- Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
-
Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn
Fürstbistum PaderbornState of the Holy Roman Empire ← 
1281–1802  →
→

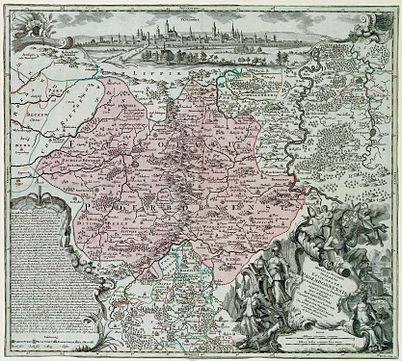
Flag Coat of arms Map of the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle around 1560,
Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn highlighted in redCapital Paderborn Government Principality Historical era Middle Ages - Bishopric established 799 - Bishopric gained
bailiwick over itself
ca 1200- Gained Reichsfreiheit 1281 - Secularised to Prussia 1802 - Ceded to Kgdm Westphalia 1807–13 Neighbouring states reduced to abbreviations in the map are as follows: AC indicates Corvey Abbey; FL is Lippe; GW is Waldeck; HD is Hesse-Darmstadt; HK is Hesse-Kassel; SY is Sayn.
More general abbreviations include Bm for Bishopric (German: Bistum); Gft for County (Grafschaft); Hzm for Duchy (Herzogtum) and Landgft for Landgraviate (Landgrafschaft).The Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn (German: Fürstbistum Paderborn) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1281 to 1802.
Contents
History
The Diocese of Paderborn was founded in 799 by Pope Leo III. In the early years it was subordinated to the bishop of Würzburg. Since 855 the clergy had the right to elect the bishop. The diocese included the larger part of Lippe, Waldeck, and nearly half of the County of Ravensberg.
In 1180 when the Duchy of Saxony ceased to exist, the rights which the old dukedom had exercised over Paderborn were transferred to the Archbishopric-Electorate of Cologne. The claims of the archbishops of Cologne were settled in the 13th century, almost wholly in favor of Paderborn. Under Bernhard II of Ibbenbüren (1198–1204) the bailiwick over the diocese, which since the middle of the 11th century had been held as a fief by the Counts of Arnsberg, returned to the bishops. This was an important advance in the development of the bishops' position as temporal sovereigns. From this time on the bishops did not grant the bailiwick as a fief, but managed it themselves, and had themselves represented in the government by one of their clergy. They strove successfully to obtain the bailiwicks over the abbeys and monasteries situated in their diocese.
Bishop Otto of Rietberg had to contend with Cologne; in 1281, when only bishop-elect, he received the regalia from Rudolph of Habsburg, and full judicial power (except penal judicature). After the defeat of the Cologne arch bishop at the Battle of Worringen 1288 the bishops of Paderborn became increasingly sovereigns, though not over the whole of their diocese. Bernhard V of Lippe (1321–41) established a first territorial constitution ("Privilegium Bernhardi"). However he had to acknowledge the city of Paderborn as free from his judicial supremacy. Henry III of Spiegel zum Desenberg (1361–80), also Abbot of Corvey, left his spiritual functions to a suffragan; in 1371 he rebuilt the Burg Neuhaus at Paderborn. Simon II of Sternberg (1380–89), involved the bishopric in feuds with the nobility, who after his death devastated the country. William I of Berg, elected 1399, sought to remedy the evils which had crept in during the foregoing feuds, but when in 1414 he interested himself in the vacancy in the Archbishopric of Cologne, the cathedral chapter in his absence chose Dietrich III of Moers (1415–63). The wars of Dietrich, also Archbishop of Cologne, brought heavy debts upon the bishopric; during the feuds of the bishop with the city of Soest (1444–49) Paderborn was devastated.
Under Eric of Brunswick-Grubenhagen (1502–32), the Protestant Reformation obtained a foothold in the diocese, although the bishop remained loyal to the Church. Hermann of Wied (1532–47), also Archbishop of Cologne, sought to introduce the new teaching at Paderborn as well as Cologne, but he was opposed by all classes. The countships of Lippe, Waldeck, and Pyrmont, the part of the diocese in the County of Ravensberg, and most of the parishes on the right bank of the Weser became Protestant.
