- Principality of Lippe
-
Principality of Lippe
Fürstentum LippeState of the Holy Roman Empire (until 1806) ← 
1123–1918  →
→

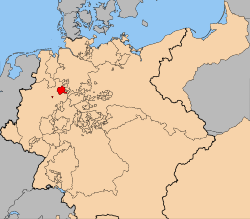
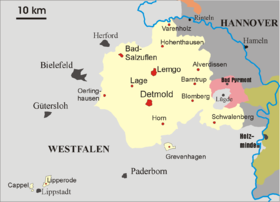
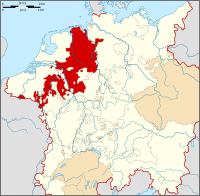
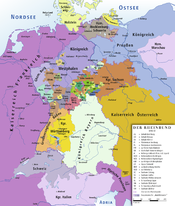
Flag (1815–1880) Coat of arms Lippe within the German Confederation (1814-1866) Capital Detmold Government Principality History - Established 1123 - Raised to County 1528 - Raised to Principality 1789 - German Revolution 1918 Lippe (later Lippe-Detmold and then again Lippe) was a historical state in Germany. It was located between the Weser River and the southeast part of the Teutoburg forest.
Contents
History
The founder of what would become the Principality of Lippe was Bernhard I, who received a grant of the territory from Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor and King of the Germans in 1123. Bernhard I assumed the title of Lord of Lippe. Bernhard's successors inherited and obtained several counties. Lord Simon V was the first ruler of Lippe to style himself as a count.
Following the death of Simon VI in 1613, the principality was split into three counties; Lippe-Detmold went to Simon VII, Lippe-Brake to Otto and Lippe-Alverdissen went to Philip I. The Lippe-Brake county was reunited with the main Detmold line in 1709. Another branch of the family was founded by Jobst Herman, a son of Simon VII, who was founder of the Lippe-Biesterfeld line.
The Counts of Lippe-Detmold were granted the title of Prince of The Empire in 1789.
Shortly after becoming a member state of the German Empire in 1871, the Lippe-Detmold line died out on 20 July 1895. This resulted in an inheritance dispute between the neighboring principality of Schaumburg-Lippe and the Lippe-Biesterfeld line. The dispute was resolved by the Imperial Court in Leipzig in 1905, with the lands passing to the Lippe-Biesterfeld line who, until this point, had no territorial sovereignty.
The Principality of Lippe came to an end on 12 November 1918 with the abdication of Leopold IV, with Lippe becoming a Free State. In 1947, Lippe merged into the state of North Rhine-Westphalia.
Lords of Lippe
- Bernard I (1123–1158)
- Herman I (1128–1167)
- Bernard II (1168–1196)
- Herman II (1196–1229)
- Bernard III (1230–1265)
- Herman III (1265–1273)
- Bernard IV (1265–1275)
- Simon I (1273–1344)
- Simon II (1344)
- Otto (1344–1360)
- Bernard V (1344–1364)
- Simon III (1360–1410)
- Bernard VI (1410–1415)
- Simon IV (1415–1429)
- Bernard VII (1429–1511)
- Simon V (1511–1536)
Raised to County to 1536.
Counts of Lippe (-Detmold from 1613)
- Simon V (1511–1536)
- Bernard VIII (1536–1563)
- Simon VI (1563–1613)
- Simon VII (1613–1627)
- Simon Louis (1627–1636)
- Simon Philip (1636–1650)
- John Bernard (1650–1652)
- Herman Adolphus (1652–1665)
- Simon Henry (1665–1697)
- Frederick Adolphus (1697–1718)
- Simon Henry Adolphus (1718–1734)
- Simon Augustus (1734–1782)
- Leopold I (1782–1789)
Raised to Principality 1789.
Princes of Lippe
- Leopold I (1789–1802)
- Leopold II (1802–1851)
- Leopold III (1851–1875)
- Woldemar (1875–1895)
- Alexander (1895–1905)
- Prince Adolphus of Schaumburg-Lippe (regent 1895–1897)
- Count Ernest of Lippe-Biesterfeld (regent 1897–1904)
- Count Leopold of Lippe-Biesterfeld (regent 1904–1905)
- Leopold IV (1905–1918)
The monarchy of Lippe was abolished in 1918.
