- History of Rajasthan
-
The history of human settlement in north Indian state of Rajasthan dates back to about 5000 years ago with parts of North Rajasthan at the heart of the Indus Valley Civilization.This region was long known as Gurjaratra that is country protected or ruled by the Gurjars[1] before it came to be called Rajputana, early in the Muslim period.[2] It is also the famous land of the Rajput warriors renowned for their heroic deeds on the battlefield. The majestic palaces, forts and other architectural edifices of historical significance tell interesting tales of the Rajput rulers who once exercised sovereignty over this northwestern state of India.
Contents
Ancient history
Parts of Rajasthan belonged to the Indus Valley Civilization between about 3500 and 1750 BCE. Excavations at Kalibanga in Northern Rajasthan have revealed the existence of human settlements of the Harappan times on the banks of a river that dried up later, which is believed to be the River Saraswati by some scholars.[3] The historical evidence found in Bairat reflects the presence of Pre-Aryan people. The first Aryan settlement was at the Dhundhar region around 1400 BCE. The foremost inhabitants of this area were the Bhils and the Meenas. They formed small kingdoms that battled with each other. Ancient Hindu scriptural epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata make reference to sites in present-day Rajasthan. According to a popular legend, Rama the seventh avatar or incarnation of Lord Vishnu, aimed an arrow towards the Sea God who inhabited the straits between India and Sri Lanka. However, when the Sea God apologised to Rama for opposing his desire to cross the straits, than Rama fired the arrow to the north-west, rendering the whole region as a desolated wasteland.[4]
Before the reign of the Gurjar and Rajput rulers, Rajasthan was a part of the illustrious Mauryan Empire around 321-184 BCE. It had also been a part of Republics like Arjunyas, Hunas, Kushans, Malavas, Saka Satraps and the Yaudheyas. The Guptas reigned in the 4th century. Some Buddhist caves and Stupas have been found in Jhalawar, in the southern part of Rajasthan.
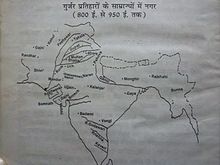
The decline of the 300 year old Gupta Empire in the 5th century led to the political unrest in the Northern India and was followed by an epoch of instability as numerous chieftains tried to gain power. The situation was stabilized when the Gurjara Pratiharas, the earliest of the Gurjar clan emerged around 700 CE.[5] Gurjar pratihars were well known for their hostility towards Arab invaders.The Arab chronicler Sulaiman describes the army of the Gurjar Pratihars as it stood in 851 CE, The king of Gurjars maintains numerous forces and no other Indian prince has so fine a cavalry. He is unfriendly to the Arabs, still he acknowledges that the king of the Arabs is the greatest of kings. Among the princes of India there is no greater foe of the Islamic faith than he. He has got riches, and his camels and horses are numerous.[6]
Around 1000-1200, the Rajputs had internal strife among themselves and were engaged in armed conflicts with each other. A struggle for supremacy took place among the Parmars, Chalukyas, and Chauhans. During the eighth - twelfth centuries, the Rajput clan gained supremacy and altogether the Rajputs were divided into 36 royal clans and 21 dynasties like the Hadas of Jhalwawar, Kota & Bundi, Sisodias of Mewar, the Bhatis of Jaisalmer, the Shekhawats of Shekhawati, the Kachhwahas of Jaipur and the Chauhans of Ajmer, the Rathores of Marwar and Jodhpur.
Rajasthan includes most of Rajputana, comprising a number of Rajput kingdoms as well as Jat kingdoms and a Muslim kingdom. The Jats were rulers in Bharatpur and Dholpur. Tonk was ruled by a Muslim Nawab. Jodhpur, Bikaner, Udaipur, and Jaipur were some of the main Rajput states. Rajput families rose to prominence in the 6th century,[citation needed] establishing kingdoms in Rajputana and across northern India.
Medieval period
 Maharana Pratap, a Rajput ruler and great warrior of his time.Mughal emperor Akbar sent many missions against him. However he survived and ultimately gained control of all areas of Mewar excluding fort of Chittor.
Maharana Pratap, a Rajput ruler and great warrior of his time.Mughal emperor Akbar sent many missions against him. However he survived and ultimately gained control of all areas of Mewar excluding fort of Chittor.
