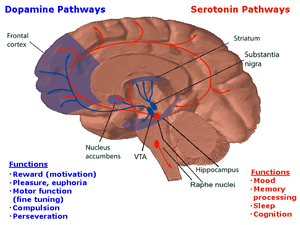
- Dopaminergic pathways
-
Dopaminergic pathways are neural pathways in the brain which transmit the neurotransmitter dopamine from one region of the brain to another.[1]
The neurons of the dopaminergic pathways have axons which run the entire length of the pathway. The neurons' soma produces the enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and they are then transmitted via the projecting axons to their synaptic destinations, where most of the dopamine is produced. Dopaminergic nerve cell bodies in such areas as the substantia nigra tend to be pigmented due to the presence of the black pigment melanin.
Examples
There are eight dopaminergic pathways, but the four major ones are:
Name Description Disorders mesolimbic pathway The mesolimbic pathway transmits dopamine from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens. The VTA is located in the midbrain, and the nucleus accumbens is in the limbic system. The "meso-" prefix in the word "mesolimbic" refers to the midbrain, or "middle brain", since "meso" means "middle" in Greek. schizophrenia mesocortical pathway The mesocortical pathway transmits dopamine from the VTA to the frontal cortex. The "meso-" prefix in "mesocortical" refers to the VTA which is located in the midbrain, and "cortical" refers to the cortex. schizophrenia nigrostriatal pathway The nigrostriatal pathway transmits dopamine from the substantia nigra to the striatum. This pathway is associated with motor control. Parkinson's disease, chorea tuberoinfundibular pathway The tuberoinfundibular pathway transmits dopamine from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland. This pathway influences the secretion of certain hormones, including prolactin. "Infundibular" in the word "tuberoinfundibular" refers to the infundibulum out of which the pituitary gland develops. hyperprolactinaemia Minor ones include the incertohypothalamic pathway within the hypothalamus, which has a role in sexual behaviour.
References
- ^ "Beyond the Reward Pathway". http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/addiction/reward/pathways.html. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
- The Reward Circuit. Part of "The Brain From Top To Bottom". The content of this page is copylefted and has been used in this article.
Neurotransmitter systems Acetylcholine BA/M Dopaminergic pathwaysMesocortical pathway: Ventral tegmental area → Frontal cortex
Mesolimbic pathway: Ventral tegmental area → Nucleus accumbens
Nigrostriatal pathway: Pars compacta → Striatum
Tuberoinfundibular pathway: Hypothalamus → Pituitary glandSerotonin pathwaysAA Categories:- Central nervous system pathways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.