- Anhalt
-
For the SS officer, see Günther Anhalt.
County (Principality, Duchy) of Anhalt
Grafschaft (Fürstentum, Herzogtum) AnhaltState of the Holy Roman Empire (until 1806) ← 
1212 – 1252
1570 – 1603
1863 – 1918 →
→

Flag of the 19th century Duchy Coat of arms of Anhalt The 19th-century Duchy of Anhalt within the German Empire Map of the Duchy of Anhalt (1863-1918) Capital Dessau (when united) Government Principality Historical era Middle Ages - Partitioned from
Stem duchy of Saxony
1212 1212- Partitioned¹ 1252–1570 - Joined Council of Princes 1582 - Partitioned² 1603–1863 - Counties³ raised to duchies 1806 - German Revolution 1918 Today part of  Germany
Germany1: 13th century partition into Anhalt-Aschersleben, Anhalt-Bernburg and Anhalt-Zerbst.
2: 17th century partition into Anhalt-Bernburg, Anhalt-Dessau, Anhalt-Köthen, Anhalt-Plötzkau and Anhalt-Zerbst.
3: The three counties raised to duchies by Napoleon in 1806 were Anhalt-Bernburg, Anhalt-Dessau and Anhalt-Köthen.Anhalt was a sovereign county (after 1806 duchy) in Germany, located between the Harz Mountains and the river Elbe in Middle Germany. It now forms part of the state of Saxony-Anhalt.
Contents
History
Dukes of Anhalt
During the 9th century, the area was part of the Duchy of Saxony. In the 12th century, it came under the rule of Esico (died 1059 or 1060). His son was Adalbert II (died 1080) and his grandson Otto the Rich appears to have been the first to assume the title of count of Anhalt. Otto, also known as count of Ballenstedt, was the father of Albert the Bear, count of Anhalt, who conquered the Slavic territory of Brandenburg. When Albert died in 1170, his son Bernhard, who received the title of duke of Saxony in 1180, became count of Anhalt. Bernhard died in 1212, and Anhalt, now separated from Saxony, passed to his son Henry I, who in 1218 took the title of prince and was the real founder of the princely house of Anhalt. Henry I is included among the Minnesingers of Codex Manesse.
Princes of Anhalt
On Henry's death in 1252, his three sons partitioned the principality and founded, respectively, the lines of Aschersleben, Bernburg and Zerbst. The family ruling in Aschersleben became extinct in 1315, and this district was subsequently incorporated in the neighboring Bishopric of Halberstadt, thus dividing the territory of Anhalt-Bernburg in two separate pieces. The last prince of the original line of Anhalt-Bernburg died in 1468 and his lands were inherited by the princes of the sole remaining line, that of Anhalt-Zerbst. The territory belonging to this branch of the family had been divided in 1396, and after the acquisition of Bernburg Prince George I made a further partition of Zerbst (Zerbst and Dessau). Early in the 16th century, however, owing to the death or abdication of several princes, the family had become narrowed down to the two branches of Anhalt-Köthen and Anhalt-Dessau (issued both from Anhalt-Dessau in 1471).
Wolfgang of Anhalt, called the Confessor, who became prince of Anhalt-Köthen in 1508, was the second ruler in the world to introduce the Reformation to his country. He was a co-signer of the Augsburg Confession in 1530, and after the Battle of Mühlberg in 1547 was placed under Imperial ban and deprived of his lands by Emperor Charles V. After the peace of Passau in 1552 he bought back his principality, but as he was childless he surrendered it in 1562 to his kinsmen the princes of Anhalt-Dessau. Ernest I, Prince of Anhalt-Dessau (d. 1516) left three sons, John V, George III, and Joachim, who ruled their lands together for many years, and who favoured the Lutheran doctrine, which thus became dominant in Anhalt. About 1546 the three brothers divided their principality and founded the lines of Zerbst, Plötzkau and Dessau. This division, however, was only temporary, as the acquisition of Köthen, and a series of deaths among the ruling princes, enabled Joachim Ernest, a son of John V, to unite the whole of Anhalt under his rule in 1570.
Joachim Ernest died in 1586, and his five sons ruled the land in common until 1603, when owing to the lack of primogeniture, Anhalt was again divided, and the lines of Dessau, Bernburg, Plötzkau, Zerbst and Köthen were re-founded. The principality was ravaged during the Thirty Years' War, and in the earlier part of this struggle Christian I of Anhalt-Bernburg took an important part. In 1635 an arrangement was made by the various princes of Anhalt, which gave a certain authority to the eldest member of the family, who was thus able to represent the principality as a whole. This proceeding was probably due to the necessity of maintaining an appearance of unity in view of the disturbed state of European politics.
