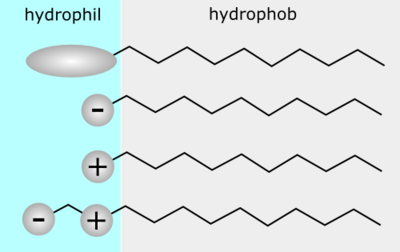
- Classification of surfactants
-
Surfactants are classified according to their chemical structure (head and tail) and their counter ion.
Contents
Classification
According to the composition of their tail
The tail of surfactants can be:
- A hydrocarbon chain: aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes), alkanes (alkyl), alkenes, cycloalkanes, alkyne-based
- An alkyl ether chain:
- Ethoxylated surfactants: polyethylene oxides are inserted to increase the hydrophilic character of a surfactant
- Propoxylated surfactants: polypropylene oxides are inserted to increase the lipophilic character of a surfactant
- A fluorocarbon chain: fluorosurfactants
- A siloxane chain: siloxane surfactants.
A surfactant can have one or two tails, these are called double-chained.
According to the composition of their head
A surfactant can be classified by the presence of formally charged groups in its head. A non-ionic surfactant has no charge groups in its head. The head of an ionic surfactant carries a net charge. If the charge is negative, the surfactant is more specifically called anionic; if the charge is positive, it is called cationic. If a surfactant contains a head with two oppositely charged groups, it is termed zwitterionic.
Some commonly encountered surfactants of each type include:
- Ionic
- Anionic: based on permanent anions (sulfate, sulfonate, phosphate) or pH-dependent anions (carboxylate):
- Sulfates
- Alkyl sulfates: ammonium lauryl sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate (SDS, sodium dodecyl sulfate, another name for the compound)
- Alkyl ether sulfates: sodium laureth sulfate, also known as sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES), sodium myreth sulfate
- Sulfonates:
- Docusates: dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate
- Sulfonate fluorosurfactants: perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS), perfluorobutanesulfonate
- Alkyl benzene sulfonates
- Phosphates:
- Alkyl aryl ether phosphate
- Alkyl ether phosphate
- Carboxylates:
- Alkyl carboxylates: Fatty acid salts (soaps): sodium stearate;
- Sodium lauroyl sarcosinate
- Carboxylate fluorosurfactants: perfluorononanoate, perfluorooctanoate (PFOA or PFO)
- Sulfates
- Anionic: based on permanent anions (sulfate, sulfonate, phosphate) or pH-dependent anions (carboxylate):
-
- Cationic: based on:
- pH-dependent primary, secondary, or tertiary amines: Primary amines become positively charged at pH < 10, secondary amines become charged at pH < 4:
- Permanently charged quaternary ammonium cation:
- Alkyltrimethylammonium salts: cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) a.k.a. hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, cetyl trimethylammonium chloride (CTAC
- Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC)
- Benzalkonium chloride (BAC)
- Benzethonium chloride (BZT)
- 5-Bromo-5-nitro-1,3-dioxane
- Dimethyldioctadecylammonium chloride
- Dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB)
- Cationic: based on:
-
- Zwitterionic (amphoteric): based on primary, secondary, or tertiary amines or quaternary ammonium cation with:
- Sulfonates:
- CHAPS (3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate);
- Sultaines: cocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine;
- Carboxylates:
- Phosphates: lecithin
- Sulfonates:
- Zwitterionic (amphoteric): based on primary, secondary, or tertiary amines or quaternary ammonium cation with:
- Nonionic
- Fatty alcohols:
- Cetyl alcohol
- Stearyl alcohol
- Cetostearyl alcohol (consisting predominantly of cetyl and stearyl alcohols)
- Oleyl alcohol
- Polyoxyethylene glycol alkyl ethers (Brij): CH3–(CH2)10–16–(O-C2H4)1–25–OH:
- Polyoxypropylene glycol alkyl ethers: CH3–(CH2)10–16–(O-C3H6)1–25–O
- Glucoside alkyl ethers: CH3–(CH2)10–16–(O-Glucoside)1–3–OH:
- Polyoxyethylene glycol octylphenol ethers: C8H17–(C6H4)–(O-C2H4)1–25–OH:
- Polyoxyethylene glycol alkylphenol ethers: C9H19–(C6H4)–(O-C2H4)1–25–OH:
- Glycerol alkyl esters:
- Polyoxyethylene glycol sorbitan alkyl esters: Polysorbate
- Sorbitan alkyl esters: Spans
- Cocamide MEA, cocamide DEA
- Dodecyldimethylamine oxide
- Block copolymers of polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol: Poloxamers
- Polyethoxylated tallow amine (POEA).
- Fatty alcohols:
According to the composition of their counter-ion
In the case of ionic surfactants, the counter-ion can be:
- Monoatomic / Inorganic:
- Cations: metals : alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, transition metal
- Anions: halides: chloride (Cl−), bromide (Br−), iodide (I−)
- Polyatomic / Organic:
- Cations: ammonium, pyridinium, triethanolamine (TEA)
- Anions: tosyls, trifluoromethanesulfonates, methylsulfate
Categories:- Surfactants
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.