assumpta Technical High School (ATHS)
- University of the Assumption (UA-HS)
- Pampanga High School (PHS)
- Proverbsville School Inc. (PSI)
- Sindalan High School (SHS)
- Potrero High School (PHS)
- Christ in You Faith Christian Academy (CIYFCA)
- Our Lady of Guadalupe School (OLGS)
- Academy of Our Lady of Fatima, inc (AOLF)
- Santa Barbara College of San Fernando (Proposed)
- Infant Jesus Learning Center (IJLC)
- Mother of Good Counsel Seminary (MGCS)
- Lyndale Academy (LA)
Tourism
Festivals and Local Events
- January 31 - Pedro Abad Santos Day
- February 4 - Cityhood Anniversary
- Good Friday - San Pedro Cutud Lenten Rites
- May 7 - Jose Abad Santos Day
- First Saturday of May - El Circulo Fernandino
- May 30 - San Fernando City Fiesta
- September 10 - San Fernando Women's Day
- First Week of October - Piestang Tugak San Fernando Frog Festival
- First Week of December - Sinukwan Festival
- December 11 - Aldo ning Kapampangan
- Saturday before Christmas Eve - Giant Lantern Festival
Places of interest
WOW Philippines Hilaga
Formerly known as the Paskuhan Village.
- Located at the mouth of the San Fernando Toll Exit along the North Luzon Expressway, North Philippines Hilaga was transformed into a cultural, historical, tourism, trade, and entertainment village by former Secretary Richard J. Gordon in 2003. Its design and concept make it a virtual window to the cultural and historical heritage of the four regions of the North Philippines as well as a showcase for their indigenous products, and arts and crafts. The star-shaped pavilions at the center pays tribute to the skilled lantern makers of San Fernando, Pampanga which produces the biggest lanterns in the world. The complex features a 1,000-seat capacity air-conditioned pavilion for conventions and special events, an open-air amphitheater for outdoor activities, air-conditioned exhibit halls, trade booths, garden restos and an 60-seat capacity conference hall.
Archdiocesan Museum and Archives
- The Archdiocesan Museum and Archives of the Archdiocese of San Fernando is housed at the University of the Assumption, and includes antiques and exquisite works of art depicting Pampanga's rich cultural heritage. It contains numerous ecclesiastical artifacts ranging from a huge churchbell to paintings; ivory and wooden statues of all shapes and sizes, vestments worn by priests during Mass and chalices, monstrances, reliquaries and ciboriums made of gold, silver and precious gems, some dating back to the 17th century.
The City of San Fernando Heritage District
- The City of San Fernando Heritage District covers the historic core of San Fernando, including Barangay Santo Rosario and parts of Barangays San Jose (Panlumacan), Santa Teresita (Baritan), Lourdes (Teopaco), Del Pilar, Santa Lucia and Santo Niño. These important sites are broken down under Heritage Houses, Historic Government Buildings, Schools, and Hospitals, and Historic Industrial Structures and Sites[5]
Churches and Other Religious Structures
- Metropolitan Cathedral of San Fernando
- Church of San Vicente Ferrer (Barangay Calulut) – heavily damaged by renovations
- Virgen de los Remedios Church (Barangay Baliti) – damaged by recent renovations
- Jeosay Shinhongkong Temple (Barangay San Jose)
Heritage Houses
- Hizon-Singian House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Henson-Hizon House (V. Tiomico Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Lazatin House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Dayrit-Cuyugan House (MacArthur Highway, Barangay Dolores)
- Consunji House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Tabacalera House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Hizon-Ocampo House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Santos-Hizon House (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Pampanga Hotel (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Archdiocesan Chancery (A. Consunji Street, Barangay San Jose)
Historic Government Buildings, Schools, and Hospitals
- City Hall of San Fernando (A. Consunji Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Pampanga Provincial Capitol (Capitol Boulevard, Barangay Santo Niño)
- Presidio (Artemio Macalino Street, Barangay Sto. Niño)
- Provincial High School Building (Capitol Boulevard, Barangay Santo Niño)
- Pampanga High School Building (High School Boulevard, Barangay Lourdes)
- San Fernando Elementary School (B. Mendoza Street, Barangay Santo Rosario)
- Old St. Scholastica's Academy (Pedro Abad Santos Road, Barangay Sta. Teresita)
- Pampanga Provincial Hospital (Barangay Dolores)
- Virgen de los Remedios Hospital (A. Consunji Street, Barangay San Jose)
Industrial Heritage Structures and Sites
- San Fernando Train Station (Barangay Santo Niño)
- PASUDECO Sugar Central (Capitol Boulevard, Barangay Santo Niño)
- PASUDECO Staff Houses and Commissary (Capitol Boulevard, Barangay Santo Niño)
- San Fernando Water Reservoir (Barangay Lourdes)
- The Sugar Pugons (Greenville Subdivision and Barangay Quebiawan)
- Calulut Train Station (Barangay Calulut) – heavily damaged by informal settlers
- Baluyut Bridge (Gen. Hizon Avenue, Barangay Santo Rosario)
Commercial Structures
- The Arcaded Shop Buildings of Consunji Street - 1950s (Barangay Santo Rosario)
Lantern Factories
Several lantern factories can be visited in Unisite Subdivision, Barangay Del Pilar, as well as in Barangays Santa Lucia, San Jose and Dolores.
