- Zazaki language
-
Zazaki Spoken in Turkey Region Main in Tunceli, Bingol, Erzincan, Sivas, Elazig, Malatya Gümüşhane Province, Şanlıurfa Province, and Adıyaman Province, diasporic in Mutki, Sarız, Aksaray, and Taraz Ethnicity Zaza Native speakers About 1.5–2.5 million [1][2] in Turkey, unknown numbers elsewhere (date missing) Language family Indo-European- Indo-Iranian
- Iranian languages
- Western
- Northwestern
- Zaza-Gorani
- Zazaki
- Zaza-Gorani
- Northwestern
- Western
- Iranian languages
Writing system Latin Language codes ISO 639-2 zza ISO 639-3 variously:
zza – Zazaki (generic)
diq – Dimli (Southern Zazaki)
kiu – Kirmanjki (Northern Zazaki)Linguasphere 58-AAA-ba 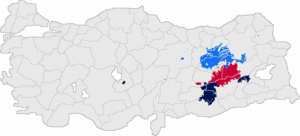
Zazaki (or Kirmanjki, Kirdki, Dimilki) is an Indo-European language spoken primarily in eastern Turkey. According to Ethnologue, the language is a part of the northwestern group of the Iranian section of the Indo-European family.[3] Zazaki shares many features, structures, and vocabulary with Gorani, Talyshi and other Caspian languages, and Kurdish languages.[4][5] According to Ethnologue (which cites [Paul 1998][5]), the number of speakers is between 1.5 and 2.5 million (including all dialects). According to Nevins, the number of Zazaki speakers is between 2 and 4 million.[6]
Contents
Zaza dialects
There are three main Zaza dialects:
- Northern Zazaki[7]: It is spoken in Tunceli, Erzincan, Erzurum, Sivas, Gumushane, Mus (Varto), Kayseri (Sariz) provinces.
Its sub-dialects are:
-
- West-Dersim
- East-Dersim
- Varto
- Border dialects like Sarız, Koçgiri (Giniyan-idiom)
- Central Zazaki[citation needed]: It is spoken in Elazığ, Bingöl, Solhan, Girvas and Diyarbakır provinces.[citation needed]
Its sub-dialects are:
-
- Bingol[citation needed]
- Palu[citation needed]
- Border dialects like Hani, Kulp, Lice, Ergani, Piran[citation needed]
- Southern Zazaki[8]: It is spoken Şanlıurfa (Siverek), Diyarbakır (Cermik, Egil), Adiyaman, Malatya provinces.
Its sub-dialects are:
-
- Siverek
- Cermik, Gerger
- Border dialects like Mutki and Aksaray
Zaza literature and broadcast programs
The first written statements in Zaza were compiled by the linguist Peter Lerch in 1850. Two other important documents are the religious writings of Ehmedê Xasi of 1899,[9] and of Usman Efendiyo Babıc (published in Damascus in 1933); both of these works were written in the Arabic alphabet.
The use of the Latin alphabet to write Zazaki became popular only in the diaspora in Sweden, France and Germany at the beginning of the 1980s. This was followed by the publication of magazines and books in Turkey, particularly in Istanbul. The efforts of Zaza intellectuals to advance the comprehensibility of their native language by alphabetizing were not fruitless; the number of publications in Zaza has multiplied. This rediscovery of the native culture by Zaza intellectuals not only caused a renaissance of Zaza language and culture, it also triggered feelings among younger generations of Zazas (who, however, rarely speak Zazaki as a mother tongue) in favor of this modern Western use of Zazaki, rekindling their interest in their ancestral language.
The diaspora has also generated a limited amount of Zaza-language broadcasting. Moreover, after restrictions were removed on local languages in Turkey during their move toward accession to the European Union, Turkish state-owned TRT television launched a Zazaki TV program and a radio program on Fridays.
Phonological Correspondences of Zazaki and other Iranian Languages
Initial /v/
Proto-Iranian initial *w (from Proto-Indo-European *w) changes to /b/ or /g/ in Persian and Kurmanci by the 10th century. Zazaki, like many Northwestern Iranian languages, has /v/.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English *w v v b / g b / g - *weh1-nt- vātā- vā bād bā wind *awer- vār- vārān bārān bārān rain *wekʷ- vāč vāc āvāz bēj sing, say *weg'h vazaiti vāz- bez- bez- run *wek- vāč vang bang bang, dang voice *wadh- vad veyv bayo buk bride, wedding *weren- – varek barre barx sheep *w̯ep vefr- vawr, vor barf befr snow *wen- veēn- vēn, vīn bīn- bīn- see *wīk'm̥tī vīsaitī vīst bist bist twenty *widhewo vīthava vīyā bīve bī widow *wei- vaeiti viyāl bid bi willow *wes- vāstra vāš giyāh giyā grass *wrdho- vard- vil gul gul flower *wl̥kʷo- vēhrke- varg gorg gurg wolf avaz: The word "avaz" in Persian is a borrowing from a Northwestern Iranian language, probably the Parthian language. Otherwise, it should have been preserved as "b".
