- Duchy of Limburg (1839–1867)
-
Duchy of Limburg
Hertogdom Limburg (nl)
Herzogtum Limburg (de)State of the German Confederation ← 
1839–1867  →
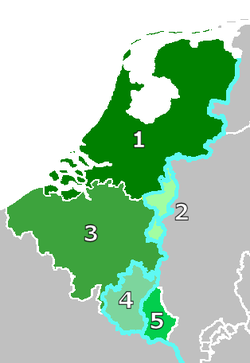
→Exchange in 1839 of Western Luxembourg (4) to Belgium (3) against the Duchy of Limburg (2) of the Netherlands (1) to the German Confederation. Capital Maastricht Language(s) Dutch, German, Limburgish Religion Roman Catholicism Government Principality Duke of Limburg - 1839 – 1840 King William I - 1840 – 1849 King William II - 1849 – 1866 King William III Historical era German Confederation - 1st Treaty of London 19 April 1839 - 2nd Treaty of London 11 May 1867 The Duchy of Limburg was created and formed from the eastern part of the Province of Limburg as a result of the Treaty of London in 1839. De jure it was a separate polity in personal union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands while at the same time a province of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Until 1866 it also was a Duchy of the German Confederation. This new Duchy of Limburg should not be confused with the old Duchy of Limburg, which had ceased to exist in 1794.
Contents
Formation
See also: Treaty of London (1839)After the occupation by the French army in 1794, the old Habsburg Duchy of Limburg was disbanded and became part of the département of Meuse-Inférieure. Following the defeat of Napoleon in 1814, the former départements Meuse-Inférieure and Ourte were merged to form the Province of Limburg within the newly founded United Kingdom of the Netherlands, corresponding to the present states of Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. That province covered an area much larger than and somewhat different from the former duchy, and Limburg's namesake town of Limbourg was located in the province of Liège.
In the Belgian Revolution of 1830 the Catholic, French and Dutch-speaking people of the former Southern Netherlands split away from the northern Netherlands. Except for the provincial capital of Maastricht and the town of Venlo, the province was almost entirely under Belgian rule. However, by the Treaty of London of 1839, the province was divided in two, with the eastern part going to the Netherlands and the western part to Belgium, a division that remains today.
With the Treaty of London, what is now the Belgian Province of Luxembourg was handed over to Belgium and removed from the German Confederation. To appease Prussia, which had also lost access to the Meuse after the Congress of Vienna, the Dutch province of Limburg was made a member of the German Confederation between 5 September 1839 and 23 August 1866 as the Duchy of Limburg. During this period the duchy existed as a separate polity in personal union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
However, the cities of Maastricht and Venlo were excluded and remained outside the German Confederation, based on that the population figure should not exceed that of the Belgian province of Luxembourg, at 150,000.[1]
Dissolution
See also: Treaty of London (1867)The Seven Week's War between Austria and Prussia in 1866 led to the collapse of the German Confederation. To clarify the position of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg and the Duchy of Limburg that were possessions of the Dutch king, but which had also been member states of the confederation, the Second Treaty of London in 1867 affirmed that Limburg was henceforth to be considered "integral parts of the Kingdom of the Netherlands". Limburg became an ordinary province of the Netherlands. Luxembourg joined the German customs union, the Zollverein, in which it would remain a member until 1 January 1919.
The style "Duchy of Limburg" continued to be used in some official capacities until February 1907. Another idiosyncrasy that survives to this day is that the Province's "Royal Commissioner" is still informally addressed as "Governor" in Limburg.
References
- ^ (German) Limburg (1839-1865)
External links
- History of Limburg during the German Confederation Website of the History of the Netherlands by historian Dr. J. W. Swaen.
 States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)Empires 
Kingdoms Electorates Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt (Bernburg2 · Dessau2 · Köthen3) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg4 · Nassau · Saxe-Lauenburg · Saxony (Altenburg5 · Coburg-Saalfeld6 · Coburg-Gotha5 · Gotha-Altenburg6 · Hildburghausen6 · Meiningen)Principalities Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen7 · Sigmaringen7) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and PyrmontCity-states Other territories
outside of the
confederacyColonial possessions · Personal unions of Habsburg (Bukovina · Croatia · Galicia and Lodomeria · Hungary · Lombardy–Venetia · Serbian Voivodeship and Banat8 · Slavonia9 · Transylvania) · Personal union of Hanover (Great Britain and Ireland10) · Personal unions of Hohenzollern (East Prussia11 · Neuchâtel12 · Posen, Gr. Duchy13 · Posen, Prov.14 · Prussia, Prov.15 · West Prussia11) · Occupied: Schleswig161 w/o areas listed under other territories. 2 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 3 until 1847. 4 from 1839. 5 from 1826. 6 until 1826. 7 until 1850. 8 1849–60. 9 as of 1849. 10 until 1837. 11 until 1829. 12 until 1848/57. 13 until 1848. 14 as of 1848. 15 as of 1829. 16 as of 1864. Categories:- Former principalities
- Former polities in the Netherlands
- Former vassal states
- States and territories established in 1839
- States and territories disestablished in 1867
- 1867 disestablishments
- States of the German Confederation
- Limburg (region)
- Dutch history stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.