- Cricoid cartilage
-
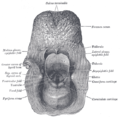
Cricoid cartilage 
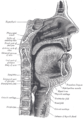
Anterolateral view of head and neck. (Cricoid cartilage labeled at center left.) 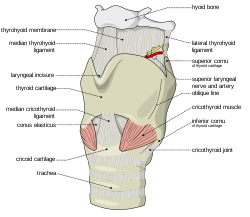
The ligaments of the larynx. Antero-lateral view. (Cricoid cartilage visible near bottom center.) Gray's subject #236 1074 Precursor 4th and 6th branchial arch MeSH Cricoid+Cartilage The cricoid cartilage, or simply cricoid (from the Greek krikoeides meaning "ring-shaped"), is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea.
Contents
Location
The cricoid cartilage sits just inferior to the thyroid cartilage in the neck, and is joined to it medially by the median cricothyroid ligament and postero-laterally by the cricothyroid joints. Inferior to it are the rings of cartilage around the trachea (which are not continuous - rather they are C-shaped with a gap posteriorly). The cricoid is joined to the first tracheal ring by the cricotracheal ligament, and this can be felt as a more yielding area between the firm thyroid cartilage and firmer cricoid.
It is also anatomically related to the thyroid gland; although the thyroid isthmus is inferior to it, the two lobes of the thyroid extend superiorly on each side of the cricoid as far as the thyroid cartilage above it.
The posterior part of the cricoid is slightly broader than the anterior and lateral parts, and is called the lamina, while the anterior part is the band; this may be the reason for the common comparison made between the cricoid and a signet ring.
Function
The function of the cricoid cartilage is to provide attachments for the various muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in speech production.
Composition
It is made of hyaline cartilage, and so can become calcified or even ossified, particularly in old age.
Clinical significance
When intubating a patient under general anesthesia prior to surgery, the anesthesiologist will press on the cricoid cartilage to compress the esophagus behind it so as to prevent gastric reflux from occurring: this is known as the Sellick manoeuvre.
The Sellick maneuver was considered the standard of care during rapid sequence induction for many years.[1] The American Heart Association still advocates the use of cricoid pressure during resuscitation using a BVM, and during emergent oral endotracheal intubation.[2] However, recent research increasingly suggests that cricoid pressure may not be as advantageous as once thought. The initial article by Sellick was based on a small sample size at a time when high tidal volumes, head-down positioning, and barbiturate anesthesia were the rule.[3]
Cricoid pressure may frequently be applied incorrectly.[4][5][6][7][8] Cricoid pressure may frequently displace the esophagus laterally, instead of compressing it as described by Sellick.[9][10] Several studies demonstrate some degree of glottic compression [11][12][13] reduction in tidal volume and increase in peak pressures.[14] Based on the current literature, the widespread recommendation that cricoid pressure be applied during every rapid sequence intubation is quickly falling out of favor.
Gastric reflux could cause aspiration if this is not done considering the general anesthesia can cause relaxation of the gastroesophageal sphincter allowing stomach contents to ascend through the esophagus into the trachea.A medical procedure known as a cricoidectomy can be performed in which part or all of the cricoid cartilage is removed. This is commonly done to relieve blockages within the trachea.[15]
Additional images
See also
- Post-cricoid carcinoma
- Tracheotomy
References
- ^ Salem MR, Sellick BA, Elam JO. The historical background of cricoid pressure in anesthesia and resuscitation. Anesth Analg 1974;53(2):230-232.
- ^ American Heart Association (2006). Textbook of Advanced Cardiac Life Support. Dallas, TX: American Heart Association.
- ^ Maltby, J. M., & Berialt, M. T. (2002). Science, pseudoscience and Sellick. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia, 49(5), 443-447
- ^ Escott MEA, Owen H, Strahan AD, Plummer JL. Cricoid pressure training: how useful are descriptions of force? Anaesth Intensive Care 2003;31:388-391
- ^ Owen H, Follows V, Reynolds KJ, Burgess G, Plummer J. Learning to apply effective cricoid pressure using a part task trainer. Anaesthesia 2002;57(11):1098-1101
- ^ Walton S, Pearce A. Auditing the application of cricoid pressure. Anaesthesia 2000;55:1028-1029
- ^ Koziol CA, Cuddleford JD, Moos DD. Assessing the force generated with the application of cricoid pressure. AORN J 2000;72:1018-1030
- ^ Meek T, Gittins N, Duggan JE. Cricoid pressure: knowledge and performance amongst anaesthetic assistants. Anaesthesia 1999;54(1):59-62.
- ^ Smith, K. J., Dobranowski, J., Yip, G., Dauphin, A., & Choi, P. T. (2003). Cricoid pressure displaces the esophagus: an observational study using magnetic resonance imaging. Anesthesiology, 99(1), 60-64;
- ^ Smith, K. J., Ladak, S., Choi, Pt L., & Dobranowski, J. (2002). The cricoid cartilage and the oesophagus are not aligned in close to half of adult patients. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia, 49(5), 503-507.
- ^ Palmer, JHM, Ball, D.R. The effect of cricoids pressure on the cricoids cartilage and vocal cords: An endoscopic study in anaesthetized patients. Anaesthesia (2000): 55; 260-287
- ^ Hartsilver, E. L., Vanner, R. G. Airway obstruction with cricoids pressure. Anesthesia (2000): 55: 208-211
- ^ Haslam, N., Parker, L., and Duggan, J.E. Effect of cricoid pressure on the view at laryngoscopy. Anesthesia (2005): 60: 41-47
- ^ Hocking, G., Roberts, F.L., Thew, M.E. Airway obstruction with cricoids pressure and lateral tilt. Anesthesia (2001), 56; 825-828
- ^ Michihiko Sonea1; Tsutomu Nakashimaa1; Noriyuki Yanagita (1995) "Laryngotracheal separation under local anaesthesia for intractable salivary aspiration: cricoidectomy with fibrin glue support" The Journal of Laryngology & Otology:Cambridge University Press
External links
- Illustration at nda.ox.ac.uk
- SUNY Figs 32:04-06 - "Skeleton of the larynx."
- lesson11 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (larynxsagsect)
Head and neck anatomy, Upper RT: Larynx (TA A06.2, TH H3.05.01, GA 11.1072) Cartilages major/unpaired: Epiglottis (Vallecula) · Thyroid (Laryngeal prominence, Oblique line, Superior thyroid notch, Superior horn, Inferior horn) · Cricoid
minor/paired: Arytenoid (Vocal process, Muscular process) · Corniculate · CuneiformLigaments/folds extrinsic ligaments: Hyoepiglottic ligament · Thyrohyoid membrane (Lateral ligament, Median ligament) · Thyroepiglottic ligament · Cricotracheal ligament
intrinsic ligaments · upper: Quadrangular membrane (Aryepiglottic, Vestibular ligament/Vestibular fold)
intrinsic ligaments · lower: Cricothyroid ligament (Median, Lateral/Conus elasticus, Vocal ligament/Vocal folds)Laryngeal cavity Other Categories:- Head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.