- Carbon–carbon bond
-
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms.[1] The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is said to be formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp3 hybridized orbitals, but single bonds formed between carbon atoms with other hybridisations do occur (e.g. sp2 to sp2). In fact, the carbon atoms in the single bond need not be of the same hybridisation. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds called alkenes or triple bonds called alkynes. A double bond is formed with an sp2 hybridized orbital and a p-orbital that isn't involved in the hybridization. A triple bond is formed with an sp hybridized orbital and two p-orbitals from each atom. The use of the p-orbitals forms a pi bond.
Carbon has the unique characteristic among all elements to form long chains of its own atoms, a property called catenation. This coupled with the strength of the carbon–carbon bond gives rise to an enormous number of molecular forms, many of which are important structural elements of life, so carbon compounds have their own field of study: organic chemistry.
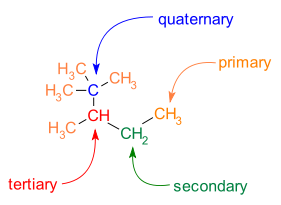
Branching is also common in C−C skeletons. Different carbon atoms can be identified with respect to the number of carbon neighbors:
- primary carbon atom: one carbon neighbor
- secondary carbon atom: two carbon neighbors
- tertiary carbon atom: three carbon neighbors
- quaternary carbon atom: four carbon neighbors
Synthesis
Carbon–carbon bond forming reactions are organic reactions in which a new carbon–carbon bond is formed. They are important in the production of many man-made chemicals such as pharmaceuticals and plastics.
Some examples of reactions which form carbon–carbon bonds are Aldol reactions, Diels–Alder reaction, the addition of a Grignard reagent to a carbonyl group, a Heck reaction, a Michael reaction and a Wittig reaction.
See also
- An extensive list is presented here: list of carbon–carbon bond forming reactions
- The chemistry of carbon bonded to other elements in the periodic table:
CH He CLi CBe CB CC CN CO CF Ne CNa CMg CAl CSi CP CS CCl CAr CK CCa CSc CTi CV CCr CMn CFe CCo CNi CCu CZn CGa CGe CAs CSe CBr CKr CRb CSr CY CZr CNb CMo CTc CRu CRh CPd CAg CCd CIn CSn CSb CTe CI CXe CCs CBa CHf CTa CW CRe COs CIr CPt CAu CHg CTl CPb CBi CPo CAt Rn Fr Ra Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Uut Uuq Uup Uuh Uus Uuo ↓ CLa CCe CPr CNd CPm CSm CEu CGd CTb CDy CHo CEr CTm CYb CLu Ac Th Pa CU Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr Chemical bonds to carbon Core organic chemistry Many uses in chemistry Academic research, but no widespread use Bond unknown / not assessed References
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
Categories:- Organic chemistry
- Chemical bonding
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.