Henry IV of Saxe-Lauenburg (1577–85) was a Lutheran; he permitted the adoption of the Augsburg Confession by his subjects. In the city of Paderborn only the cathedral and the Monastery of Abdinghof remained faithful. To save the Catholic cause, the cathedral chapter summoned the Jesuits to Paderborn in 1580. Dietrich IV of Fürstenberg (1585–1618) restored the practice of the Catholic religion, built a gymnasium for the Jesuits, and founded the University of Paderborn in 1614.
During the German Mediatisation in 1802, the bishopric became Prussian, from 1807 until 1813 it was part of the Kingdom of Westphalia, and then part of the Prussian province of Westphalia.
Prince-bishops
- Bernhard V, Lord of Lippe (1321–41)
- Baldwin of Steinfurt (1341–61)
- Henry III of Spiegel zum Desenberg OSB (1361–80; also abbot of Corvey)
- Simon II of Sternberg (1380–89)
- Rupert of Berg (1389–94; also bishop of Passau)
- John I of Hoya (1394–99;l subsequently bishop of Hildesheim)
- Bertrando d'Arvazzano (1399–1401)
- William I of Berg (1400–14; subsequently Count of Ravensberg)
- Dietrich III of Moers (1414–63; also Elector of Cologne)
- Simon III of Lippe (1463–98)
- Herman I of Hesse (1498–1508; also Elector of Cologne)
- Eric of Brunswick-Grubenhagen (1508–32; also bishop of Osnabrück and, briefly, of Münster)
- Hermann of Wied (1532–47; also Elector of Cologne)
- Rembert of Kerssenbrock (1547–68)
- John II of Hoya (1568–74; also bishop of Osnabrück and Münster)
- Salentin of Isenburg (1574–77; also Elector of Cologne, subsequently Count of Isenburg-Grenzau)
- Henry IV of Saxe-Lauenburg (1577–85; Protestant, also archbishop of Bremen and bishop of Osnabrück)
- Dietrich IV of Fürstenberg (1585–1618)
- Ferdinand I of Bavaria (1618–50; also Elector of Cologne, Provost of Berchtesgaden and bishop of Hildesheim, Freising, Liège and Münster)
- Dietrich Adolf of Recke (1650–61)
- Ferdinand II of Fürstenberg (1661–83; also bishop of Münster)
- Hermann Werner von Wolff-Metternich zur Gracht (1683–1704)
- Franz Arnold von Wolff-Metternich zur Gracht (1704–18; also bishop of Münster)
- Clemens August of Bavaria (1719–61; also Elector of Cologne, provost of Altötting, bishop of Regensburg, Hildesheim, Münster and Osnabrück, and Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights)
- William Anton of Asseburg (1763–82)
- Frederick William of Westphalia (1782–89; also bishop of Hildesheim)
- Franz Egon von Fürstenberg (1789–1825)
See also
- Paderborn Cathedral
- Archdiocese of Paderborn
References
- This article incorporates information from the German Wikipedia.
External links
 Media related to Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Prince-Bishopric of Paderborn at Wikimedia Commons Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman Empire
Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireEcclesiastical Prelates Secular Counts
and lordsfrom 1500Bentheim · Bronkhorst (until 1719) · Diepholz · East Frisia (until 1667) · Horne3 (until 1614) · Hoya · Lingen3 · Lippe · Manderscheid (until 1546) · Moers (until 1541) · Nassau (Diez · Hadamar · Dillenburg (until 1664)) · Oldenburg (until 1777) · Pyrmont · Ravensberg3 · Reichenstein · Rietberg · Salm-Reifferscheid · Sayn · Schaumburg · Tecklenburg · Virneburg · Wied · Winneburg and Beilstein · Zimerauff?from 1792Anholt · Blankenheim and Gerolstein · Gemen · Gimborn · Gronsfeld · Hallermund · Holzapfel · Kerpen-Lommersum · Myllendonk · Reckheim · Schleiden · Wickrath · Wittemstatus
uncertainCities 1 from 1792. 2 until 1792. 3 without Reichstag seat. ? status uncertain.Categories:- Former principalities
- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1281
- States and territories disestablished in 1802
- 799 establishments
- Dioceses established in the 8th century
- Paderborn
- Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle
- History of North Rhine-Westphalia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.