- Geologic record
-
The geologic record in stratigraphy, paleontology and other natural sciences refers to the entirety of the layers of rock strata — deposits laid down in volcanism or by sediment deposition of weathering detritus (clays, sands etc.) including all its fossil content and the information it yields about the history of the Earth: its past climate, geography, geology and the evolution of life on its surface. According to the law of superposition sedimentary and volcanic rock layers are deposited on top of each other. They harden over time to become a solidified (competent) rock column, that may be intruded by igneous rocks and disrupted by tectonic events over time.
Contents
Correlating the rock record
At a certain locality on the Earth's surface, the rock column provides a cross section of the natural history in the area during the time covered by the age of the rocks. This is sometimes called the rock history and gives a window into the natural history of the location that spans many geological time units such as ages, epochs, or in some cases even multiple major geologic periods—for the particular geographic region or regions. The geologic record is in no one place entirely complete[1] for where geologic forces one age provide a low lying region accumulating deposits much like a layer cake, in the next may have uplifted the region, and the same area is instead one that is weathering and being torn down by chemistry, wind, temperature, and water. This is to say that in a given location, the geologic record can be and is quite often interrupted as the ancient local environment was converted by geological forces into new landforms and features. Sediment core data at the mouths of large riverine drainage basins, some of which go 7 miles (11 km) deep thoroughly support the law of superposition.
However using broadly occurring deposited layers trapped within differently located rock columns, geologists have pieced together a system of units covering most of the geologic time scale using the law of superposition, for where tectonic forces have uplifted one ridge newly subject to erosion and weathering in folding and faulting the strata, they have also created a nearby trough or structural basin region that lies at a relative lower elevation that can accumulate additional deposits. By comparing overall formations, geologic structures and local strata, calibrated by those layers which are widespread, a nearly complete geologic record has been constructed since the 17th century.
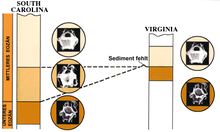
Discordant strata example
Correcting for discordancies can be done in a number of ways and utilizing a number of technologies or field research results from studies in other disciplines.
In this example, the study of layered rocks and the fossils they contain is called biostratigraphy and utilizes amassed geobiology and paleobiological knowledge. Fossils can be used to recognize rock layers of the same or different geologic ages, thereby coordinating locally occurring geologic stages to the overall geologic timeline.
The pictures of the fossils of monocellular algae in this USGS figure were taken with a scanning electron microscope and have been magnified 250 times.
In the U.S. state of South Carolina three marker species of fossil algae are found in a core of rock whereas in Virginia only two species of the species are found in the Eocene Series of rock layers spanning three stages and the geologic ages from 37.2–55.8 Ma.
Comparing the record about the discordance in the record to the full rock column shows the non-occurrence of the missing species and that portion of the local rock record, from the early part of the middle Eocene is missing there. This is one form of discordancy and the means geologists use to compensate for local variations in the rock record. With the two remaining marker species it is possible to correlate rock layers of the same age (early Eocene and latter part of the middle Eocene) in both South Carolina and Virginia, and thereby "calibrate" the local rock column into its proper place in the overall geologic record.
Units in geochronology and stratigraphy[2] Segments of rock (strata) in chronostratigraphy Periods of time in geochronology Notes Eonothem Eon 4 total, half a billion years or more Erathem Era 10 total, several hundred million years System Period Series Epoch tens of millions of years Stage Age millions of years Chronozone Chron smaller than an age/stage, not used by the ICS timescale Lithology vs paleontology
Consequently, as the picture of the overall rock record emerged, and discontinuities and similarities in one place were cross-correlated to those in others, it became useful to subdivide the overall geologic record into a series of component sub-sections representing different sized groups of layers within known geologic time, from the shortest time span stage to the largest thickest strata eonothem and time spans eon. Concurrent work in other natural science fields required a time continuum be defined, and earth scientists decided to coordinate the system of rock layers and their identification criteria with that of the geologic time scale. This gives the pairing between the physical layers of the left column and the time units of the center column in the table at right.
-
Well stratified and fully exposed Dinosaur Park formations (in Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta, Canada) and like formations that extend for over a thousand miles exposing eons of rock history through numerous wind and water exposed strata layers— which in the Colorado Plateau are miles thick.[1]
-
New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina: Unlithified sediment layers laid down in historic times. This cut was an attempt to find bedrock near a residential street near the lower breach of the London Avenue Canal after restoring the levees which has been plowed/excavated clear by the Army Corp of Engineers, showing a nascent stratigraphy in the large deposits of silt deposited by flooding in recent earth history.
-
Three eras of deposition and two discordancies are visible in this highway cut in the Netherlands. Note the color and slight angular change between the lower red bed layering and the middle strata. The upper strata are tilted yet again relative to the bottom layerings well demonstrating the cycles this land formation went through as part of the sea floor.
-
An ancient rockfall which protected the rock records beneath its impact site from further large scale erosion. Taken along Burr Trail, Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, Utah, USA.
-
Sediment core, taken with a gravity corer by the research vessel POLARSTERN in the South Atlantic; light/dark-coloured changes are due to climatic variation of the Quaternary; basis age of the core is about 1 million years.
Notes
- ^ a b "An Overview of the Geologic Record". http://www.wcg.org/lit/booklets/science/burky2.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-23.
- ^ International Commission on Stratigraphy. "International Stratigraphic Chart". Archived from the original on 2009-12-29. http://web.archive.org/web/20091229003212/http://www.stratigraphy.org/upload/ISChart2009.pdf.
Chronology Main articles Time · Astronomy · Geology · Paleontology · Archaeology · History
Eras and epochs Canon of Kings · Lists of kings · Limmu · Seleucid era
Astronomic time Geologic time ConceptsStandardsMethodsArchaeological
methodsGenetic methods Related topics Chronicle · New Chronology · Periodization · Synchronoptic view · Timeline · Year zero · Circa · Floruit · ASPRO chronology
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.