- Dosage form
-
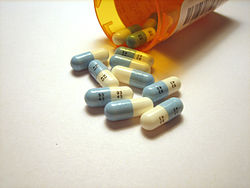 Fluoxetine (Prozac) in a capsule dosage form intended for oral administration.
Fluoxetine (Prozac) in a capsule dosage form intended for oral administration.
Contents
Introduction
dosage form is a mixture of active drug component and nondrug component.depending on the type of admistration it is of several types.they are liquid dosage form,solid dosage form and semisolid dosage forms.A Liquid dosage form is the liquid form of a dose of a chemical compound used as a drug or medication intended for administration or consumption. Common dosage forms include pill, tablet, or capsule, drink or syrup, (e.g., via oral ingestion or freebase smoking), and natural or herbal form such as plant or food of sorts, among many others. Notably, the route of administration (ROA) for drug delivery is dependent on the dosage form of the substance in question.
Various dosage forms may exist for a single particular drug, since different medical conditions can warrant different routes of administration. For example, persistent nausea and emesis or vomiting may make it difficult to use an oral dosage form, and in such a case, it may be necessary to utilize an alternate route such as inhalational, buccal, sublingual, nasal, suppository or parenteral instead.
Additionally, a specific dosage form may be a requirement for certain kinds of drugs, as there may be issues with various factors like chemical stability or pharmacokinetics. As an example, insulin cannot be given orally because upon being administered in this manner, it is extensively metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) before reaching the blood stream, and is thereby incapable of sufficiently reaching its therapeutic target destinations. The oral and intravenous doses of a drug such as paracetamol will differ for the same reason.[1]
Types
Oral
- Pill, tablet, or capsule
- Specialty tablet like buccal, sub-lingual, or orally-disintegrating
- Thin film (e.g., Listerine Pocketpaks)
- Liquid solution or suspension (e.g., drink or syrup)
- Powder or liquid or solid crystals
- Natural or herbal plant, seed, or food of sorts (e.g., marijuana such as that found in "special brownies")
Pastes(Colgate)
Inhalational
- Aerosol
- Inhaler
- Nebulizer
- Smoking (often in natural herb (e.g., tobacco, marijuana) or freebase powder form (e.g., cocaine, methamphetamine))
- Vaporizer (usually to vaporize natural herbs like marijuana)
Parenteral Injection
- Intradermal (ID)
- Intramuscular (IM)
- Intraosseous (IO)
- Intraperitoneal (IP)
- Intravenous (IV)
- Subcutaneous (SC)
- Intrathecal (IT) Injection into the spinal column
Topical
- Cream, gel, liniment or balm, lotion, or ointment, etc.
- Ear drops (otic)
- Eye drops (ophthalmic)
- Skin patch (transdermal)
Suppository
See also
References
External links
Routes of administration / Dosage forms Oral Buccal / Sublabial / Sublingual- Mouthwash
- Toothpaste
- Ointment
- Oral spray
- Oxygen mask
- Oxygen concentrator
- Anaesthetic machine
- Relative analgesia machine





Ocular / Otologic / Nasal - Nasal spray
- Ear drops
- Eye drops
- Ointment
- Hydrogel
- Nanosphere suspension
- Mucoadhesive microdisc (microsphere tablet)
Urogenital - Ointment
- Pessary (vaginal suppository)
- Vaginal ring
- Vaginal douche
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Extra-amniotic infusion
- Intravesical infusion
Rectal (enteral) - Ointment
- Suppository
- Enema (Solution • Hydrogel)
- Murphy drip
- Nutrient enema
Dermal Injection / Infusion
(into tissue/blood)- Intracavernous
- Intravitreal
- Intra-articular or intrasynovial injection
- Transscleral
- Intracerebral
- Intrathecal
- Epidural
Additional explanation: Mucous membranes are used by the human body to absorb the dosage for all routes of administration, except for "Dermal" and "Injection/Infusion".
Administration routes can also be grouped as Topical (local effect) or Systemic (defined as Enteral = Digestive tract/Rectal, or Parenteral = All other routes).Routes of administration by organ system Gastrointestinal Respiratory system Pulmonary • NasalVisual system / Auditory system Ocular (Ocular-topical / Intravitreal / Transscleral) • Otologic (Oto-topical)Reproductive system Intracavernous • Intravaginal • Intrauterine (Extra-amniotic)Urinary system IntravesicalPeritoneum Central nervous system Intracerebral • Intrathecal • EpiduralCirculatory system Musculoskeletal system Skin Epicutaneous • Intradermal • SubcutaneousCategories:- Pharmacology
- Dosage forms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