/z/ and /s/
Proto-Iranian *z and *s (from Proto-Indo-European *kʲ and *gʲ) turn to /d/ and /h/ Persian. However, Zazaki and Kurmanci keep /z/ and /s/.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Kurmanci Persian English *k/*g z/s z/s z/s d/h - *k'erd- zerdeye- zerri dil dil heart *g'hol- zaranya- zerd zêr zar gold *g'no- zan- zan- zan- dān- know *g'eme zamat- zama zava dāmād groom *eg'om ezēm ez ez (min) ed- (man) I *bhrg'h berezant berz bilind boland borough, high *dek'm̥ dasa des deh dah ten zer: The Old Persian word for "gold" was "daraniya-". It changes back to a "z" sound. It is a borrowing most likely from the Parthian Language
ed-: The Modern Persian word for "I" is "man", which replaces Old Persian word "edēm"
ez: In southern Kurdish dialect of Sorani, the word for "I" is "men", like in Persian. It replaced the word "ez".
dıl, deh, bilind: These Kurdish words should be Persian borrowings./ĵ/
Proto-Iranian *j and *ĵ (from Proto-Indo-European *gʷ and *kʷ) are /ĵ/ (written as "c" in Zazaki-Latin alphabet) in Zazaki. In Kurmanci they change to /ž/ and in Persian to /z/.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English *gw / *kw j / č ĵ z ž - *gwen- jainiš ĵeni zan žın woman *gwhen- jan ĵin- zan- žen- playing music, to beat *gwiwo- jiv ĵiwiyayıš zīstan žıyan live *gwiwo- jiv ĵinde zende zındi (loan) alive *sekw-uper hača-upairi ĵor zabar- (bala) žor up *sekw-ndhero- hača-athara ĵêr zīr žêr down *sekw- hača- ĵi az/ze ži from *leuk- reočah - roĵ rūz rož day *wekw- vač- vaĵ āvāz bêž say, sing *pekw- pač- pewĵ- paz- pêž cook Kurdish words zindi and erzan should be borrowings from Persian.
Note: In some southern Zazaki dialects, /-ĵ/ endings like roc, vac, vic, and pewc become /z/ or /ž/. This is mostly a deaffrication of the affricate in intervocalic position.Initial /b/
Proto-Iranian *dw turns to /b/ in Zazaki. Persian and Kurmanci have /d/.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English d d b d d - *dhwer- dvara ber dar deri door Initial /hr/
Proto-Iranian *θr (from Proto-Indo-European *tr) changes to /hr/ in Zazaki and to /s/ in Persian (†ç in Old Persian) and Kurmanji.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English tr θr hr s s - *trejes θri hri se se (loan)[10] three *trikomt θrisaiti hris si si (loan)[10] thirty /rz/ and /rr/
Proto-Iranian *rd and *rz are /rr/ and /rd/ in Zazaki. They change to /l/ in Persian and in Kurmanci.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English *rg,*lg / *rd rz / rd rz / rr l l - *bhrg'h berezant berz boland bilind borough, high – herez- erz hil- hel sprinkle, throw – – wurz liz alez dash off, stand up, fly *spleg'h- spērēzan serpez seporz sıpıl spleen – sered-, yare serre sāl sal year *k'e'rd'- ze'rd'- zerre dil dil heart *w'rd'ho- ve'rd'- vıl gul gul rose seporz: In Persian, seporz is probably a borrowing from a Northwestern Iranian language.
vıl: In Zazaki, the "l" ending in the word "vıl" should have been "rr". This word should be a borrowing from a Northwestern Iranian languages given that it has an initial "v".Initial /w/
Proto-Indo-European *sw turns to *hw in Proto-Iranian. Zazaki drops *h in some words, and *w in others. In Persian and Kurmanci *h turns to /x/, however, Persian drops *w while Kurdish keeps it. Proto-Iranian *hw turns to /xv/ in Avestan.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English *sw xv w x(u) x(w) - *'sw'ep- xvefne- witiš xwāb xew sleep – xveš- weš xoš xweš sweet *'sw'enh- xven- wend- xānd- xwend- read *'sw'esor xveher wa xāhar xweh sister – xver- werd- xord- xward- swallow, eat - Zazaki words xo and gun should be borrowings from other Iranian Languages.
/m/
Zazaki and Persian keep Proto-Indo-European *m while Kurmanci turns it to /v/.
