- Articulatory phonetics
-
Manners of articulation Obstruent Plosive (occlusive) Affricate Fricative Sibilant Sonorant Nasal Flap/Tap Approximant Liquid Vowel Semivowel Lateral Trill Airstreams Pulmonic Ejective Implosive Click Alliteration Assonance Consonance See also: Place of articulation This page contains phonetic information in IPA, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help] Places of
articulation
LabialBilabial Labial–velar Labial–coronal Labiodental Dentolabial
Bidental
CoronalLinguolabial Interdental Dental Denti-alveolar Alveolar Postalveolar Palato-alveolar Alveolo-palatal Retroflex
DorsalPalatal Labial–palatal Velar Uvular Uvular–epiglottal
RadicalPharyngeal Epiglotto-pharyngeal Epiglottal
GlottalTongue shape
ApicalLaminal Subapical
LateralSulcal
PalatalPharyngeal
See also: Manner of articulationThis page contains phonetic information in IPA, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help]
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics. In studying articulation, phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures.
Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound.[1]
Contents
Overview
The vocal tract can viewed through an aerodynamic-biomechanic model that includes three main components:
- air cavities
- pistons
- air valves
Air cavities are containers of air molecules of specific volumes and masses. The main air cavities present in the articulatory system are the supraglottal cavity and the subglottal cavity. They are so-named because the glottis, the openable space between the vocal folds internal to the larynx, separates the two cavities. The supraglottal cavity or the orinasal cavity is divided into an oral subcavity (the cavity from the glottis to the lips excluding the nasal cavity) and a nasal subcavity (the cavity from the velopharyngeal port, which can be closed by raising the velum to the nostrils). The subglottal cavity consists of the trachea and the lungs. The atmosphere external to the articulatory stem may also be consisted an air cavity whose potential connecting points with respect to the body are the nostrils and the lips.
Pistons are initiators. The term initiator refers to the fact that they are used to initiate a change in the volumes of air cavities, and, by Boyle's Law, the corresponding air pressure of the cavity. The term initiation refers to the change. Since changes in air pressures between connected cavities lead to airflow between the cavities, initiation is also referred to as an airstream mechanism. The three pistons present in the articulatory system are the larynx, the tongue body, and the physiological structures used to manipulate lung volume (in particular, the floor and the walls of the chest). The lung pistons are used to initiate a pulmonic airstream (found in all human languages). The larynx is used to initiate the glottalic airstream mechanism by changing the volume of the supraglottal and subglottal cavities via vertical movement of the larynx (with a closed glottis). Ejectives and implosives are made with this airstream mechanism. The tongue body creates a velaric airsteam by changing the pressure within in the oral cavity: the tongue body changes the mouth subcavity. Click consonants use the velaric airstream mechanism. Pistons are controlled by various muscles.
Valves regulate airflow between cavities. Airflow occurs when an air valve is open and there is a pressure difference between in the connecting cavities. When an air valve is closed, there is no airflow. The air valves are the vocal folds (the glottis), which regulate between the supraglottal and subglottal cavities, the velopharyngeal port, which regulates between the oral and nasal cavities, the tongue, which regulates between the oral cavity and the atmosphere, and the lips, which also regulate between the oral cavity and the atmosphere. Like the pistons, the air valves are also controlled by various muscles.
Initiation
To produce any kind of sound their must movement of air. To produce sounds that people today can interpret as words, the movement of air must pass though the vocal chords, up through the throat and, into the mouth or nose to then leave the body. What forms the different sounds and allows people to create different words is though the different position's of the mouth (or as linguists call it "the oral cavity". This is to distinguish it from the nasal cavity)
The Two Classes of Sounds
Sounds of all languages fall under two categories: Consonants and Vowels.
Consonants
Consonants are produced with some form of restriction or closing in the vocal tract that hinders the air flow from the lungs. consonants are classified according to where in the vocal tract the airflow has been restricted. This is also known as places of articulation.
