- Committee of the Regions
-
Committee of the Regions 
Established 1994 Type EU body President Mercedes Bresso Members 344 Represents Local government Powers Advisory; approach the Court of Justice with regard to the subsidiarity of legislation Seat Delors building, Brussels Website cor.europa.eu European Union 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
the European UnionPolicies and issuesCoordinates: 50°50′26″N 4°22′38″E / 50.84056°N 4.37722°E
The Committee of the Regions (CoR) is European Union's (EU) assembly of local and regional representatives that provides sub-national authorities with a direct voice within the EU's institutional framework.
Established in 1994, the CoR was set up to address two main issues. Firstly, about three quarters of EU legislation is implemented at local or regional level, so it made sense for local and regional representatives to have a say in the development of new EU laws. Secondly, there were concerns that there was a widening gap between the public and the process of European integration; involving the elected level of government closest to the citizens was one way of closing the gap.
Contents
Principles
There are three main principles at the heart of the Committee's work:
This principle, written into the Treaties at the same time as the creation of the CoR, means that decisions within the European Union should be taken at the closest practical level to the citizen. The European Union, therefore, should not take on tasks which are better suited to national, regional or local administrations.
- Proximity
All levels of government should aim to be 'close to the citizens', in particular by organising their work in a transparent fashion, so people know who is in charge of what and how to make their views heard.
- Partnership
Sound European governance means European, national, regional and local government working together – all four are indispensable and should be involved throughout the decision making process.
Scope
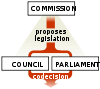
The Treaties oblige the European Commission and Council to consult the Committee of the Regions whenever new proposals are made in areas that have repercussions at regional or local level. The Treaty on European Union set out 5 such areas – economic and social cohesion, trans-European infrastructure networks, health, education and culture. The Amsterdam Treaty added another five areas to the list – employment policy, social policy, the environment, vocational training and transport – which now covers much of the scope of the EU's activity.
Outside these areas, the Commission, Council and European Parliament have the option to consult the CoR on issues if they see important regional or local implications to a proposal. The CoR can also draw up an opinion on its own initiative, which enables it to put issues on the EU agenda. On certain issues it works in partnership with the Economic and Social Committee (EESC or EcoSoC).
The CoR has gained the right (privileged status) to approach the European Court of Justice now that Treaty of Lisbon (Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union – TFEU) has entered into force following ratification by all EU Member States (Article 8, Protocol (No. 2) on the Application of the Principles of Subsidiarity and Proportionality [1]).
Composition
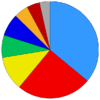
CoR has 344 members – the number from each EU country roughly reflecting the size of its population. The numbers per country are as follows:
Internal structure
- President
Elected for a two-and-a-half year term, the president guides the Committee’s work, chairs plenary sessions and is the CoR’s official representative. Mercedes Bresso, the former President of Piedmont from the centre-left, was elected president in February 2010.
- First vice-president
The first vice-president is also elected by the plenary assembly for two-and-a-half years, to represent the president in the latter’s absence. Ramón Luis Valcárcel Siso (ES/PPE), President of the Spanish region of Murcia, will hold this office until 2012 when he will, according to an agreement between the CoR's PES and the EPP Groups, take over the presidency from Mercedes Bresso.
- Bureau
The Bureau is the ruling body of the CoR. It comprises 60 members: the president, first vice-president, 27 vice-presidents (one per Member State), the four presidents of the CoR political groups and 27 other members, enabling it to reflect national and political balances. The Bureau generally meets seven times a year, draws up the CoR’s policy programme and instructs the administration on the implementation of its decisions.
- Plenary assembly
The 344 members of the CoR meet in plenary session in Brussels five times a year, to discuss and adopt opinions, reports and resolutions.
- CoR commissions
The CoR structures its work by means of six commissions, which specialise in the following areas: territorial cohesion policy; economic and social policy; environment, climate change and energy; natural resources; culture, education and research; citizenship, governance, institutional and external affairs. They prepare draft opinions and hold conferences and seminars focused on their areas of competence. Each commission has approximately 100 members and is supported by a secretariat within the administration.
- Committee for Administrative and Financial Affairs (CAFA)
This committee – which has eight members – advises the Bureau on administrative and financial questions.
- The political groups
The CoR has four political groups: the European People’s Party (EPP), the Party of European Socialists(PES), the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe (ALDE) and the European Alliance (EA). The members of each political group meet before major meetings to adopt common positions. The CoR president, first vice-president and presidents of the political groups also gather before each plenary session and other important meetings, with the aim of reaching a political consensus on key questions.
- National delegations
The CoR also comprises 27 national delegations. Members meet in their national delegations before plenary sessions and other events to discuss common positions.
- Secretary-general
The secretary-general is appointed for five years by the Bureau. As head of the CoR administration, the secretary-general must not hold a political mandate. He is responsible for implementing Bureau decisions and the smooth running of the administration. Gerhard Stahl is the Secretary-General of the CoR since 2004 (reappointed in 2009).
