- Köpenick
-
Köpenick Quarter of Berlin Town hall on Dahme river 
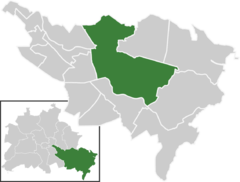
Coordinates 52°26′45″N 13°34′38″E / 52.44583°N 13.57722°ECoordinates: 52°26′45″N 13°34′38″E / 52.44583°N 13.57722°E Administration Country Germany State Berlin City Berlin Borough Treptow-Köpenick Quarter subdivisions 8 zones Basic statistics Area 34.9 km2 (13.5 sq mi) Elevation 34 - 115 m Population 59,201 (30 June 2008) - Density 1,696 /km2 (4,393 /sq mi) Founded 1209 Other information Time zone CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) Licence plate B Postal codes (nr. 0910) 12459, 12555, 12557, 12559, 12587 Website Official website Köpenick is a historic town and locality (Ortsteil) that is situated at the confluence of the rivers Dahme and Spree in the south-east of the German capital city of Berlin. It was formerly known as Copanic and then Cöpenick, only officially adopting the current spelling in 1931. It is known for the famous imposter Hauptmann von Köpenick.
Prior to its incorporation into Berlin in 1920, Köpenick was an independent town. It then became a borough of Berlin, with an area of 128 km2 (49 sq mi), making it Berlin's largest borough. In Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, the borough of Köpenick was merged with that of Treptow to create the current borough of Treptow-Köpenick.
Contents
Geography
Overview
A large percentage of Köpenick's area is covered with forests and water, most notably the Müggelsee lake. The historic town lies in the centre of the Berlin Urstromtal glacial valley at the confluence of the rivers Dahme and Spree. Shortly before its conflux with the Spree, the Schlossinsel lies on the Dahme, a small island with Köpenick Castle.
The Spree connects Köpenick with the Müggelsee and the Berlin city centre. The Oder-Spree Canal links the Dahme, at nearby Schmöckwitz, with the Oder river, at Eisenhüttenstadt, thus providing a navigable connection between Köpenick and the Oder.
Köpenick is sometimes called the "green lungs" of Berlin (Grüne Lunge Berlins). The Müggelberge hills in the south-east of Köpenick reach 115 m (377 ft), making them the highest natural point of Berlin.
Subdivision
Köpenick is divided into 8 zones:
- Altstadt
- Kietzer Vorstadt
- Dammvorstadt
- Köpenick-Nord
- Siedlung Dammfeld
- Elsengrund
- Uhlenhorst
- Wolfsgarten
- Amtsfeld-Kämmereiheide
- Salvador-Allende-Viertel
- Köllnische Vorstadt
- Spindlersfeld
- Wendenschloß
- Siedlung Kietzer Feld
Panorama
History
Statue of "Captain" Wilhelm Voigt
Köpenick had a long history as an independent town. Its first known mentioning as a stronghold dates back to a 1209 deed issued by Margrave Conrad II of Lusatia, then under the name Copanic (from Old Slavic: Kopanica). It is therefore considered "older" than Berlin-Cölln, which was first mentioned in a 1237 deed. For the most part of Köpenick's history, the town was known as Cöpenick.
The former Slavic castle from about 800 was conquered by the Ascanian margraves John I and Otto III of Brandenburg in 1245, defeating their rivals Margrave Henry III of Meissen and the Archbishop of Magdeburg territory.
In 1631, during the Thirty Years' War, the emissaries of George William, Elector of Brandenburg met at Köpenick - then some distance outside Berlin - with the approaching army of Gustav Adolph, King of Sweden, in a vain effort to stop the ongoing devastation of Brandenburg.
In 1906, a shoemaker called Wilhelm Voigt masqueraded as a Prussian officer and took over the town hall of Köpenick. Carl Zuckmayer perpetuated the incident in his play The Captain of Köpenick, the model for several Der Hauptmann von Köpenick films and television shows.
Under the terms of the Greater Berlin Act of 1920, Köpenick became a borough of Berlin, with an area of 128 km2 (49 sq mi), making it Berlin's largest borough. Besides the locality of Köpenick, the former borough included the localities of Oberschöneweide, Grünau, Schmöckwitz, Müggelheim, Rahnsdorf and Friedrichshagen. In 1931, the current name was officially adopted.
During the Cold War, Köpenick was part of East Berlin. In Berlin's 2001 administrative reform, the borough of Köpenick was merged with that of Treptow to create the current borough of Treptow-Köpenick.
Until 2002 a large radio facility for MW and FM was located near the Uhlenhorst neighbourhood, including a 248 m (814 ft) self-radiating radio mast, which was insulated against earth. The FM services of this facility were moved to the Fernsehturm at Alexanderplatz and the AM transmitters were moved to a new aerial mast at Zehlendorf bei Oranienburg.
Köpenick Castle
Main article: Köpenick CastleThe castle (Schloss Köpenick) was originally built in 1558 as a hunting lodge by order of Elector Joachim II Hector of Brandenburg. The building in a Renaissance style was located on the river island at the site of the former medieval fort. Joachim II died here in 1571. In 1631 it served as the headquarters of King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, where he - without results - asked his brother-in-law Elector George William for assistance in the Thirty Years' War.
