- Chronology of European exploration of Asia
-
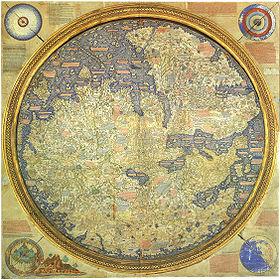 The Fra Mauro map, completed around 1459, is a map of the then-known world. Following the standard practice at that time, south is at the top. The map was said by Giovanni Battista Ramusio to have been partially based on the one brought from Cathay by Marco Polo.
The Fra Mauro map, completed around 1459, is a map of the then-known world. Following the standard practice at that time, south is at the top. The map was said by Giovanni Battista Ramusio to have been partially based on the one brought from Cathay by Marco Polo.
This article attempts to list every significant event in the history of the European exploration of Asia.[1] It proposes a chronological inventory of these events including every people involved and the places they helped to demystify (from a European point of view).
Contents
First wave of exploration (mainly by land)
Antiquity
- 330 BC
- Alexander the Great conquers parts of Central Asia and parts of northwestern India
- 300 BC
- Seleucus Nicator, founder of the Seleucid Empire, forays into northwestern India but is defeated by Chandragupta Maurya, founder of the Maurya Empire, and they become allies soon after.
- 250-120 BC
- Greco-Bactrian rule in parts of Central Asia and parts of the Punjab region.
- 180 BC-10 AD
- Rule of the Indo-Greek kingdom in parts of northwestern India.
- 30 BC-640 AD
- The Romans begin trading with India.
- 100 AD-166 AD
- Sino-Roman relations begin.
Middle ages
- ~500-1000
- The Radhanites were medieval Jewish merchants who dominated trade between the Christian and Islamic worlds during the early Middle Ages and travelled as far as Tang dynasty China.
- 568
- The Byzantine general Zemarchus travels to Samarkand and the court of the Western Turkic Kaganate.
- 1160-1173
- The Navarrese Jewish Rabbi Benjamin of Tudela visits Syria, Palestine, Baghdad, Persia, and the Arabian Peninsula.
- 1180-1186
- Pethahiah of Regensburg goes to Baghdad.
- 1245-1247
- The Italian Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, accompanied by Stephen of Bohemia, and later by Benedykt Polak, reaches Karakorum in present-day Mongolia. First European embassy to the Great Khan.
- 1245-1248
- The Italian Ascelin of Lombardia, Simon of St Quentin and Andrew of Longjumeau go to Armenia and Persia.
- 1249-1251
- Andrew of Longjumeau guide a French ambassador to the great Kuyuk Khan. His brother Guy and several others — John Goderiche, John of Carcassonne, Herbert "Le Sommelier", Gerbert of Sens, Robert (a clerk), a certain William, and an unnamed clerk of Poissy go with him. They reached Talas in northwestern Kyrgyzstan.
- ≈1254
- The Flemish William of Rubruck reached China and Mongolia through Central Asia.
- 1264-≈1269
- First travel of the Italians Niccolò and Maffeo Polo to China. In 1266, they reach Kublai Khan's seat at Dadu, now known as Beijing, China.
- 1271-1295
- Second trip of Niccolò and Maffeo Polo to China. This time with Marco, Niccolo's son, who would write a colorful account of their experiences.
- 1275-1289 & 1289-1328
- The Italian John of Montecorvino (1246–1328) was a Franciscan missionary, traveller and statesman, founder of the earliest Roman Catholic missions in India and China, and archbishop of Peking, and Patriarch of the Orient.
- ≈1318-1329
- Travels of the Franciscan monks, the Italian Odoric of Pordenone and James of Ireland via India and the Malay Peninsula to China where they stayed in Dadu (present day Beijing) for approximately three years before returning to Italy overland through Central Asia.
- ~1321-1330/1338(?)
- The French Dominican missionary Jordanus, made bishop over the whole Indian subcontinent in 1329, wrote down his travels through India and the Middle East in his book Mirabilia.
- 1338-1353
- The Italian Giovanni de' Marignolli, one of four chief envoys sent by Pope Benedict XII to Peking.
- 1401-1402
- Travel of Payo Gómez de Sotomayor, first ambassador of Henry III of Castile to the Timurid Empire.
- 1403-1404
- Travel of Ruy González de Clavijo, second ambassador of Henry III of Castile to the Timurid Empire. He passed along the Black Sea coast of Turkey to Trabzon and then overland through Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran and Turkmenistan to Uzbekistan. He also visited Tehran.
- 1420-1436
- Travels of the Italian explorer Niccolò Da Conti to India and Southeast Asia.
- 1470
- Travels of Afanasy Nikitin, the first Russian to visit India.
- 1471-79
- The Italian Venetian diplomats Caterino Zeno, Ambrogio Contarini, and Giosafat Barbaro travel to Persia.