Places of articulation
Movement of the tongue and lips can create these constrictions and by forming the oral cavity in different ways, different sounds can be produced.
Bilabial
when producing a [b], [p] or [m] articulation is done by bringing both lips together.
Labiodental
[f] and [v] are also used with the lips. They however are also articulated by touching the bottom lip to the upper teeth.
Interdental
[θ] and [ð] these sounds are both spelled as "th". they are pronounced by inserting the tip of the tongue between the teeth. (θ as in think) (ð as in thy)
Alveolar
[t][d][n][s][z][l][r] these seven sounds are produced in many ways where the tongue is raised towards the alveolar ridge.
Palatal
[ʃ][ʒ][ʧ][ʤ][j] with these sounds the constriction occurs by raising the front part of the tongue to the palate.
Velar
[k][g][ŋ] with these sounds, the constriction occurs by raising the back part of the tongue to the soft palate or the velum. they are generally the final or initial sounds of words. for example: bac[k] or ba[g].
Glottal
[h][ʔ] the sound [h] is from the flow of air coming from an open glottis, past the tongue and lips as they prepare to pronounce a vowel sound, which always follows [h]. if the air is stopped completely at the glottis by tightly closed vocal chords the sound upon release of the chords is called a glottal stop [ʔ].
Uvulars
[ʀ][q][ԍ] these sounds are produced by raising the back of the tongue to the uvula. The the 'r' in french is often a uvular trill (symbolized by [ʀ]). the uvular sounds [q] and [ԍ] occur in Arabic. these do not normally occur in English.
Vowels
Airflow
For all practical purposes, temperature can be treated as constant in the articulatory system. Thus, Boyle's Law can usefully be written as the following two equations.
What the above equations express is that given an initial pressure P1 and volume V1 at time 1 the product of these two values will be equal to the product of the pressure P2 and volume V2 at a later time 2. This means that if there is an increase in the volume of cavity, there will be a corresponding decrease in pressure of that same cavity, and vice versa. In other words, volume and pressure are inversely proportional (or negatively correlated) to each other. As applied to a description of the subglottal cavity, when the lung pistons contract the lungs, the volume of the subglottal cavity decreases while the subglottal air pressure increases. Conversely, if the lungs are expanded, the pressure decreases.
A situation can be considered where (1) the vocal fold valve is closed separating the supraglottal cavity from the subglottal cavity, (2) the mouth is open and, therefore, supraglottal air pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure, and (3) the lungs are contracted resulting in a subglottal pressure that has increased to a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. If the vocal fold valve is subsequently opened, the previously two separate cavities become one unified cavity although the cavities will still be aerodynamically isolated because the glottic valve between them is relatively small and constrictive. Pascal's Law states that the pressure within a system must be equal throughout the system. When the subglottal pressure is greater than supraglottal pressure, there is a pressure inequality in the unified cavity. Since pressure is a force applied to a surface area by definition and a force is the product of mass and acceleration according to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the pressure inequality will be resolved by having part of the mass in air molecules found in the subglottal cavity move to the supraglottal cavity. This movement of mass is airflow. The airflow will continue until a pressure equilibrium is reached. Similarly, in an ejective consonant with a glottalic airstream mechanism, the lips or the tongue (i.e., the buccal or lingual valve) are initially closed and the closed glottis (the laryngeal piston) is raised decreasing the oral cavity volume behind the valve closure and increasing the pressure compared to the volume and pressure at a resting state. When the closed valve is opened, airflow will result from the cavity behind the initial closure outward until intraoral pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. That is, air will flow from a cavity of higher pressure to a cavity of lower pressure until the equilibrium point; the pressure as potential energy is, thus, converted into airflow as kinetic energy.
Sound sources
Sound sources refer to the conversion of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. There are two main types of sound sources in the articulatory system: periodic (or more precisely semi-periodic) and aperiodic. A periodic sound source is vocal fold vibration produced at the glottis found in vowels and voiced consonants. A less common periodic sound source is the vibration of an oral articulator like the tongue found in alveolar trills. Aperiodic sound sources are the turbulent noise of fricative consonants and the short-noise burst of plosive releases produced in the oral cavity.