Indo-European Avestan Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English *m m m m v - *h1nomn̥ nama name nām nav name *sem- hama- āmnān (hāmīn) hāvīn summer *samos- hama- embaz hambaz heval same - The Persian form hāmīn is from Middle Persian.
/wt/
The Proto-Indo-European cluster *pt turns to *ft in Proto-Iranian. In Zazaki this turns to /wt/. The outcome in Kurmanci is most commonly /t/, /wt/, and /ft/ in some dialects. Persian also retains the original Proto-Iranian /ft/.
Zazaki Persian Kurmanci English w f f - hawt haft haft seven kawt kaft kaft get in Note: In Bingol dialect of Zazaki, /ew/ further turns to /o/ sound, like hewt to hot, kewt to kot, grewt to grot, kew to ko, and vewr to wor.
Alphabet
The Zaza alphabet contains 31 letters [11]:
A, B, C, Ç, D, E, Ê, F, G, H, I, Î, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, Ş, T, U, Û, V, W, X, Y, Z
a, b, c, ç, d, e, ê, f, g, h, i, î, j, k, l, m, n, o, p, q, r, s, ş, t, u, û, v, w, x, y, z
A(a): The "A" in Bar
B(be): The "B" in Ball or Book
C(ce): Before "A", "E", "I", "O" or "U", the "Ds" in Lids, before "Ê", "İ", or "Ü" the "J" in Job
Ç(Çe): Before "A", "E", "I", "O" or "U", the "Ts" in Fits, before "Ê", "İ", or "Ü" the "Ch" in Check
D(de): The "D" Door or Desk
E(e): The "A" in Accept and "e" in Test
Ê(Ê): the "e" in Hell or "Ai" in Air
F(fe): The "F" in Far
G(ge): The "G" in Grass
H(he): The "H" in Hot
I(i): The "I" in Fin
Î(î): The "Ee" in Flee and Seek
J(je): The "s" in Pleasure or Persian
K(ke): The "C" in Cop or "K" in Kangaroo
L(le): The "L" in Love
M(me): The "M" in Men
N(ne): The "N" in Never
O(o): The "O" in Old or Fort
P(pe): The "P" in Police
Q(qe): The "Q" in Iraq
R(re): The "R" in the Spanish Rapido
S(se): The "S" in Star
Ş(Şe): The "Sh" in Shoes
T(te): The "T" in Tower
U(u): The "U" in the German in Gut
Û(Û): The "OO" in the English Cool
V(ve): The "V" in Vehicle or Valve
W(we): The "W" in Water or Wood
X(xe): The "Ch" in the Scots Loch.
Y(ye): The "Y" in Yes
Z(ze): The "Z" in Zero
Grammar
Grammatical gender
The Zazaki language distinguishes between masculine and feminine grammatical gender. Each noun belongs to one of those two genders. In order to correctly decline any noun and any modifier or other type of word affecting that noun, one must identify whether the noun is feminine or masculine. This distinguishes Zazaki from many other Western Iranian languages that have lost this feature over time.
For example, the masculine preterite participle of the verb kerdene ("to make" or "to do") is kerde; the feminine preterite-participle is kerdiye. Both have the sense of the English "made" or "done". The grammatical gender of the preterite-participle would be determined by the grammatical gender of the noun representing the thing that was made or done.
The linguistic notion of grammatical gender is distinguished from the biological and social notion of gender, although they interact closely in many languages. Both grammatical and natural gender can have linguistic effects in a given language.
Vocabulary
Words in Zazaki can be divided into five groups in respect to their origins. Most words in Zazaki are Proto-Indo-European, Proto-Indo-Iranian and Proto-Iranian in origin. The fourth group consists of words that developed when Zazaki speakers divided from the Proto-Iranian language. The fifth group consists of loan words. Loan words in Zazaki are chiefly from Arabic and Persian.
Classification
Zazaki is an Iranian language in the Indo-European family. From the point of view of the spoken language, its closest relatives are Mazandarani, Hewrami, Gilaki and other Caspian languages. However, the classification of Zazaki has been an issue of political discussion. There are many Zazaki-speakers who identify themselves as ethnic Kurds while others do not.[12]
Ethnologue favors the following hierarchy:[3]
- Northwestern Iranian languages
- Zaza-Gorani language group
- Dimli/Zazaki
- Gorani language
- other sublanguages/dialects of Zazaki-Gorani group
- Caspian Languages group
- Mazandarani
- Gilaki
- others
- Zaza-Gorani language group
The US State Department "Background Note" lists the Zazaki language as one of the major languages of Turkey, along with Turkish (official), Kurdish, Armenian, Greek, and Arabic.[13] Linguists connect the word Dimli with the Daylamites in the Alborz Mountains near the shores of Caspian Sea in Iran and believe that the Zaza have immigrated from Deylaman towards the west. Zazaki shows many connections to the Iranian dialects of the Caspian region, especially the Gilaki language.