Prithviraj Chauhan fought a brave battle against the foreign invader Muhammad Ghori and defeated him in the first battle of Tarain in 1191 (but was defeated in the Second Battle of Tarain in 1192), but was defeated in the seventeenth battle with Ghori. After getting defeated for sixteen times, Ghori begged for his life saying a sentence with a literal meaning "I am your cow, Forgive". In the seventeenth battle, a traitor from Chauhan's kingdom supported Ghori's army and landed up in the defeat. What happens after this is clear from the local folk songs still prominent in Rajasthan. It is said that Prithviraj was taken to Afghanistan along with his raj-kavi cum friend, Chandbhar. In Ghori's court, Prithviraj and Chandbhar were brought in shackles. Prithviraj was asked to show the art of archery, wherein he could aim and shoot just by hearing the sound. It is also known as Shabdbhedi-baan. Ghori asked him to show him this art. To make game interesting for himself, he got his eyes pierced with hot iron rods. Chandbhar says, "A king, though as a prisoner, can receive command only from a king. So it would be an honour if you command Him to shoot". Then he says few verses or poetry, few of those lines were,"Char baans chobis guz, aangal asht pravan, taa upar sultan hai, mat chooko Chauhan". Chaar baans meant four bamboos stick, chaubis guz as approximately 24 yards, aangal asht praval meant eight fingers width. All this combined gave the exact location of Ghori sitting on his throne i.e. 4 bamboos stick high, 24 yards away and exactly eight fingers up was the Ghori sitting. "Go ahead O Chauhan and don't miss the aim". This is how PrithviRaj kills Ghori in his court and obviously to meet his own death. Grave of PrithviRaj Chauhan is present till date next to Ghori's grave. And after the defeat of Chauhan around 1200, a part of Rajasthan came under Muslim rulers. The principal centers of their powers were Nagaur and Ajmer. Ranthambhor was also under their suzerainty.In the 12th century the Bhatti rajputs of jaselmer so enragged the emperor Alo Din Khilji by looting his rich carvan,so his army attacked the state and captured the fort.At their conqure the rajput women committed the jauhar. At the beginning of the 13th century, the most prominent and powerful state of Rajasthan was Mewar. The Rajputs resisted the Muslim incursions into India, although a number of Rajput kingdoms eventually became subservient to the Delhi Sultanate. Mewar led others in resistance to Muslim rule: Rana Sanga fought the Battle of Khanua against Babur, the founder of the Mughal empire.
In order to gain the trust of the Rajput rulers, the Mughal Emperor Akbar arranged matrimonial alliances. He also sought reconciliation with the hostile Rajputs after performing the matrimonial alliances. He himself married the Rajput princess- Jodha Bai who was the daughter of the Maharaja of Amber. He granted high offices to a large number of Rajput princes and this maintained very cordial relations with these Rajputs. Soon most of the Rajputs were transformed into friends of Akbar from adversaries and many of them surrendered their kingdoms to Akbar. Rulers like Raja Maan Singh of Amber were trusted allies. However all Rajput rulers were not ready to accept Akbar’s dominance and preferred to remain independent. One such ruler was Raja Uday Singh of Mewar, who founded the city of Udaipur. He never accepted Akbar’s supremacy and was at constant war with him. Akbar forcefully seized Chittor, his capital. After his death, this struggle was continued by his son – Rana Pratap. He fought a terrible battle with Akbar at the Haldighati pass where he was defeated and wounded. Since then Rana Pratap remained in recluse for 12 years and attacked the Mughal ruler from time to time. He fought valiantly throughout his life never ceded his independence to the Mughal ruler.
The traditional sacrifice and the self-respect of the Rajput women are also worth mentioning while discussing the imperial rule of Rajasthan during the medieval epoch. When the Rajput rulers were forced to surrender their kingdoms to other invaders, the Rajput women in order to protect their chastity and self-respect used to light up a pyre and together they used to jump into the fire thus sacrificing and ending their own lives. This custom of collective sacrifice was known as Jauhar.
Rajasthan's formerly independent kingdoms created a rich architectural and cultural heritage, seen today in their numerous forts and palaces (Mahals and Havelis) which are enriched by features of Muslim and Jain architecture.
Modern period
Rajasthan had never been united politically until its domination by Mughal Emperor Akbar. Akbar created a unified province of Rajasthan. Mughal power started to decline after 1707. The political disintegration of Rajasthan was caused by the dismemberment of the Mughal Empire. The Marathas penetrated Rajasthan upon the decline of the Mughal Empire. In 1755 the Maratha general Scindia occupied Ajmer. The beginning of the 19th Century was marked by the onslaught of the Pindaris.
 Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II,
Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II,
inspecting Jaipur State forces deployed in the Middle East during World War II.The Rajput kings concluded treaties with the British in the early 19th century, accepting British sovereignty in return for local autonomy and protection from the Marathas. Following the Mughal tradition and more importantly due to its strategic location Ajmer became a province of British India, while the autonomous Rajput states, the Muslim state (Tonk), and the Jat states (Bharatpur and Dholpur) were organized into the Rajputana Agency. In 1817-18, the British Government concluded treaties of alliance with almost all the states of Rajputana. Thus began the British rule over Rajasthan, then called Rajputana.
Post independence
At the time of India's Independence in 1947, Rajasthan consisted of 19 Princely States, two chieftains and a British administered province of Ajmer-Merwara besides a few pockets and territories outside its main boundaries.