Periodic sources
- Non-vocal fold vibration: 20-40 cycles per second
- Vocal fold vibration
- Lower limit: 70-80 modal (bass), 30-40 creaky
- Upper limit: 1170 (soprano)
Vocal fold vibration
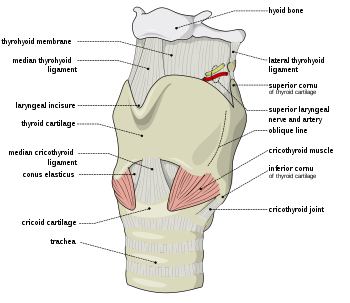
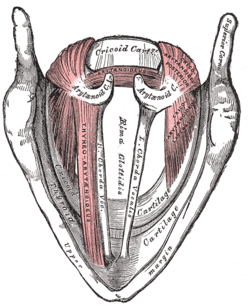
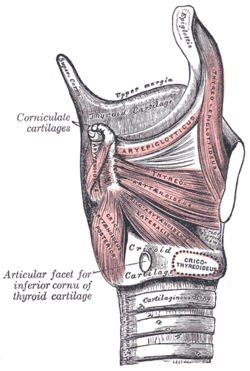
- larynx:
- cricoid cartilage
- thyroid cartilage
- arytenoid cartilage
- interarytenoid muscles (fold adduction)
- posterior cricoarytenoid muscle (fold abduction)
- lateral cricoarytenoid muscle (fold shortening/stiffening)
- thyroarytenoid muscle (medial compression/fold stiffening, internal to folds)
- cricothyroid muscle (fold lengthening)
- hyoid bone
- sternothyroid muscle (lowers thyroid)
- sternohyoid muscle (lowers hyoid)
- stylohyoid muscle (raises hyoid)
- digastric muscle (raises hyoid)
Control of fundamental frequency
Experimental techniques
Articulation visualized by Real-time MRI
- Plethysmography
- Electromyography
- Photoglottography
- Electrolaryngography
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Radiography
- Medical ultrasonography
- Electromagnetic articulography
- Aerometry
- Endoscopy
- Videokymography
Palatography
In order to understand how sounds are made, experimental procedures are often adopted. Palatography is one of the oldest instrumental phonetic techniques used to record data regarding articulators.[4] In traditional, static palatography, a speaker's palate is coated with a dark powder. The speaker then produces a word, usually with a single consonant. The tongue wipes away some of the powder at the place of articulation. The experimenter can then use a mirror to photograph the entire upper surface of the speaker's mouth. This photograph, in which the place of articulation can be seen as the area where the powder has been removed, is called a palatogram.[5]
Technology has since made possible electropalatography (or EPG). In order to collect EPG data, the speaker is fitted with a special prosthetic palate, which contains a number of electrodes. The way in which the electrodes are "contacted" by the tongue during speech provides phoneticians with important information, such as how much of the palate is contacted in different speech sounds, or which regions of the palate are contacted, or what the duration of the contact is.
See also
- list of phonetics topics
- manner of articulation
- place of articulation
- vowel
- consonant
- International Phonetic Alphabet
References
- ^ Note that although sound is just air pressure variations, the variations must be at a high enough rate to be perceived as sound. If the variation is too slow, it will be inaudible.
- ^ Stated in a less abbreviatory fashion: pressure1 * volume1 = pressure2 * volume2
- ^ volume1 divided by sum of volume1 and change in volume = sum of pressure1 and the change in pressure divided by pressure1
- ^ Ladefoged, Peter: A Course In Phonetics: Third Edition, page 60. Harcourt Brace College Publishers, 1993
- ^ Palatography
- Bickford, Anita (2006). Articulatory Phonetics: Tools For Analyzing The World's Languages (4th ed.). Summer Institute of Linguistics. ISBN 1-55671-165-4.
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.