- Secretariat-general
The secretariat-general consists of five directorates: Administration and Finance; Members Service and Registry; Consultative Works; Communication, Press and Events; and Horizontal Policies and Networks. The units for budget, personnel, commission work and interinstitutional relations are organised within this structure. The secretariat-general also includes the political group secretariatsand internal audit service. The Logistics and Translations Directorates are jointly managed with the European Economic and Social Committee.
Work
- Opinions
The European Commission, Council of Ministers and European Parliament consult the CoR when drawing up legislative texts (directives, regulations, etc.) on areas affecting local and regional authorities. The draft texts are forwarded to the relevant CoR commission. A rapporteur is then appointed to draw up the Committee’s opinion. This draft opinion must be adopted by the CoR commission before being discussed at the plenary session. Once it has been approved in plenary, the official opinion is sent to all the European institutions and published in the Official Journal of the European Union.
- Resolutions
Resolutions enable the Committee to express its view on important and topical issues. The CoR’s political groups can also draw up resolutions.
- Outlook opinions and impact reports
The CoR’s work is not only to react to legislative proposals, but also to provide input based on members’ experience for future EU policy development. Outlook opinions allow the CoR to participate in the development of policy at a very early stage, thereby having greater impact. Similarly, the European Commission may ask the CoR to draw up an impact report. As the name suggests, these reports serve to evaluate the impact of a policy at local or regional level.
- Studies and other publications
The CoR produces studies on various aspects of the local and regional dimension of the EU (education, transport, social issues, enlargement, etc.). They are drawn up with the help of outside experts. The CoR also produces publications for both the general public and for regional and local players, aimed at explaining its activities and outlining current political developments.
- Events
As a meeting place for regions and cities, the CoR organises conferences, seminars and exhibitions in cooperation with local and regional partners and other EU institutions. Once a year, during the European Week of Regions and Cities (Open Days), the CoR welcomes to its headquarters thousands of participants who take part in lively discussions or seek partners to collaborate on joint projects.
Budget controversy
The Committee of the Regions (COR) wants its 2010 budget of €79.66 million to rise to €91.07 million in 2011, signifying an increase of 14 per cent. This was criticised by the think tank Open Europe, which complained that the institution's work overlaps with other EU institutions, duplicating work, while calling for its abolishment.[1]
History
1992: Maastricht Treaty EU leaders decide to set up the Committee of the Regions (CoR) as a consultative assembly which will provide regions and cities with a voice in the EU decision-making process and act as a direct link between Brussels and the citizens. The Treaty makes it mandatory for the European Commission and the Council of Ministers to consult the CoR on key areas of regional concern. CoR members are to be nominated by the governments of Member States and will serve for four years. In March 1994 the CoR holds its first plenary session in Brussels. European People’s Party 1995: EU enlargement The CoR’s membership increases from 189 to 222, following the accession of Austria, Finland and Sweden.
1997: Amsterdam Treaty Extends the CoR’s remit to cover around two thirds of the EU’s legislative proposals. The Treaty also makes it possible for the Committee to be consulted by the European Parliament.
2001: Nice Treaty Underlines the democratic legitimacy of the CoR by requiring that its members are elected or politically accountable to an elected regional or local assembly. Caps the number of members at 350.
2002–03: Convention on the Future of the EU CoR members take part in the convention responsible for drafting an EU constitution. The text expressly recognises the role and powers of local and regional government; it also gives the CoR the right to go to the Court of Justice of the European Communities to challenge EU laws which do not comply with the principle of subsidiarity.
May 2004: EU enlargement Number of CoR members increases from 222 to 317, following the accession of 10 new Member States.
February 2006: new term of office The CoR starts a new four-year term. Its political priorities include boosting the role of local and regional authorities in line with the Lisbon Strategy for Jobs and Growth, strengthening cohesion and solidarity, and spearheading the ‘Communicating Europe – Going local’ campaign to bring the EU closer to its citizens.
January 2007: EU enlargement With the accession of Bulgaria and Romania, the number of CoR members rises from 317 to 344.
December 2007: Lisbon Treaty The Lisbon Treaty confirms the CoR’s right to appeal to the Court of Justice of the European Communities to safeguard its prerogatives and the subsidiarity principle – a right already recognised by the Convention on the Future of the EU. This new entitlement will strengthen the CoR’s political role, by enabling it to act more effectively on the EU stage for the benefit of regional and local authorities. The Lisbon Treaty extends the term of office of CoR members from four to five years.
See also
References
External links
- Committee of the Regions
- List of Members
- The committee of the Regions : European Navigator
- Subsidiarity Monitoring Network of the Committee of the Regions
- Atlas of Decentralised cooperation for Development, a website dedicated to decentralised cooperation developed joinly by the Committee of the Regions and the European Commission
Categories:- Non-institutional bodies of the European Union
- Regionalism (politics)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.