 Coat of arms of the duchy 1703.[1]
Coat of arms of the duchy 1703.[1]
In 1665, the branch of Anhalt-Köthen became extinct, and according to a family compact this district was inherited by Lebrecht, Prince of Anhalt-Plötzkau, who surrendered Plötzkau to Bernburg, and took the title of prince of Anhalt-Köthen. In the same year the princes of Anhalt decided that if any branch of the family became extinct its lands should be equally divided between the remaining branches. This arrangement was carried out after the death of Frederick Augustus, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst in 1793, and Zerbst was divided between the three remaining princes. During these years the policy of the different princes was marked, perhaps intentionally, by considerable uniformity. Once or twice Calvinism was favoured by a prince, but in general the house was loyal to the doctrines of Martin Luther. The growth of Prussia provided Anhalt with a formidable neighbour, and the long-delayed establishment of primogeniture by all branches of the family prevented further divisions of the principality.
19th-century duchies
In 1806, Napoleon elevated the remaining states of Anhalt-Bernburg, Anhalt-Dessau and Anhalt-Köthen to duchies; in the meantime, Anhalt-Plötzkau and Anhalt-Zerbst had ceased to exist. These duchies were united again in 1863, due to the extinction of the Köthen and Bernburg lines. The new duchy consisted of two large portions, Eastern and Western Anhalt, separated by the interposition of a part of the Prussian Province of Saxony and of five exclaves surrounded by Prussian territory: Alsleben, Mühlingen, Dornburg, Gödnitz and Tilkerode-Abberode. The eastern and larger portion of the duchy was enclosed by the Prussian government district of Potsdam (in the Prussian province of Brandenburg) and by Magdeburg and Merseburg, belonging to the Prussian province of Saxony. The western or smaller portion, the so-called Upper Duchy or Ballenstedt, was also enclosed by the two latter districts as well as by the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg.
When a united state, the capital of Anhalt was Dessau.
Along with the fall of all German monarchies, the Duchy of Anhalt came to an end in 1918–19 during the revolution that followed the end of World War I. It was replaced by the Free State of Anhalt within the Weimar Republic. After World War II, the Free State was united with the Prussian parts of Saxony to form Saxony-Anhalt. Subsequently, Saxony-Anhalt was dissolved in 1952, but re-established prior to the German reunification in 1990, since when it has been one of the sixteen (Bundes)länder (states) of Germany.
Geography
In the west, the land is undulating and in the extreme northwest, where it forms part of the Harz range, hilly, the Ramberg (Harz) peak being the tallest at 1,900 ft (579 m). From the Harz the country gently shelves down to the Saale; and between this river and the Elbe is particularly fertile. East of the Elbe, the land is mostly a flat sandy plain, with extensive pine forests, interspersed with bog-land and rich pastures. The Elbe is the chief river, intersecting the eastern portion of the former duchy, from east to west, and at Rosslau is met by the Mulde. The navigable Saale takes a northerly direction through the central portion of the territory and receives, on the right, the Fuhne and, on the left, the Wipper and the Bode.
The climate is generally mild, less so in the higher regions to the south-west. The area of the former duchy is 906 miles² (2300 km²), and the population in 1905 was 328,007, a ratio of about 351 to the square mile (909 km²).
Population
The country was divided into the districts of Dessau, Köthen, Zerbst, Bernburg and Ballenstedt, of which that of Bernburg was the most, and that of Ballenstedt the least, populated. Of the towns, four, viz. Dessau, Bernburg, Köthen and Zerbst, had populations exceeding 20,000. The inhabitants of the former duchy, with the exception of about 12,000 Roman Catholics and 1700 Jews, were members of the Evangelical State Church of Anhalt (German: Evangelische Landeskirche Anhalts). The supreme ecclesiastical authority was the consistory in Dessau; while a synod of 39 members, elected for six years, assembled at periods to deliberate on internal matters touching the organization of the church. The Roman Catholics were under the bishop of Paderborn.