- 1557-1572
- The English Anthony Jenkinson traveled across the Caspian Sea to Bukhara and Persia.
- ≈1580-1585
- The Cossack Yermak Timofeyevich reaches the Siberian Tatar city of Qashliq near the right bank of Irtysh.
- 1583-1591
- The English merchant Ralph Fitch traveled via the Levant and Mesopotamia to India and Malacca (in Malaysia).
Second wave of exploration (by sea)
 The Cantino planisphere (or Cantino World Map) of 1502 is the earliest surviving map showing Portuguese Discoveries in the east and west.
The Cantino planisphere (or Cantino World Map) of 1502 is the earliest surviving map showing Portuguese Discoveries in the east and west.
- 1497-1499
- The Portuguese Vasco da Gama, accompanied by Nicolau Coelho and Bartolomeu Dias, is the first European to reach India by an all-sea route from Europe.
- 1500-1501
- After discovering Brazil, Pedro Álvares Cabral, with the half of an original fleet of 13 ships and 1,500 men, accomplished the second Portuguese trip to India. Boats were commanded by Cabral, Bartolomeu Dias, Nicolau Coelho, Sancho de Tovar, Simão de Miranda, Aires Gomes da Silva, Vasco de Ataíde, Diogo Dias, Simão de Pina, Luís Pires, Pêro de Ataíde and Nuno Leitão da Cunha.[2] It is not known which one between Gaspar de Lemos and André Gonçalves, commanded the ship which returned to Portugal with the news of the discovery. Luís Pires returned to Portugal just after reaching Cape Verde. Vasco de Ataíde, Bartolomeu Dias, Simão de Pina and Aires Gomes' ships were lost near the Cape of Good Hope. The ship commanded by Diogo Dias separated and discovered Madagascar. He was then the first to reach the Red Sea by boat. Nuno Leitão da Cunha, Nicolau Coelho, Sancho de Tovar, Simão de Miranda, Pero de Ataíde did the entire trip to India. Among other passengers were: Pêro Vaz de Caminha and the Franciscan father, Frei Henrique de Coimbra.
- 1501-?
- João da Nova commands the third Portuguese expedition to India. He discovers Ascension Island (1501) and Saint Helena (1502) along the way.
- 1502-1503
- Second trip of Vasco de Gama to India.
- 1503-1504
- Afonso de Albuquerque establishes the first Portuguese fort in Kochi, India.
- 1505
- Francisco de Almeida is appointed as the first viceroy of Portuguese India (Estado da Índia). He leaves Lisbon with an armada of 22 ships, including 14 carracks and 6 caravels carrying a crew of 1,000 and 1,500 soldiers. His son, Lourenço de Almeida, explores the southern coast and reaches the modern island of Sri Lanka.
- 1507-1513
- In 1507, Afonso de Albuquerque captures the kingdom of Ormus in the Persian Gulf. He is then appointed second viceroy of India in 1508. In 1510 he captures Goa, soon to became the most flourishing of the Portuguese settlements in India.
- 1511
- Albuquerque conquers Malacca discovered by Lopes de Sequeira in 1509. Malacca becomes a strategic base for Portuguese expansion in the East Indies. In November of that year, after having secured Malacca and learning of the "Spice islands" (Banda Islands) location, in Maluku Albuquerque sent an expedition of three vessels led by António de Abreu to find them. In 1511 Ayutthaya Kingdom (Thailand) received a diplomatic mission from the Portuguese. These were probably the first Europeans to visit the country. Five years after that initial contact, Ayutthaya and Portugal concluded a treaty granting the Portuguese permission to trade in the kingdom.
- 1512
- Malay pilots guided the Portuguese via Java, the Lesser Sundas and Ambon to Banda, arriving in early 1512.[3] The first Europeans to reach the Banda Islands, the expedition remained in Banda for about one month, purchasing nutmeg and mace, and cloves in which Banda had a thriving entrepôt trade.[4] D'Abreu sailed through Ambon while his second in command Francisco Serrão went ahead towards Maluku islands, was shipwrecked and ended up in Ternate.[5] Francisco Serrão establishes a fort on Ternate Island.
- 1513
- Albuquerque laid siege to Aden in 1513, but was repulsed. He then led a voyage into the Red Sea, the first ever made by a European fleet.
- Jorge Álvares is the first European to land in China at Lintin Island in the Zhujiang (Pearl River) estuary.
- 1517
- The Portuguese merchant Fernão Pires de Andrade establishes the first modern trading contact with the Chinese at the Zhujiang (Pearl River) estuary and then in Canton (Guangzhou).