Notable Fernandinos
- Jose Abad Santos, a former Chief Justice (featured in PHP1000 bill)
- Pedro Abad Santos, a former assemblyman and founder of the Socialist Party
- Sotero J. Baluyut, a former senator and cabinet secretary
- Dennis Gabriel Paras Bondoc,CCA, frog collector and a multi-awarded Fusion Chef who contributed various Frog Recipes and advocacies with Frogs in the City's celebration of the Annual Pyestang Tugak (Feast of the Frogs).
- Vivencio Cuyugan, first Socialist mayor in the Philippines
- Amando G. Dayrit, a renowned pre-war newspaper columnist
- Conrado Dayrit [1], a cardiologist, virgin coconut oil proponent and President of the National Academy of Science and Technology (1992–1999)
- Nicolasa Dayrit, a revolutionary hero
- Zoilo Hilario, an assemblyman and poet
- Fernando H. Ocampo, a founder of the UST College of Architecture and Fine Arts
- Honesto F. Ongtioco, bishop of Cubao
- Tony Perez, a playwright
Television Networks
- InfoMax 8 (cable)
- MBC-TV Natin: Channel 12
- CLTV 36
- GNN TV 44 San Fernando
- ABS-CBN TV46 Pampanga
- GMA Network: Channel 7 & Channel 10
- TV5: Channel 28 & Channel 5
References
- ^ Henares, Ivan Anthony S. "A Brief History of San Fernando, Pampanga 1754–2004"
- ^ Henares, Ivan Anthony S. "A Brief History of San Fernando, Pampanga 1754–2004"
- ^ Camiling ,Alejandro S. Fernando, Pampanga The Nerve Center of Central Luzon
- ^ Province of Pampanga, A Profile of Region III September, 2001.
- ^ Henares, Ivan Anthony S. "San Fernando: a city rich in architectual [sic] heritage"
External links
- City of San Fernando Official Website
- More photos and information on City of San Fernando, Pampanga
- Philippine Tourism Authority Official Website
- Profile of Mayor Oscar Rodriguez
- Central Luzon TV 36 Official Website
- eK! - electronic Kabalen: a Kapampangan journal of ideas
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- 1995 Philippine Census Information
- 2000 Philippine Census Information
- 2007 Philippine Census Information
- Biosphere Facility in City of San Fernando Pampanga
- Establishment of Pilot Biosphere / Ecology Zone in Pampanga
Municipalities Component city San FernandoHighly urbanized city (Administratively independent from the province, but grouped under Pampanga by the National Statistics Office) Cities of the Philippines
Cities of the PhilippinesHighly-urbanized Cities Angeles · Bacolod · Baguio · Butuan · Cagayan de Oro · Caloocan · Cebu · Davao · General Santos · Iligan · Iloilo · Lapu-Lapu · Las Piñas · Lucena · Makati · Malabon · Mandaluyong · Mandaue · Manila · Marikina · Muntinlupa · Navotas · Olongapo · Parañaque · Pasay · Pasig · Puerto Princesa · Quezon City · San Juan · Tacloban · Taguig · Zamboanga
Independent
Component CitiesComponent Cities Alaminos · Antipolo · Bago · Bais · Balanga · Batangas · Batac · Bayawan · Baybay · Bayugan · Biñan · Bislig · Bogo · Borongan · Cabadbaran · Cabanatuan · Cadiz · Calamba · Calapan · Calbayog · Candon · Canlaon · Carcar · Catbalogan · Cauayan · Cavite · Danao · Dapitan · Dasmariñas · Digos · Dipolog · Dumaguete · El Salvador · Escalante · Gapan · Gingoog · Guihulngan · Himamaylan · Iriga · Isabela · Kabankalan · Kidapawan · Koronadal · La Carlota · Lamitan · Laoag · Legazpi · Ligao · Lipa · Maasin · Malaybalay · Malolos · Marawi · Masbate · Mati · Meycauayan · Muñoz · Naga, Cebu · Oroquieta · Ozamiz · Pagadian · Palayan · Panabo · Passi · Roxas · Sagay · Samal · San Carlos, Negros Occidental · San Carlos, Pangasinan · San Fernando, La Union · San Fernando, Pampanga · San Jose · San Jose del Monte · San Pablo · Santa Rosa · Silay · Sipalay · Sorsogon · Surigao · Tabaco · Tabuk · Tacurong · Tagaytay · Tagbilaran · Tagum · Talisay, Cebu · Talisay, Negros Occidental · Tanauan · Tandag · Tangub · Tanjay · Tarlac · Tayabas · Toledo · Trece Martires · Tuguegarao · Urdaneta · Valencia · Victorias · Vigan
Regional Center San Fernando, Pampanga
Highly Urbanized Cities Metropolitan Areas Provinces Component Cities Balanga City • Cabanatuan City • Gapan City • City of Malolos • Meycauayan City • Munoz City • Palayan City • San Fernando, Pampanga • San Jose City • San Jose del Monte City • Tarlac CityLuzon, Republic of the Philippines Coordinates: 15°01′12″N 120°41′57″E / 15.02007°N 120.69923°E
Categories:- Cities in the Philippines
- San Fernando, Pampanga
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.