Heads of the House of Lippe
- Leopold IV (1918–1949)
- Armin (1949–present)
Heir Stephan, Hereditary Prince of Lippe (born 1959)
See also
- List of consorts of Lippe
- Ostwestfalen-Lippe
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.- German Genealogy: Lippe (-Detmold)
External links
- Ordinances and by-laws of the county of Lippe online (German)
- Guidelines for the integration of the Land Lippe within the territory of the federal state North-Rhine-Westphalia of 17 January 1947 (German)
 Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman Empire
Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireEcclesiastical Prelates Secular Counts
and lordsfrom 1500Bentheim · Bronkhorst (until 1719) · Diepholz · East Frisia (until 1667) · Horne3 (until 1614) · Hoya · Lingen3 · Lippe · Manderscheid (until 1546) · Moers (until 1541) · Nassau (Diez · Hadamar · Dillenburg (until 1664)) · Oldenburg (until 1777) · Pyrmont · Ravensberg3 · Reichenstein · Rietberg · Salm-Reifferscheid · Sayn · Schaumburg · Tecklenburg · Virneburg · Wied · Winneburg and Beilstein · Zimerauff?from 1792Anholt · Blankenheim and Gerolstein · Gemen · Gimborn · Gronsfeld · Hallermund · Holzapfel · Kerpen-Lommersum · Myllendonk · Reckheim · Schleiden · Wickrath · Wittemstatus
uncertainCities 1 from 1792. 2 until 1792. 3 without Reichstag seat. ? status uncertain. States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)
States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)Rank elevated
by NapoleonKingdomsGrand DuchiesStates created KingdomsGrand DuchiesPrincipalitiesPre-existing
statesDuchiesAnhalt (Bernburg · Dessau · Köthen) · Arenberg · Mecklenburg (Schwerin · Strelitz) · Nassau · Oldenburg · Saxony (Coburg-Saalfeld · Gotha-Altenburg · Hildburghausen · Meiningen · Weimar3 · Eisenach3 · Weimar-Eisenach4)PrincipalitiesHohenzollern (Hechingen · Sigmaringen) · Isenburg-Birstein · Liechtenstein · Lippe-Detmold · Reuss (Ebersdorf · Greiz · Lobenstein · Schleiz) · Salm5 · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck1 from 1810. 2 until 1810. 3 until 1809. 4 from 1809. 5 until 1811. States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)Empires 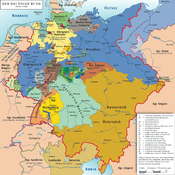
Kingdoms Electorates Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt (Bernburg2 · Dessau2 · Köthen3) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg4 · Nassau · Saxe-Lauenburg · Saxony (Altenburg5 · Coburg-Saalfeld6 · Coburg-Gotha5 · Gotha-Altenburg6 · Hildburghausen6 · Meiningen)Principalities Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen7 · Sigmaringen7) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and PyrmontCity-states Other territories
outside of the
confederacyColonial possessions · Personal unions of Habsburg (Bukovina · Croatia · Galicia and Lodomeria · Hungary · Lombardy–Venetia · Serbian Voivodeship and Banat8 · Slavonia9 · Transylvania) · Personal union of Hanover (Great Britain and Ireland10) · Personal unions of Hohenzollern (East Prussia11 · Neuchâtel12 · Posen, Gr. Duchy13 · Posen, Prov.14 · Prussia, Prov.15 · West Prussia11) · Occupied: Schleswig161 w/o areas listed under other territories. 2 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 3 until 1847. 4 from 1839. 5 from 1826. 6 until 1826. 7 until 1850. 8 1849–60. 9 as of 1849. 10 until 1837. 11 until 1829. 12 until 1848/57. 13 until 1848. 14 as of 1848. 15 as of 1829. 16 as of 1864. States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)
States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)Kingdoms 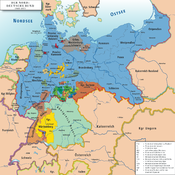
Grand Duchies Duchies Principalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states  States of the German Empire (1871–1918)
States of the German Empire (1871–1918)Kingdoms 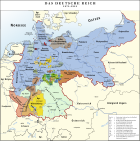
Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt · Brunswick · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg and Gotha · Saxe-Lauenburg (until 1876) · Saxe-MeiningenPrincipalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt · Schwarzburg-Sondershausen · Lippe · Reuss Elder Line · Reuss Junior Line · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states Other territories Elsaß-Lothringen · Colonial possessionsCategories:- Former principalities
- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1123
- States and territories disestablished in 1918
- 1918 disestablishments
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle
- Lists of princes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.