- Nuclear power by country
-
 The Cattenom Nuclear Power Plant in France. France produces around three quarters of its electricity by nuclear power.[1]
The Cattenom Nuclear Power Plant in France. France produces around three quarters of its electricity by nuclear power.[1]
 The Grafenrheinfeld Nuclear Power Plant in Germany. Chancellor Angela Merkel's coalition announced on May 30, 2011, that Germany’s 17 nuclear power stations will be shut down by 2022, in a policy reversal following Japan's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.[2]
The Grafenrheinfeld Nuclear Power Plant in Germany. Chancellor Angela Merkel's coalition announced on May 30, 2011, that Germany’s 17 nuclear power stations will be shut down by 2022, in a policy reversal following Japan's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.[2]
Thirty countries operate nuclear power stations, and there are a considerable number of new reactors being built in China, South Korea, India, Pakistan, and Russia.[3] As of June 2011, Germany and Switzerland are phasing-out nuclear power.[4][5]
As of June 2011, countries such as Australia, Austria, Denmark, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Portugal, Israel, Malaysia, New Zealand, and Norway remain opposed to nuclear power.[4][6]
Contents
Overview
Of the thirty countries which operate nuclear power plants, only France uses them as its primary source of electricity, although many countries have a significant nuclear power generation capacity. Some nations have plans to start a nuclear power program; these include OECD members, such as Poland, and developing countries, such as Bangladesh and Vietnam.[7] China, South Korea and India are pursuing an ambitious expansion of their nuclear power capacities. China is aiming to increase nuclear power generation capacity to 200 GW by 2020. South Korea is constructing seven reactors with combined capacity of 8.6 GW, all of which will be operationalised by 2017. India's Nuclear power expansion program is the third largest in the world next only to China & South Korea. In India, seven reactors with a combined capacity of 5.3 GW are under construction.
Country Megawatt capacity Nuclear share of
electricity production Argentina
Argentina935 7.0%  Armenia
Armenia376 45.0%  Belgium
Belgium5,943 51.7%  Brazil
Brazil1,901 3.0%  Bulgaria
Bulgaria1,906 35.9%  Canada
Canada12,679 14.8%  China
China10,234 1.9%  Czech Republic
Czech Republic3,686 33.8%  Finland
Finland2,721 32.9%  France
France63,236 75.2%  Germany
Germany20,339 26.1%  Hungary
Hungary1,880 43.0%  India
India4,780 2.9%  Japan
Japan47,348 28.9%  Korea, South (ROK)
Korea, South (ROK)18,716 31.1%  Mexico
Mexico1,310 4.8%  Netherlands
Netherlands485 3.7%  Pakistan
Pakistan725 2.7%  Romania
Romania1,310 20.6%  Russia
Russia23,084 17.8%  Slovakia
Slovakia1,760 53.5%  Slovenia
Slovenia
696 37.9% + 8.0%  South Africa
South Africa1,800 4.8%  Spain
Spain7,448 17.5%  Sweden
Sweden9,399 37.4%  Switzerland
Switzerland3,252 39.5%  Taiwan (ROC)
Taiwan (ROC)4,927 20.7%  Ukraine
Ukraine13,168 48.6%  United Kingdom
United Kingdom10,962 17.9%  United States
United States101,229 20.2% World 378,910 14% Nuclear power output in megawatts
Country/region Operable Suspended Decommissioned Shut down Construction Planned Cancelled  United States
United States97,603 3,603 2,340 6,675 3,704  France
France61,443 600 40 2,623 1,600 1,600  Japan
Japan43,692 13  Germany
Germany20,844 4,936 1,358  Russia
Russia19,897 950 248 1,701 2,825 9,850 2,850  South Korea
South Korea18,716 8,600 5,600  Ukraine
Ukraine13,045 1,900 4,750  Canada
Canada12,728 1,364  United Kingdom
United Kingdom10,306 5,452 466 5,232  Sweden
Sweden10,002  Spain
Spain7,085 2,797 480 2,950  Belgium
Belgium5,712  Taiwan
Taiwan4,884  India
India4,780 [9] 4,800 [10]  Czech Republic[11]
Czech Republic[11]3,830 2,000  Bulgaria
Bulgaria2,000  Switzerland
Switzerland2,985 9  Lithuania
Lithuania2,760  Finland
Finland2,520  China
China2,100 3,100  South Africa
South Africa1,840  Hungary
Hungary1,729  Slovakia
Slovakia1,632 840 104 824  Mexico
Mexico1,308  Argentina
Argentina935 692  Pakistan
Pakistan725 300  Brazil
Brazil626 1,229 1,229  Slovenia
Slovenia620  Romania
Romania620 620 620  Netherlands
Netherlands452 55  Armenia
Armenia440 440  Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan135  Cuba
Cuba834  Philippines
Philippines605  Italy
Italy1,423 List of nuclear reactors by country
Only the commercial reactors registered with the International Atomic Energy Agency are listed below. If a country does not appear in this table, it means it has no nuclear power plants and no current plans to build them. Research reactors are not included in the list.
