- Mumps virus
-
Mumps virus 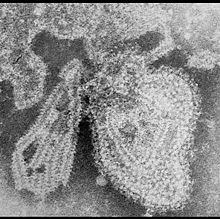
TEM micrograph of the mumps virus. Virus classification Group: Group V ((-)ssRNA) Order: Mononegavirales Family: Paramyxoviridae Genus: Rubulavirus Type species Mumps virus Mumps virus is the causative agent of mumps, a well-known common childhood disease characterised by swelling of the parotid glands and other epithelial tissues, causing high morbidity and in some cases more serious complications such as deafness. Natural infection is currently restricted to humans and the virus is transmitted by direct contact, droplet spread, or contaminated objects.
It is considered a vaccine-preventable disease, although significant outbreaks have occurred in recent years in developed countries such as America, in areas of poor vaccine uptake. These have allowed the further evaluation and ennumeration of its efficacy (~75-85% after two doses of MMR)[1].
Mumps virus belongs to the genus Rubulavirus in the family Paramyxoviridae and is seen to have a roughly spherical, enveloped morphology of about 200 nm in diameter. It contains a linear, single-stranded molecule of negative-sense RNA 15,384 nucleotides long.
Structure
The Mumps virus is a roughly spherical particle made up of concentric layers of fatty lipids, large protein molecules, and nucleic acid. It is dotted with large 'spikes' made up of protein that enable it to gain entry to host cells. Inside lies a core of a single, long molecule of RNA wrapped up in protein that is released into the cell.
Basic Morphology
Electron microscopy (EM) revealed that Mumps virus (MuV), like other members of the Paramyxoviridae, has an enveloped virion of roughly spherical or pleiomorphic (variable) shape. Paramyxovirus particles can have sizes ranging from 120 – 450 nm in diameter.
These particles consist of what is known as a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex: a single-stranded, linear RNA genome coated by nucleocapsid proteins (NP) in association with an RNA polymerase complex of both large (L) and phosphoprotein (P) subunits. It has been estimated that over 2,000 such NP molecules coat the genome along with about 250 P and 25 L molecules.
This RNP structure interacts with the viral envelope via matrix (M) proteins that are evenly distributed around the virion. The envelope, a lipid bilayer derived from the host-cell plasma membrane, harbours multiple copies of a number of glycoproteins required for virus entry and exit: haemagluttin-neuraminidase (HN), fusion (F), and the small hydrophobic (SH) protein.
This molecular assembly of protein, RNA, and lipids allows a single virus to bind to and infect specific cells and replicate itself and finally exit the cell to be transmitted to the next susceptible host.
References
Infectious diseases · Viral systemic diseases (A80–B34, 042–079) Oncovirus Immune disorders Central
nervous systemEncephalitis/
meningitisDNA virus: JCV (Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy)
RNA virus: MeV (Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis) · LCV (Lymphocytic choriomeningitis) · Arbovirus encephalitis · Orthomyxoviridae (probable) (Encephalitis lethargica) · RV (Rabies) · Chandipura virus · Herpesviral meningitis · Ramsay Hunt syndrome type IIEyeCardiovascular Respiratory system/
acute viral nasopharyngitis/
viral pneumoniaDigestive system Urogenital Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