Constitution
The duchy, by virtue of a fundamental law, proclaimed on September 17, 1859 and subsequently modified by various decrees, was a constitutional monarchy. The duke, who bore the title of "Highness", wielded the executive power while sharing the legislation with the estates. The diet (Landtag) was composed of thirty-six members, of whom two were appointed by the duke, eight were representatives of landowners paying the highest taxes, two of the highest assessed members of the commercial and manufacturing classes, fourteen of the other electors of the towns and ten of the rural districts. The representatives were chosen for six years by indirect vote and must have completed their twenty-fifth year. The duke governed through a minister of state, who was the praeses of all the departments — finance, home affairs, education, public worship and statistics.
Rulers of Anhalt, Middle Ages
- Esico of Ballenstedt ?–1059/1060, first Count of Anhalt
- Otto, Count of Ballenstedt
- Albert the Bear ?–1170
- Bernhard 1170–1212
- Henry I 1212–1252 (Prince from 1218)
Partitioned between Anhalt-Aschersleben, Anhalt-Bernburg, and Anhalt-Zerbst in 1252
Dukes of Anhalt, 1863–1918
- Leopold IV 1863–1871
- Frederick I 1871–1904
- Frederick II 1904–1918
- Eduard 1918
- Joachim Ernst 1918
Heads of the House of Anhalt since 1918
- Duke Joachim Ernst 1918–1947
- Prince Friedrich 1947–1963
- Prince Eduard 1963–present
See also
References
- ^ Siebmacher, Johann (1703). Erneuertes und vermehrtes Wappenbuch.... Nürnberg: Adolph Johann Helmers. pp. Part I Table 8.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
- http://www.deutsche-schutzgebiete.de/herzogtum_anhalt.htm
- Map of Saxony and Anhalt in 1789
- Overview over the various splits of German principalities
 Upper Saxon Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman Empire
Upper Saxon Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireElectorates 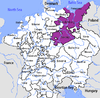
Ecclesiastical Secular Anhalt (Bernburg · Köthen · Zerbst) · Barby · Hatzfeld-Gleichen · Pomerania (Further · Hither) · Querfurt · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg · Saxe-Eisenach · Saxe-Gotha · Saxe-Weimar · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen)Prelates Counts / Lords Hohnstein · Lohra / Klettenberg · Mansfeld · Schönburg (Saale) · Stolberg (Stolberg · Wernigerode · Rossla) States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)Empires 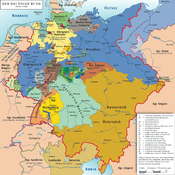
Kingdoms Electorates Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt (Bernburg2 · Dessau2 · Köthen3) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg4 · Nassau · Saxe-Lauenburg · Saxony (Altenburg5 · Coburg-Saalfeld6 · Coburg-Gotha5 · Gotha-Altenburg6 · Hildburghausen6 · Meiningen)Principalities Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen7 · Sigmaringen7) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and PyrmontCity-states Other territories
outside of the
confederacyColonial possessions · Personal unions of Habsburg (Bukovina · Croatia · Galicia and Lodomeria · Hungary · Lombardy–Venetia · Serbian Voivodeship and Banat8 · Slavonia9 · Transylvania) · Personal union of Hanover (Great Britain and Ireland10) · Personal unions of Hohenzollern (East Prussia11 · Neuchâtel12 · Posen, Gr. Duchy13 · Posen, Prov.14 · Prussia, Prov.15 · West Prussia11) · Occupied: Schleswig161 w/o areas listed under other territories. 2 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 3 until 1847. 4 from 1839. 5 from 1826. 6 until 1826. 7 until 1850. 8 1849–60. 9 as of 1849. 10 until 1837. 11 until 1829. 12 until 1848/57. 13 until 1848. 14 as of 1848. 15 as of 1829. 16 as of 1864. States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)
States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)Kingdoms 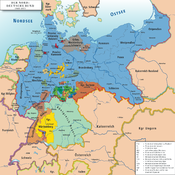
Grand Duchies Duchies Principalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states  States of the German Empire (1871–1918)
States of the German Empire (1871–1918)Kingdoms 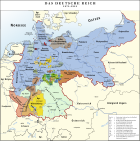
Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt · Brunswick · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg and Gotha · Saxe-Lauenburg (until 1876) · Saxe-MeiningenPrincipalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt · Schwarzburg-Sondershausen · Lippe · Reuss Elder Line · Reuss Junior Line · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states Other territories Elsaß-Lothringen · Colonial possessionsCategories:- Former principalities
- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1212
- States and territories disestablished in 1918
- 1918 disestablishments
- States of the German Confederation
- States of the North German Confederation
- States of the German Empire
- Lists of princes
- History of Saxony-Anhalt
- History of Anhalt
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