The Zazaki language shows similarities with (Hewrami or Gorani), Shabaki and Bajelani. Gorani, Bajelani, and Shabaki languages are spoken around Iran-Iraq border; however, it is believed that they are also immigrated from Northern Iran to their present homelands. These languages are sometimes put together in the Zaza-Gorani language group.
See also
- Iranian Languages vocabulary comparison table
- Zaza people
References
- ^ http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=diq
- ^ http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=kiu
- ^ a b Ethnologue on Dimili
- ^ http://books.google.de/books?id=LuVSkpVuAkAC&pg=PA385&dq=zazaki+paul+ludwig&hl=de&ei=SJ5NTs-oKcvG8QOagL26Bw&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=2&ved=0CDUQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=zazaki%20paul%20ludwig&f=false
- ^ a b The Position of Zazaki Among West Iranian languages by Paul Ludwig
- ^ http://www.fas.harvard.edu/~lingdept/IndexicalityWorkshop/anandnevins04.pdf
- ^ Ethnologue on Kirmanjki
- ^ Ethnolgue on Dimili
- ^ Xasi, Ehmedê (1899) Mewlude nebi, reprinted in 1994 in Istambul OCLC 68619349, (Poems about the birth of Mohammed and songs praising Allah.)
- ^ a b Numerical system of Balochi and Kurdish
- ^ Zazaki alphabet
- ^ http://www.jamestown.org/programs/gta/single/?tx_ttnews[tt_news]=34423&tx_ttnews[backPid]=458&no_cache=1
- ^ The US State Department "Background Note" on Turkey
Notes
- Zazaki.net- Zazas and Zazaki
- Blau, Gurani et Zaza in R. Schmitt, ed., Compendium Linguarum Iranicarum, Wiesbaden, 1989, ISBN 3-88226-413-6, pp. 336–40 (About Daylamite origin of Zaza-Guranis)
- Mesut Keskin, Zur dialektalen Gliederung des Zazaki. Magisterarbeit, Frankfurt 2008. (PDF)
Literature
- Paul, Ludwig. (1998) "The Position of Zazaki Among West Iranian languages" University of Hamburg.
- Lynn Todd, Terry. (1985) "A Grammar of Dimili" University of Michigan.
- Gippert, Jost. (1996) "Historical Development of Zazaki" University of Frankfurt.
- Gajewski, Jon. (2003) "Evidentiality in Zazaki" Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Gajewski, Jon. (2004) "Zazaki Notes" Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Larson, Richard. and Yamakido, Hiroko. (2006) "Zazaki as Double Case-Marking" Stony Brook University and University of Arizona.
- Iremet, Faruk. (1996) "The difference between Zaza, Kurdish and Turkish" Stockholm, Sweden.
- Brigitte Werner. (2007) "Features of Bilingualism in the Zaza Community" Marburg, Germany.
- Mesut Keskin, Zur dialektalen Gliederung des Zazaki. Magisterarbeit, Frankfurt 2008. (PDF)
External links
- Genetic Study on Zaza & Kurmanji Kurds (the two groups are similar genetically & not related to Northern-Iranian Groups)
- Zazaki (In Zazaki, German, Turkish and English)
- Dimli (on the Ethnologue site)
- Kirmanjki (on the Ethnologue site)
- Academic Research Center of Zazaki (several languages, including English)
- ZazaPress (In Zazaki, Turkish, English and Swedish)
- Iremet Publishing (In Zazaki, Turkish and Swedish)
- Zazaki Language Institute (In German, Zazaki, and Turkish)
- Ethnic Differentiation among the Kurds: Kurmancî, Kizilbash and Zaza
- MIT OpenCourseWare online course in Zazaki
- A Zazaki Radio: Miraz FM
- Web Center of Zaza People (Weblinks of Zaza people)
- With An Eye and an Ear Towards Zazaki (23-min film, produced/directed by Gulcem Aktas and Andrew Nevins
- A web Portal on Zazaki
- Website of Zazaki Institute Frankfurt
Iranian languages Old EasternWesternMedian · Old PersianMiddle EasternWesternModern EasternWesternOld Azari · Balochi · Bashkardi · Central Iran dialects · Dari (Zoroastrian) · Taleshi · Gilaki · Mazandarani · Kurdic (Kurmanji · Laki · Sorani · Southern Kurdish · ) · Luri · Bakhtiari Lori · Sangsari · Persian (Dari · Tajik · Hazaragi) · Tat · Tati · Zaza · Dialects of FarsItalics indicate extinct languagesCategories:- Language articles with undated speaker data
- Northwestern Iranian languages
- Languages of Turkey
- Zazas
- Indo-Iranian
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