- 1519-
- Leaving Spain with five ships and 270 men in 1519, the Portuguese Ferdinand Magellan is the first to reach Asia from the East. In 1520, he discovers what is now known as the Strait of Magellan. In 1521 he reaches the Marianas and then the island of Homonhon in the Philippines. Some time after, Magellan is killed in what is known as the Battle of Mactan. The rest of the crew sails to Palawan (Philippines), and then to Brunei and Borneo. They then reach Tidore in the Maluku Islands avoiding the Portuguese. Only one ship, commanded by Juan Sebastián Elcano, returns to Spain in 1522 with 18 men remaining.
- 1524
- Third trip of Vasco de Gama to India.
- 1542
- After a journey through Sumatra, Malaysia, Siam (Thailand), China, possibly Korea and Cochinchina (Vietnam), Fernão Mendes Pinto is one of the first Europeans to land in Japan.
- 1542
- António de Mota is thrown by a storm on the island of Nison, called by the Chinese Jepwen (Japan).
- 1549
- On return of his second trip to Japan Fernão Mendes Pinto takes with him a Japanese fugitive known as Anjiro and introduces him to the Jesuit Saint Francis Xavier.
- 1549
- Saint Francis Xavier arrive in Japan accompanied by Father Cosme de Torrès, Brother Juan Fernández, the Japanese Anjiro, two baptized Japanese named Antonio and Joane, a Chinese named Manuel, and an Indian named Amador. The captain of the ship is named Avan aka "The Pirate".
- 1556
- The Dominican Gaspar da Cruz is the first modern missionary to go in China. He traveled to Guangzhou in 1556 and wrote the first complete book on China and the Ming Dynasty that was published in Europe; it included information on its geography, provinces, royalty, official class, bureaucracy, shipping, architecture, farming, craftsmanship, merchant affairs, clothing, religious and social customs, music and instruments, writing, education, and justice. (See also Jesuit China missions)
- 1595
- The Dutchman Jan Huyghen van Linschoten published his Reys-gheschrift vande navigatien der Portugaloysers in Orienten (Travel Accounts of Portuguese Navigation in the Orient) which was translated in to English and German in 1598. It gave access to secret Portuguese information, including the nautical maps which had been well guarded for over a century. The book thus broke the Portuguese monopoly on the sea trade with Asia.
Noteworthy Others
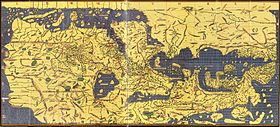 The Tabula Rogeriana (1154), by Muhammad al-Idrisi
The Tabula Rogeriana (1154), by Muhammad al-Idrisi
- ~118 BCE
- Eudoxus of Cyzicus was a Greek navigator from the Asian-Greek city of Cyzicus who explored the Arabian Sea for Ptolemy VIII, king of the Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt.
- 522~550
- Cosmas Indicopleustes (lit. "who sailed to India") of Alexandria was a Greek merchant, and later monk, who made several voyages to India during the reign of emperor Justinian. His Topografia Christiana contained some of the earliest and most famous world maps.
- 1154
- Although not known for his travels, Muhammad al-Idrisi was most important for the exploration of Asia for Europeans when he made the Tabula Rogeriana, a map of the whole known world, in 1154 for the Norman King Roger II of Sicily, based on his knowledge of the Arab trade routes.
- 1247 & 1254
- Hetoum I, king of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia and ally of the Frankish crusader states, visits the Mongol court in Karakoram in 1254 after first sending his brother Sempad in 1247.
- 1275-1288
- Rabban Bar Sauma and Markos, the Turkic/Chinese Nestorian monks, traveled to the Middle East and Europe. The Rabban Bar Sauma met with many of the European monarchs, as well as the Pope, in attempts to arrange a Franco-Mongol alliance.
- 1325-1355
- Travels of Ibn Battuta, a Muslim traveller from Morocco, across much of the Old World. His Travels would be influential with Europeans starting in the 19th century.
See also
- Silk Road
- List of explorers
- List of Russian explorers
- European exploration of Arabia
- Timeline of European exploration
References
- ^ ANCIENT SILK ROAD TRAVELLERS
- ^ Vera Lucia Bottrel Tostes, Bravos homens de outrora, Camoes - Revista de Latras e Culturas Lusofonas, no. 8, January - March 2000
- ^ Hannard (1991), page 7; Milton, Giles (1999). Nathaniel's Nutmeg. London: Sceptre. pp. 5 and 7. ISBN 978-0-340-69676-7.
- ^ Hannard (1991), page 7
- ^ Ricklefs, M.C. (1993). A History of Modern Indonesia Since c.1300, 2nd Edition. London: MacMillan. pp. 25. ISBN 0-333-57689-6.
Exploration and explorers by nation or region Explorers by country Explorers by type Circumnavigators · Climbers · Desert explorers · Polar explorers · Seafarers · Space travelers · Undersea explorersExploration by region Asia · Central Asia · Africa · Australia · North America · South America · Oceania · Space explorationExploration timelines Categories:- History of Asia
- Explorers of Asia
- Regional timelines
- Exploration of Asia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.