- Chromosome abnormality
-
A chromosome anomaly, abnormality or aberration reflects an atypical number of chromosomes or a structural abnormality in one or more chromosomes. A Karyotype refers to a full set of chromosomes from an individual which can be compared to a "normal" Karyotype for the species via genetic testing. A chromosome anomaly may be detected or confirmed in this manner. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. There are many types of chromosome anomalies. They can be organized into two basic groups, numerical and structural anomalies.
Contents
Numerical Disorders
This is called Aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes), and occurs when an individual is missing either a chromosome from a pair (monosomy) or has more than two chromosomes of a pair (Trisomy, Tetrasomy, etc.).
In humans an example of a condition caused by a numerical anomaly is Down Syndrome, also known as Trisomy 21 (an individual with Down Syndrome has three copies of chromosome 21, rather than two). Turner Syndrome is an example of a monosomy where the individual is born with only one sex chromosome, an X.
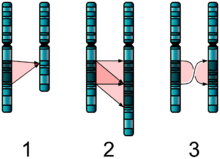
Structural abnormalities
When the chromosome's structure is altered. This can take several forms:
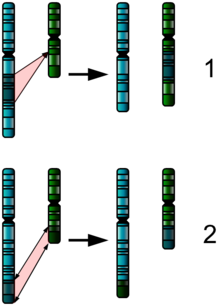
- Deletions: A portion of the chromosome is missing or deleted. Known disorders in humans include Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome, which is caused by partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4; and Jacobsen syndrome, also called the terminal 11q deletion disorder.
- Duplications: A portion of the chromosome is duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material. Known human disorders include Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A which may be caused by duplication of the gene encoding peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP22) on chromosome 17.
- Translocations: When a portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome. There are two main types of translocations. In a reciprocal translocation, segments from two different chromosomes have been exchanged. In a Robertsonian translocation, an entire chromosome has attached to another at the Centromere - in humans these only occur with chromosomes 13, 14, 15, 21 and 22.
- Inversions: A portion of the chromosome has broken off, turned upside down and reattached, therefore the genetic material is inverted.
- Rings: A portion of a chromosome has broken off and formed a circle or ring. This can happen with or without loss of genetic material.
- Isochromosome: Formed by the mirror image copy of a chromosome segment including the centromere.
Chromosome instability syndromes are a group of disorders characterized by chromosomal instability and breakage. They often lead to an increased tendency to develop certain types of malignancies.
Inheritance
Most chromosome abnormalities occur as an accident in the egg or sperm, and are therefore initially not inherited. Therefore, the anomaly is present in every cell of the body. Some anomalies, however, can happen after conception, resulting in Mosaicism (where some cells have the anomaly and some do not). Chromosome anomalies can be inherited from a parent or be "de novo". This is why chromosome studies are often performed on parents when a child is found to have an anomaly.
References
- NHGRI. 2006. Chromosome Abnormalities
External links
Categories:- Chromosomal abnormalities
- Chromosomes
- Cytogenetics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.