- Ministry of Petroleum (Iran)
-
Ministry of Petroleum وزارت نفت 
Agency overview Formed March 12, 1951 Jurisdiction Islamic Republic of Iran Headquarters  Tehran, Iran
Tehran, IranMinister responsible Rostam Ghasemi Child agencies *National Iranian Oil Company,
*National Iranian Petrochemical Company,
*National Iranian Gas Company,
*National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution CompanyWebsite Official Website Iran 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
IranConstitution- Constitution (1979)
- Constitution (1906)
LeadershipExecutive- President (List)
- Vice President
- Cabinet
- 90th Government
- Supreme National Security Council
- Secretary
- Supreme Council of the Cultural Revolution
- Chairman
Legislative- Islamic Consultative Assembly
- Speaker
- Expediency Council
- Chairman
- Supreme Audit Court
- City and Village Councils
Judicial- Supreme Court
- Attorney General
- General Inspection Office
- Ministry of Justice
- Human rights
ElectionsPolitical Parties- Political parties in Iran
- Reformists
- Conservatives
Foreign Policy
The Ministry of Petroleum (MoP) manages the oil industry, the producer of oil and petrochemical products. MoP is in charge of all issues pertaining to exploration, extraction, exploitation, distribution and exportation of crude oil and oil products. In addition, according to the "Imports and Exports Regulation Act", issuing import licenses for such products is also among the functions of the Ministry of Petroleum.[1] According to BP, Iran's has 137.6 billion barrels (2.188×1010 m3) of proven oil reserves and 29.61 trillion cubic meters of proven gas reserves. Iran ranks third in the world in oil reserves and second in gas reserves.[2]
According to the Fourth Economic, Social and Cultural Development Plan, the Government has been required to transfer at least 10% of the activities related to the exploration, extraction and production of crude oil to the private sector, while in the meantime retaining its ownership of oil resources. This is also the case in other fields of the Ministry of Petroleum's activities.[1]
Iran plans to invest $500 billion in the oil sector until 2025.[3] As of 2010, $70 billion worth of oil and gas projects are under construction.[4] Iran's annual oil and gas revenues will reach $250 billion by 2015.[4]
Contents
Constitution
The Iranian constitution prohibits the granting of petroleum rights on a concessionary basis or direct equity stake. However, the 1987 Petroleum Law permits the establishment of contracts between the Ministry of Petroleum, state companies and "local and foreign national persons and legal entities." Buyback contracts, for instance, are arrangements in which the contractor funds all investments, receives remuneration from the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) in the form of an allocated production share, then transfers operation of the field to NIOC after a set number of years, at which time the contract is completed.
Since the 1979 revolution in Iran, the country has been under constant US unilateral sanctions. The first U.S. sanctions against Iran were formalized in November 1979, and during the hostage crisis, many sanctions were leveled against the Iranian government. By 1987 the import of Iranian goods into the United States had been banned. In 1995, President of the United States Bill Clinton issued Executive Order 12957,[5] banning U.S. investment in Iran's energy sector, followed a few weeks later by Executive Order 12959 [5] eliminating all trade and investment and virtually all interaction between the United States and Iran.
National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC)
NIOC is in charge of oil and gas exploration and production, refining and oil transportation.
National Iranian Tanker Company (NITC), a subsidiary of NIOC, controls the second largest fleet of tankers in OPEC.[6] Iranian Offshore Engineering and Construction Company (IOEC) is also an important subsidiary of NIOC. It is a joint-venture between NIOC and IDRO.
National Iranian Gas Company
National Iranian Gas Company (NIGC) manages gathering, treatment, processing, transmission, distribution, and exports of gas and gas liquids.
The huge reserves of natural gas put Iran in the second place, in terms of the natural gas reserve quantity, among other countries, only next to the Russian Federation, with an estimate of proven reserve quantity close to 23 bcm.[1] Iran's gas reserves are exploited primarily for domestic use.
National Iranian Petrochemical Company
National Iranian Petrochemical Company (NPC) handles petrochemical production, distribution, and exports. National Iranian Petrochemical Company's output capacity will increase to over 100 million tpa by 2015 from an estimated 50 million tpa in 2010 thus becoming the world' second largest chemical producer globally after Dow Chemical with Iran housing some of the world's largest chemical complexes.[7][8][9]
National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution Company
National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution Company (NIORDC) handles oil refining and transportation, with some overlap to NIOC.
There are eight refineries with a potential capacity of 950,000 barrels per day (151,000 m3/d) and one refinery complex in the country with a total refining capacity of over 15 kbbl/d (2,400 m3/d) (in Tehran, Tabriz, Isfahan, Abadan, Kermanshah, Shiraz, Bandar Abbas, Arak and Lavan Island) and a storage capacity of 8 milliard litre. Abundance of basic material, like natural gas, in the country provide favorable conditions for development and expansion of petrochemical plants.
