- Anhalt-Bernburg
-
Principality (Duchy) of Anhalt-Bernburg
Fürstentum (Herzogtum) Anhalt-BernburgState of the Holy Roman Empire (until 1806) ← 
1252–1468
1603–1863 →
→
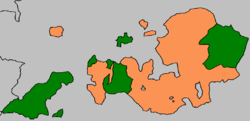
Flag Coat of arms Anhalt territories in 1853, Anhalt-Bernburg in green Capital Bernburg Government Principality Historical era Middle Ages - Partitioned from Anhalt 1252 - Inherited by
Anhalt-Dessau1468 - Repartitioned from
Anhalt1603 - Split off
Anhalt-Zeitz-Hoym1718 - Riased to duchy 1803 - Anhalt re-united 1863 Today part of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany Anhalt-Bernburg was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire and a duchy of the German Confederation ruled by the House of Ascania with its residence at Bernburg in present-day Saxony-Anhalt. It emerged as a subdivision from Anhalt from 1252 to 1468 and again from 1603 until the re-unification in 1863.
It was created in 1252, when the Principality of Anhalt was partitioned among the sons of Henry I into Anhalt-Aschersleben, Anhalt-Bernburg and Anhalt-Zerbst. Bernburg was allotted to Henry's second son Bernhard I. When the line of Anhalt-Aschersleben became extinct in 1315, Prince Bernhard II of Anhalt-Bernburg claimed their territory, he could however not prevail against his cousin Albert, Bishop of Halberstadt. After the ruling family became extinct upon the death of Prince Bernhard VI in 1468, Anhalt-Bernburg was inherited by Prince George I of Anhalt-Dessau. With Anhalt-Dessau it was inherited by Prince Joachim Ernest of Anhalt-Zerbst in 1561, who unified all Anhalt lands under his rule in 1570.
Re-united Anhalt was again divided in 1603 among Prince Joachim Ernest's sons into the lines of Anhalt-Dessau, Anhalt-Köthen, Anhalt-Plötzkau, Anhalt-Bernburg and Anhalt-Zerbst. His second son Prince Christian I took his residence at Bernburg. Christian's younger son Frederick established the separate Principality of Anhalt-Harzgerode in 1635, which existed until 1709. Prince Victor Amadeus of Anhalt-Bernburg inherited Anhalt-Plötzkau in 1665. Upon his death in 1718 his lands were further divided and the Principality of Anhalt-Zeitz-Hoym was created for his second son Lebrecht, which was reunited with Anhalt-Bernburg in 1812.
In 1803 Prince Alexius Frederick Christian of Anhalt-Bernburg was elevated to the rank of a duke by Emperor Francis II of Habsburg. His son Duke Alexander Karl however died without issue in 1863, whereafter Anhalt-Bernburg was inherited by Duke Leopold IV of Anhalt-Dessau, re-uniting all Anhalt lands under his rule.
Princes of Anhalt-Bernburg 1252–1468
- 1252–1287 Bernhard I
- 1287–1291 John I, son, co-regent with his brother
- 1323–1348 Bernhard III, son of Bernhard II
- 1348–1354 Bernhard IV, son
- 1354–1374 Henry IV, brother
- 1374–1404 Otto III, brother
- 1404–1420 Bernhard V, son of Henry IV, co-regent with his cousin
- 1420–1468 Bernhard VI, brother of Otto IV, left no male heirs
Princes of Anhalt-Bernburg 1603–1807
- 1603–1630 Christian I, second son of Prince Joachim Ernest of Anhalt
- 1630–1656 Christian II, son
- 1656–1718 Victor Amadeus, son
- 1718–1721 Karl Frederick, son
- 1721–1765 Victor Frederick, son
- 1765–1796 Frederick Albert, son
- 1796–1803 Alexius Frederick Christian, son
- Raised to duchy
Dukes of Anhalt-Bernburg 1803–1863
- 1803–1834 Alexius Frederick Christian
- 1834–1863 Alexander Karl, son, died without issue
- To re-united Anhalt
 Upper Saxon Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman Empire
Upper Saxon Circle (1512–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireElectorates 
Ecclesiastical Secular Anhalt (Bernburg · Köthen · Zerbst) · Barby · Hatzfeld-Gleichen · Pomerania (Further · Hither) · Querfurt · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg · Saxe-Eisenach · Saxe-Gotha · Saxe-Weimar · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen)Prelates Counts / Lords Hohnstein · Lohra / Klettenberg · Mansfeld · Schönburg (Saale) · Stolberg (Stolberg · Wernigerode · Rossla) States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)
States of the Confederation of the Rhine (1806–13)Rank elevated
by NapoleonKingdomsGrand DuchiesStates created KingdomsGrand DuchiesPrincipalitiesPre-existing
statesDuchiesAnhalt (Bernburg · Dessau · Köthen) · Arenberg · Mecklenburg (Schwerin · Strelitz) · Nassau · Oldenburg · Saxony (Coburg-Saalfeld · Gotha-Altenburg · Hildburghausen · Meiningen · Weimar3 · Eisenach3 · Weimar-Eisenach4)PrincipalitiesHohenzollern (Hechingen · Sigmaringen) · Isenburg-Birstein · Liechtenstein · Lippe-Detmold · Reuss (Ebersdorf · Greiz · Lobenstein · Schleiz) · Salm5 · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck1 from 1810. 2 until 1810. 3 until 1809. 4 from 1809. 5 until 1811. States of the German Confederation (1815–66)
States of the German Confederation (1815–66)Empires 
Kingdoms Electorates Grand Duchies Duchies Anhalt (Bernburg2 · Dessau2 · Köthen3) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg4 · Nassau · Saxe-Lauenburg · Saxony (Altenburg5 · Coburg-Saalfeld6 · Coburg-Gotha5 · Gotha-Altenburg6 · Hildburghausen6 · Meiningen)Principalities Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen7 · Sigmaringen7) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and PyrmontCity-states Other territories
outside of the
confederacyColonial possessions · Personal unions of Habsburg (Bukovina · Croatia · Galicia and Lodomeria · Hungary · Lombardy–Venetia · Serbian Voivodeship and Banat8 · Slavonia9 · Transylvania) · Personal union of Hanover (Great Britain and Ireland10) · Personal unions of Hohenzollern (East Prussia11 · Neuchâtel12 · Posen, Gr. Duchy13 · Posen, Prov.14 · Prussia, Prov.15 · West Prussia11) · Occupied: Schleswig161 w/o areas listed under other territories. 2 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 3 until 1847. 4 from 1839. 5 from 1826. 6 until 1826. 7 until 1850. 8 1849–60. 9 as of 1849. 10 until 1837. 11 until 1829. 12 until 1848/57. 13 until 1848. 14 as of 1848. 15 as of 1829. 16 as of 1864.Categories:- Former principalities
- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1252
- States and territories disestablished in 1863
- 1863 disestablishments
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- States of the German Confederation
- House of Ascania
- Lists of princes
- History of Anhalt
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.