Country Operating Under
constructionPlanned References and notes  Argentina
Argentina2 1 2  Armenia
Armenia1 0 1 Replacement[12]  Bangladesh
Bangladesh0 0 1 [13]  Belarus
Belarus0 0 2  Belgium
Belgium7 0 0  Brazil
Brazil2 1 0 [14]  Bulgaria
Bulgaria2 0 2 Four reactors were shutdown in 2004 and 2007.  Canada
Canada18 2 4  China
China13 27 50 70 GWe by 2020(~5%)[15]  Croatia
Croatia1 0 0 The reactor is in Slovenia, but 50% is owned by Croatia  Czech Republic
Czech Republic6 0 2  Egypt
Egypt0 0 1 Four plants by 2025?[16][17] with help and training from Russia, Korea, US, France, China, and Australia.[18]  Finland
Finland4 1 0 [19]  France
France58 1 1  Germany
Germany17 0 0 Phase-out in place.  Hungary
Hungary4 0 0  India
India20 4 20  Indonesia
Indonesia0 0 2  Iran
Iran0 1 2 The Bushehr reactor has been loaded with fuel, but is not connected to the grid yet.[20]  Japan
Japan55 2 12  Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan0 0 2  Korea, South (ROK)
Korea, South (ROK)21 7 4  Mexico
Mexico2 0 0  Netherlands
Netherlands1 0 0  Pakistan
Pakistan3 1 2  Poland
Poland0 0 6  Romania
Romania2 0 2  Russia
Russia32 10 14  Slovakia
Slovakia4 2 0  Slovenia
Slovenia1 0 0  South Africa
South Africa2 0 3  Spain
Spain8 0 0 Stable[21]  Sweden
Sweden10 0 0  Switzerland
Switzerland5 0 0 Phase-out in place.  Taiwan (ROC)
Taiwan (ROC)6 2 1  Thailand
Thailand0 0 2  Turkey
Turkey0 0 4 To be built by Japan, Russia and South-Korea[22][23]  Ukraine
Ukraine15 0 2 2 new reactors by 2030[24][25]  United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates0 0 4 To be built by 2017 by S. Korean consortium?[26]  United Kingdom
United Kingdom19 0 4  United States
United States104 1 9  Vietnam
Vietnam0 0 4 World 441 60 150 See also
- List of nuclear reactors
- Uranium reserves
- World Nuclear Industry Status Report
- Nuclear energy policy by country
- Nuclear power accidents by country
References
- ^ a b c "World Nuclear Power Reactors & Uranium Requirements". World Nuclear Association. 2010-10-01. http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/reactors.html. Retrieved 2010-10-23.
- ^ Annika Breidthardt (May 30, 2011). "German government wants nuclear exit by 2022 at latest". Reuters. http://uk.reuters.com/article/2011/05/30/us-germany-nuclear-idUKTRE74Q2P120110530.
- ^ Michael Dittmar. Taking stock of nuclear renaissance that never was Sydney Morning Herald, August 18, 2010.
- ^ a b Duroyan Fertl (June 5, 2011). "Germany: Nuclear power to be phased out by 2022". Green Left. http://www.greenleft.org.au/node/47834.
- ^ James Kanter (May 25, 2011). "Switzerland Decides on Nuclear Phase-Out". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2011/05/26/business/global/26nuclear.html?_r=1.
- ^ "Nuclear power: When the steam clears". The Economist. March 24, 2011. http://www.economist.com/node/18441163.
