- Tosyl
-
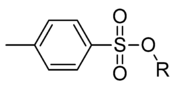
A tosyl group (abbreviated Ts or Tos) is CH3C6H4SO2. This group is usually derived from the compound 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl, which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic or tosylic acid. The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.
Tosylate refers to the anion of p-toluenesulfonic acid (CH3C6H4SO3−) and it is abbreviated as TsO−, or it may refer to esters of p-toluenesulfonic acid.
Applications
For SN2 reactions, alkyl alcohols can also be converted to alkyl tosylates. This is useful because alcohols are poor leaving groups in SN2 reactions, as opposed to the tosylate group which poses as a good leaving group. It is the transformation of alkyl alcohols to alkyl tosylates that allows an SN2 reaction to occur in the presence of a good nucleophile.
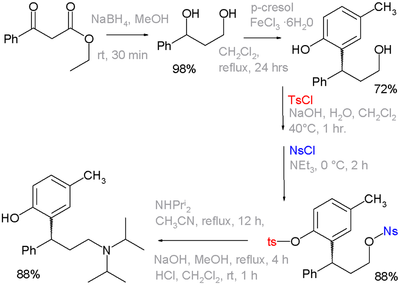
A tosyl group can function as a protecting group in organic synthesis. Alcohols can be converted to tosylate groups so that they do not react. The tosylate group may later be converted back into an alcohol. The use of these functional groups is exemplified in organic synthesis of the drug tolterodine, wherein one of the steps a phenol group is protected as its tosylate and the primary alcohol as its nosylate. The latter is a leaving group for displacement by diisopropylamine [1][2]:
References
- ^ Kathlia A. De Castro, Jungnam Ko, Daejong Park, Sungdae Park, and Hakjune Rhee (2007). "Reduction of Ethyl Benzoylacetate and Selective Protection of 2-(3-Hydroxy-1-phenylpropyl)-4-methylphenol: A New and Facile Synthesis of Tolterodine" (ASAP article). Organic Process Research & Development 11 (5): 918. doi:10.1021/op7001134.
- ^ Reaction sequence: organic reduction of ethyl benzoylacetate by sodium borohydride to a diol, followed by Friedel-Crafts alkylation with p-cresol and iron(III) chloride to a phenol. The eat and nosyl groups are introduced as their respective chlorides with either sodium hydroxide or triethylamine as a base. The next step is nucleophilic displacement of the nosyl group by diisopropylamine, the remaining tosyl group is removed by another round of NaOH. Not shown: optical resolution by L-tartaric acid to optically pure (R)-isomer
See also
- Tosylic acid
- Sulfonyl group
Categories:- Sulfonyl groups
- Leaving groups
- Sulfonate esters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.