It took seven stages to form Rajasthan as defined today. In March 1948 the Matsya Union consisted of Alwar, Bharatpur, Dhaulpur and Karauli was formed. Also, in March 1948 Banswara, Bundi, Dungarpur, Jhalawar, Kishangarh, Kota, Pratapgarh, Shahpura and Tonk joined the Indian union and formed a part of Rajasthan. In April 1948 Udaipur joined the state and the Maharana of Udaipur was made Rajpramukh. Therefore in 1948 the merger of south and southeastern states was almost complete. Still retaining their independence from India were Jaipur and the desert kingdoms of Bikaner, Jodhpur and Jaisalmer. From a security point of view, it was vital to the new Indian Union to ensure that the desert kingdoms were integrated into the new nation. The princes finally agreed to sign the Instrument of Accession, and the kingdoms of Bikaner, Jodhpur, Jaisalmer and Jaipur were merged in March 1949. This time the Maharaja of Jaipur, Man Singh II was made the Rajpramukh of the state and Jaipur became its capital. Later in 1949, the United States of Matsya, comprising the former kingdoms of Bharatpur, Alwar, Karauli and Dholpur, was incorporated into Rajasthan. On January 26, 1950, 18 states of united Rajasthan merged with Sirohi to join the state leaving Abu and Dilwara to remain a part of Greater Bombay and now Gujarat.
In November 1956 under the State Re-organisation Act, 1956 the erstwhile part 'C' State of Ajmer, Abu Road Taluka, former part of princely State Sirohi (which were merged in former Bombay), State and Sunel Tappa region of the former Madhya Bharat merged with Rajasthan and Sirohi sub district of Jhalawar was transferred to Madhya Pradesh. Thus giving the existing boundary Rajasthan. Today with further reorganisation of the states of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Bihar. Rajasthan has become the largest state of the Indian Republic.
The princes of the former kingdoms were constitutionally granted handsome remuneration in the form of privy purses and privileges to assist them in the discharge of their financial obligations. In 1970, Indira Gandhi, who was then the Prime Minister of India, commenced under-takings to discontinue the privy purses, which were abolished in 1971. Many of the former princes still continue to use the title of Maharaja but the title has little else power other than status symbol. Many of the Maharajas still hold their palaces and have converted them into profitable hotel while some have made good in politics. The democratically elected Government runs the state with a Chief Minister as its executive head and the Governor as the head of the state. Currently, including the new district of Pratapgarh, there are 32 districts, 105 sub-divisions, 37889 villages, 241 tehsils and 222 towns in Rajasthan.
Gurumukh Nihal Singh was appointed as first governor of Rajasthan.Hiralal Shastri was first nominated cheifminister who worked from 7th April 1949,after two more nominated chiefminiters Tikaram Paliwal became first elected cheifminister from 03-03-1951.
See also
- Gurjar
- Rajput
- Rajput clans
References
- ^ Kumar Suresh Singh; Rajendra Behari Lal, Anthropological Survey of India (2003). Gujarat, Part 1. Popular Prakashan. ISBN 978-81-7991-104-4. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=d8yFaNRcYcsC&pg=PR17&dq.
- ^ R.C. Majumdar (1994). Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass Publ.. p. 263. ISBN 8120804368, ISBN 9788120804364. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=XNxiN5tzKOgC&pg=PA263&dq.
- ^ "Pune archaeologists hope the Saraswati will unlock mysteries of the past". rediff.com. http://www.rediff.com/news/1998/apr/29rigved.htm. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
- ^ "Thar Desert in Rajasthan". rajasthanunlimited.com. http://www.rajasthanunlimited.com/thar. Retrieved 2007-08-27.
- ^ Krishna Chandra Sagar (1992). Foreign influence on ancient India. Northern Book Centre. ISBN 8172110286, ISBN 9788172110284. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=0UA4rkm9MgkC&pg=PA254&dq.
- ^ Radhey Shyam Chaurasia (2002). History of Ancient India: Earliest Times to 1000 A. D.. Atlantic Publishers & Distributors. p. 207. ISBN 81-269-0027-X,ISBN 978-81-269-0027-5. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=cWmsQQ2smXIC&pg=PA207&dq. "The king of Gurjars maintain numerous faces and no other Indian prince has so fine a cavalry .He has"
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Further reading
- Tod, James. Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan: or, The Central and Western Rajpoot States of India Asian Educational Services, 2001. ISBN 8120612892
History of India States Andhra Pradesh · Arunachal Pradesh · Assam · Bihar · Chhattisgarh · Goa · Gujarat · Haryana · Himachal Pradesh · Jammu and Kashmir · Jharkhand · Karnataka · Kerala · Madhya Pradesh · Maharashtra · Manipur · Meghalaya · Mizoram · Nagaland · Orissa · Punjab · Rajasthan · Sikkim · Tamil Nadu · Tripura · Uttar Pradesh · Uttarakhand · West BengalNCT Territories Andaman and Nicobar Islands · Chandigarh · Dadra and Nagar Haveli · Daman and Diu · Lakshadweep · PuducherryCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.