Frederick I of Prussia had the lodge rebuilt and enlarged from 1677 and lived here together with his first wife Elizabeth Henrietta of Hesse-Kassel. In 1730 Frederick II of Prussia, then Crown Prince, and his friend Hans Hermann von Katte faced the court-martial for desertion at Schloss Köpenick. Today the castle surrounded by a small park serves as a museum of decorative art, run by the Berlin State Museums.
Transportation
Both the rivers Dahme and Spree are navigable. The Spree connects Köpenick with the Havel and hence the waterway systems of western and central Germany. The Dahme links with the Oder-Spree Canal at nearby Schmöckwitz, thus providing a navigable connection to Eisenhüttenstadt, the Oder river and Poland.[1]
Köpenick is served by Köpenick, Wuhlheide and Hirschgarten stations on the S3 line of the Berlin S-Bahn network, and by the Spindlersfeld terminus of S47 line. Köpenick is also a node on the Berlin tram network, with routes 27, 60, 61, 62, 63, 67 and 68 passing through the locality.[2]
Sport
The Stadion An der Alten Försterei is home of the 1. FC Union Berlin football club.
The Mellowpark, the biggest outdoor skatepark in Europe.
References
- ^ Sheffield, Barry (1995). Inland Waterways of Germany. St Ives: Imray Laurie Norie & Wilson. ISBN 0-85288-283-1.
- ^ Liniennetzplan der Straßenbahn "Liniennetzplan der Straßenbahn". BVG. http://www.bvg.de/index.php/de/binaries/asset/download/21111/file/1-1 Liniennetzplan der Straßenbahn. Retrieved 2010-05-11.
External links
 Media related to Köpenick at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Köpenick at Wikimedia Commons- (German) Köpenick official site
- (German) Köpenick page on www.berlin.de
Districts and localities of Berlin  Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf
Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg
Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg LichtenbergAlt-Hohenschönhausen • Falkenberg • Fennpfuhl • Friedrichsfelde • Karlshorst • Lichtenberg • Malchow • Neu-Hohenschönhausen • Rummelsburg • Wartenberg
LichtenbergAlt-Hohenschönhausen • Falkenberg • Fennpfuhl • Friedrichsfelde • Karlshorst • Lichtenberg • Malchow • Neu-Hohenschönhausen • Rummelsburg • Wartenberg Marzahn-Hellersdorf
Marzahn-Hellersdorf Mitte
Mitte Neukölln
Neukölln PankowBlankenburg • Blankenfelde • Buch • Französisch Buchholz • Heinersdorf • Karow • Niederschönhausen • Pankow • Prenzlauer Berg • Rosenthal • Stadtrandsiedlung Malchow • Weißensee • Wilhelmsruh
PankowBlankenburg • Blankenfelde • Buch • Französisch Buchholz • Heinersdorf • Karow • Niederschönhausen • Pankow • Prenzlauer Berg • Rosenthal • Stadtrandsiedlung Malchow • Weißensee • Wilhelmsruh ReinickendorfFrohnau • Heiligensee • Hermsdorf • Konradshöhe • Lübars • Märkisches Viertel • Reinickendorf • Tegel • Waidmannslust • Wittenau
ReinickendorfFrohnau • Heiligensee • Hermsdorf • Konradshöhe • Lübars • Märkisches Viertel • Reinickendorf • Tegel • Waidmannslust • Wittenau SpandauFalkenhagener Feld • Gatow • Hakenfelde • Haselhorst • Kladow • Siemensstadt • Spandau • Staaken • Wilhelmstadt
SpandauFalkenhagener Feld • Gatow • Hakenfelde • Haselhorst • Kladow • Siemensstadt • Spandau • Staaken • Wilhelmstadt Steglitz-Zehlendorf
Steglitz-Zehlendorf Tempelhof-Schöneberg
Tempelhof-Schöneberg Treptow-KöpenickAdlershof • Alt-Treptow • Altglienicke • Baumschulenweg • Bohnsdorf • Friedrichshagen • Grünau • Johannisthal • Köpenick • Müggelheim • Niederschöneweide • Oberschöneweide • Plänterwald • Rahnsdorf • SchmöckwitzDistricts > Localities > Zones • Greater Berlin Act • Former boroughs
Treptow-KöpenickAdlershof • Alt-Treptow • Altglienicke • Baumschulenweg • Bohnsdorf • Friedrichshagen • Grünau • Johannisthal • Köpenick • Müggelheim • Niederschöneweide • Oberschöneweide • Plänterwald • Rahnsdorf • SchmöckwitzDistricts > Localities > Zones • Greater Berlin Act • Former boroughsWest boroughs
(1920–2000)Charlottenburg • Kreuzberg • Neukölln • Reinickendorf • Schöneberg • Spandau • Steglitz • Tempelhof • Tiergarten • Wedding • Wilmersdorf • Zehlendorf
East boroughs
(1920–2000)Friedrichshain • Hellersdorf (1986) • Hohenschönhausen (1985) • Köpenick • Lichtenberg • Marzahn (1979) • Mitte • Pankow • Prenzlauer Berg • Treptow • WeissenseeCategories:- Populated places established in 1209
- Localities of Berlin
- Treptow-Köpenick
- Former boroughs of Berlin
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.