- ^ http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/inf102.html World Nuclear Association - Emerging Nuclear Energy Countries
- ^ a b Nuclear Power Plant Information, International Atomic Energy Agency, URL accessed 12 June 2006
- ^ "India's 20th nuclear power plant goes critical". Hindustan Times. 2010-11-27. http://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/bangalore/India-s-20th-nuclear-power-plant-goes-critical/Article1-631532.aspx. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
- ^ "Status of Projects under construction- NPCIL". NPCIL official website. 2011-07-18. http://www.npcil.nic.in/main/ProjectConstructionStatus.aspx. Retrieved 2011-07-18.
- ^ "CEZ Group Nuclear Power Plants 2009 annual report". Cez.cz. http://www.cez.cz/en/power-plants-and-environment/nuclear-power-plants/annual-report.html. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
- ^ "USA supports new nuclear build in Armenia". World Nuclear News. 2007-11-23. http://www.world-nuclear-news.org/newNuclear/USA_supports_new_nuclear_build_in_Armenia-231107.shtml?jmid=1165903138. Retrieved 2007-11-25.
- ^ "Bangladesh signs up for nuclear power". 2011-05-16. http://www.atimes.com/atimes/South_Asia/MC16Df01.html. Retrieved 2011-07-26.
- ^ Agência Estado (12-09-2008). "Lobão diz que país fará uma usina nuclear por ano em 50 anos" (in Portuguese). G1.globo.com. http://g1.globo.com/Noticias/Economia_Negocios/0,,MUL758157-9356,00-LOBAO+DIZ+QUE+PAIS+FARA+UMA+USINA+NUCLEAR+POR+ANO+EM+ANOS.html. Retrieved 2008-10-15.
- ^ "Nuclear Power in China". World Nuclear Association. September 2008. http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/inf63.html. Retrieved 2008-09-22.
- ^ Egypt To Construct Four Nuclear Power Plants By 2025
- ^ "Egypt to have 4 nuclear power plants by 2025". English.people.com.cn. 2010-07-16. http://english.people.com.cn/90001/90777/90855/7069804.html. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
- ^ "Egypt, Russia - Training Cooperation in Nuclear Power". English.globalarabnetwork.com. 2010-07-09. http://www.english.globalarabnetwork.com/201007096495/Energy/egypt-russia-training-cooperation-in-nuclear-power.html. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
- ^ "Kolme uutta reaktoria, Jees!". Tekniikka ja talous. 2009-10-15. http://www.tekniikkatalous.fi/kommentit/uutiskommentti/article54930.ece. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
- ^ "Fuel loading starts at Bushehr 1". World Nuclear News. 2010-08-23. http://www.world-nuclear-news.org/newsarticle.aspx?id=28276. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ Nuclear power in Spain, World Nuclear Association, URL accessed 13 June 2006
- ^ "Turkey, South Korea eye more business". Hürriyet Daily News. 2010-04-12. http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/n.php?n=turkey-south-korea-eye-more-business-2010-04-12. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ "Turkey, Japan could reach deal on nuclear plant, minister says". Hürriyet Daily News. 2011-02-09. http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/n.php?n=minister-says-turkey-japan-could-reach-deal-on-nuke-plant--2011-02-09. Retrieved 2011-03-03.
- ^ "BBC NEWS | Politics | New nuclear plants get go-ahead". News.bbc.co.uk. Last Updated:. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/7179579.stm. Retrieved 2008-10-15.
- ^ "Nuclear Power in Ukraine". World Nuclear Association. August 2008. http://world-nuclear.org/info/inf46.html. Retrieved 2008-09-22.
- ^ "Saudi readies nuclear energy agreement with France". Af.reuters.com. 2010-07-05. http://af.reuters.com/article/energyOilNews/idAFLDE6641DG20100705?pageNumber=2&virtualBrandChannel=0. Retrieved 2011-03-13.
External links
Nuclear power by country GWe > 10 Canada · China · EU (France · Germany · United Kingdom) · Japan · Russia · South Korea · Ukraine · United States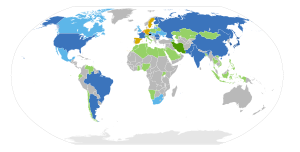
GWe > 2 EU (Belgium · Czech Republic · Finland · Spain · Sweden) · India · Republic of China (Taiwan) · SwitzerlandGWe > 1 GWe < 1 Planned Phasing-out Opposed List of nuclear power stations · Nuclear energy policy · Nuclear energy policy by country · Nuclear technology portal Lists of countries by energy rankings Oil Natural gas Coal Nuclear power Renewable energy Electric energy Total energy Lists by country · List of international rankings · List of top international rankings by country
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


