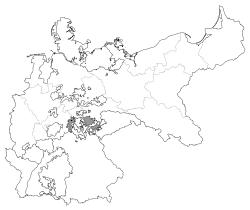
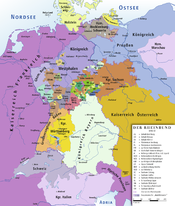
- Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
-
(Grand) Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
(Groß-)herzogtum Sachsen-Weimar-EisenachState of the Confederation of the Rhine
State of the German Confederation
State of the North German Confederation
State of the German Empire
State of the Weimar Republic← 
←
1809–1920  →
→

Flag (1813–1897) Coat of arms Anthem
Weimars VolksliedSaxe-Weimar-Eisenach within the German Empire Capital Weimar Government Principality Grand Duke - 1809–28 Charles Augustus (first) - 1901–18 William Ernest (last) Historical era Middle Ages - Saxe-Eisenach and
Saxe-Weimar held in
personal union
1741- Merger of Eisenach
and Weimar1809 - Raised to
grand duchy1815 - German Revolution 1918 - Joined Thuringia 1920 Area - 1905 3,617 km2 (1,397 sq mi) Population - 1905 est. 388,000 Density 107.3 /km2 (277.8 /sq mi) The Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (German: Herzogtum Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was created in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach. It was raised to a Grand duchy in 1815 by resolution of the Vienna Congress. In 1877, it officially changed its name to the Grand Duchy of Saxony (German: Großherzogtum Sachsen), but this name was rarely used. The Grand Duchy came to an end in the German Revolution of 1918–19 with the other monarchies of the German Empire. It was succeeded by the Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, which was merged into the new state of Thuringia two years later.
The full grand ducal style was Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Landgrave in Thuringia, Margrave of Meissen, Princely Count of Henneberg, Lord of Blankenhayn, Neustadt and Tautenburg.
Contents
History
The duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach had been ruled in personal union by the House of Wettin since 1741, after the Eisenach line had died out upon the death of Duke Wilhelm Heinrich. In 1804 Duke Charles Augustus' eldest son and heir Charles Frederick married Maria Pavlovna Romanova, sister of Emperor Alexander I of Russia, a conjugal union which decisively promoted the rise of the Ernestine Saxe-Weimar dynasty. Though at first an ally of Prussia in the Napoleonic War of the Fourth Coalition, Duke Charles Augustus escaped his deposition by joining the Confederation of the Rhine on 15 December 1806.
After the official merger in 1809, the Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach consisted of the separate districts around the capital Weimar in the north and Eisenach in the west, further enlarged in 1815 by the district of Neustadt an der Orla in the east.
Princes of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, 1809–1815
- Charles Augustus, 1809–15; Duke of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach since 1758, until 1775 under the tutelage of his mother Duchess Anna Amalia of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel
Grand Dukes of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, 1815–1918
- Charles Augustus, 1815–28
- Charles Frederick, 1828–53
- Charles Alexander, 1853–1901
- William Ernest, 1901–18
Heads of the House of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, 1918–present
- Grand Duke Wilhelm Ernst, 1918–23
- Hereditary Grand Duke Carl August, 1923–88
- Prince Michael, 1988–present
See also
External links
- Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach genealogy
 "Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.
"Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913. Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). "Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Saxe-Weimar (1572–1806) · Saxe-Coburg-Eisenach (1572–1596, 1633-1638) · Saxe-Coburg (1596–1633, 1681–1699) · Saxe-Eisenach (1596–1638, 1640–1644, 1672–1806) · Saxe-Altenburg (1603–1672, 1826–1918) · Saxe-Gotha (1640–1680) · Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg (1681–1826) · Saxe-Marksuhl (1662–1672) · Saxe-Jena (1672–1690) · Saxe-Eisenberg (1680–1707) · Saxe-Hildburghausen (1680–1826) · Saxe-Römhild (1680–1710) · Saxe-Saalfeld (1680–1735) · Saxe-Meiningen (1681–1918) · Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld (1735–1826) · Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1806–1918) · Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1826–1918)

 States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)
States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)Rank elevated
by NapoleonKingdomsGrand DuchiesStates created KingdomsGrand DuchiesPrincipalitiesPre-existing
statesDuchiesAnhalt (Bernburg · Dessau · Köthen) · Arenberg · Mecklenburg (Schwerin · Strelitz) · Nassau · Oldenburg · Saxony (Coburg-Saalfeld · Gotha-Altenburg · Hildburghausen · Meiningen · Weimar3 · Eisenach3 · Weimar-Eisenach4)PrincipalitiesHohenzollern (Hechingen · Sigmaringen) · Isenburg-Birstein · Liechtenstein · Lippe-Detmold · Reuss (Ebersdorf · Greiz · Lobenstein · Schleiz) · Salm5 · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck1 from 1810. 2 until 1810. 3 until 1809. 4 from 1809. 5 until 1811. States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)Empires 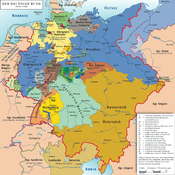
Kingdoms Electorates Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt (Bernburg2 · Dessau2 · Köthen3) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg4 · Nassau · Saxe-Lauenburg · Saxony (Altenburg5 · Coburg-Saalfeld6 · Coburg-Gotha5 · Gotha-Altenburg6 · Hildburghausen6 · Meiningen)Principalities Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen7 · Sigmaringen7) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and PyrmontCity-states Other territories
outside of the
confederacyColonial possessions · Personal unions of Habsburg (Bukovina · Croatia · Galicia and Lodomeria · Hungary · Lombardy–Venetia · Serbian Voivodeship and Banat8 · Slavonia9 · Transylvania) · Personal union of Hanover (Great Britain and Ireland10) · Personal unions of Hohenzollern (East Prussia11 · Neuchâtel12 · Posen, Gr. Duchy13 · Posen, Prov.14 · Prussia, Prov.15 · West Prussia11) · Occupied: Schleswig161 w/o areas listed under other territories. 2 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 3 until 1847. 4 from 1839. 5 from 1826. 6 until 1826. 7 until 1850. 8 1849–60. 9 as of 1849. 10 until 1837. 11 until 1829. 12 until 1848/57. 13 until 1848. 14 as of 1848. 15 as of 1829. 16 as of 1864. States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)
States of the North German Confederation (1866–71)Kingdoms 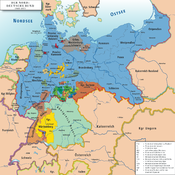
Grand Duchies Duchies Principalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states  States of the German Empire (1871–1918)
States of the German Empire (1871–1918)Kingdoms 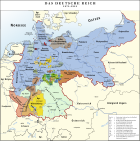
Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt · Brunswick · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg and Gotha · Saxe-Lauenburg (until 1876) · Saxe-MeiningenPrincipalities Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt · Schwarzburg-Sondershausen · Lippe · Reuss Elder Line · Reuss Junior Line · Waldeck-PyrmontCity-states Other territories  States of Germany during the Weimar Republic (1919–33)
States of Germany during the Weimar Republic (1919–33)States Anhalt · Baden · Bavaria · Brunswick · Hesse · Lippe · Mecklenburg-Schwerin · Mecklenburg-Strelitz · Oldenburg · Prussia · Saxony · Schaumburg-Lippe · Thuringia (from 1920) · Waldeck (until 1929) · Württemberg
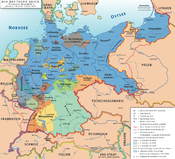
City-states Until 1920 Unofficial Categories:- Former principalities
- Former countries in Europe
- Former vassal states
- States and territories established in 1809
- States and territories disestablished in 1920
- 1920 disestablishments
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- States of the German Confederation
- States of the North German Confederation
- States of the German Empire
- States of the Weimar Republic
- Ernestine duchies
- Grand Dukes of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
- Dukes of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
- House of Wettin
- History of Thuringia
- House of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.