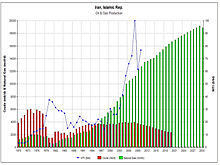
Revenues from crude oil
See also: Iran's foreign reserves, Iranian government's budget, Iranian energy subsidy reforms, and Supreme Audit Court of Iran Iran's oil and gas projected revenues chart by the International Monetary Fund. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015 once the current projects come on stream.[4]
Iran's oil and gas projected revenues chart by the International Monetary Fund. Officials in Iran estimate that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015 once the current projects come on stream.[4]
Iran’s total revenues from the sale of oil amounted to $77 billion in Iranian year 1387 (2008–09).[10] The average sale price of Iran’s crude oil during that year was $100 per barrel.[10] According to the National Iranian Oil Company, Iran’s average daily production of crude oil stood at 4 million barrels (640,000 m3) per day. Of this amount, 55% was exported and the remainder was consumed domestically.[10] As of 2010, oil income accounts for 80% of Iran's foreign currency revenues and 60% of the nation's overall budget.[11] Iran exported over 844 million barrels (134,200,000 m3) of oil in the one year to March 21, 2010, averaging around 2.3 million barrels (370,000 m3) a day. The exports included around 259 million barrels (41,200,000 m3) of light crude and more than 473 million barrels (75,200,000 m3) of heavy crude oil. Japan, China, South Africa, Brazil, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Spain, India and the Netherlands are the main importers of Iran's crude oil.[11] Iran's annual oil and gas revenues are expected to reach $250 billion by 2015.[4]
Reserves and production
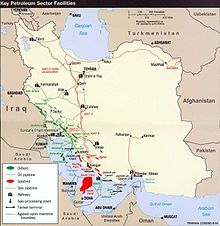 Iran holds 10% of the world's proven oil reserves and 15% of its gas. It is OPEC's second largest exporter and the world's fourth oil producer.
Iran holds 10% of the world's proven oil reserves and 15% of its gas. It is OPEC's second largest exporter and the world's fourth oil producer.
PROVEN OIL RESERVES Country Billions of Barrels Saudi Arabia 262.7 Canada 178.9 Iran 133.3 Iraq 112.5 United Arab Emirates 97.8 Kuwait 96.5 Venezuela 75.6 TOP OIL PRODUCERS Country Millions of Barrels Saudi Arabia 9.5 Russia 9.2 United States 7.6 Iran 4.0 China 3.5 European Union 3.4 Mexico 3.4 See also
- Petroleum industry in Iran
- International Rankings of Iran in Energy
- 2007 Gas Rationing Plan in Iran
- Iranian Economic Reform Plan
- Oil megaprojects
- Energy Superpower
External links
- Official website (MoP)
- SHANA - Official News Service for Oil and Gas in Iran
- National Iranian Oil Company
- Oil & Gas in Iran - Brief study (2003)
- US Department of Energy - Iran's entry
- Oil & Gas Industry Profile for Iran - Australian trade
- Oil & Gas in Iran (Q1 2010 report)
- Ministry of Petroleum Overview
- BBC - Iran in Maps
 Energy in Iran
Energy in IranOil 
Gas National Iranian Gas Company · Persian LNG · Gas reserves · South Pars Gas Field · Gas Exporting Countries ForumGasoline National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution Company · 2007 Gas Rationing Plan in Iran · Fuel smugglingPetrochemicals Pipelines Tabriz–Ankara · Korpezhe–Kurt Kui · Dauletabad–Sarakhs–Khangiran · Iran–Pakistan–India · Neka–Jask · Iran-Armenia · Gas Trunkline · Persian · NabuccoNuclear Wind See also Ministry of Energy · Ministry of Petroleum · Petroleum industry in Iran · Environment · Caspian Sea · Strait of Hormuz · Kharg Island · List of power stations · Reservoirs and dams · Transport · Privatization (MAPNA · AZAR AB · IDRO) · Construction (Khatam al-Anbia · SADRA · ISOICO · DESA - Iran Heavy Diesel Manufacturing Company) · Foreign direct investment · Economy of Iran · Subsidy reform plan · Oil Stabilization Fund · Sanctions against Iran · Energy superpower · Anglo-Persian Oil CompanyReferences
- ^ a b c http://www.irantradelaw.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Irans-Foreign-Trade-Regime-Report.pdf
- ^ http://www.presstv.com/detail/156997.html
- ^ Iran Daily - Domestic Economy - 04/24/08
- ^ a b c d Mehr News Agency: Iran eyes $250 billion annual revenue in 5 years Retrieved December 22, 2010
- ^ a b U.S. Treasury - Sanctions Program Summaries - Iran
- ^ http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/cabs/Iran/Profile.html
- ^ http://www.allbusiness.com/finance-insurance/credit-intermediation-related-activities/4022282-1.html
- ^ http://www.tehrantimes.com/index_View.asp?code=212109
- ^ http://www.sabic.com/corporate/en/newsandmediarelations/speeches/20050330.aspx
- ^ a b c http://www.turquoisepartners.com/iraninvestment/IIM-AprMay09.pdf
- ^ a b http://www.presstv.com/detail.aspx?id=130736§ionid=351020102
Coordinates: 35°42′25.85″N 51°24′41.91″E / 35.7071806°N 51.4116417°E
Categories:- Economy of Iran
- Energy in Iran
- Government ministries of Iran
- Constitution (1979)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.