- Archbishopric of Magdeburg
-
Archbishopric of Magdeburg
Erzbistum MagdeburgState of the Holy Roman Empire ← 
1180–1680  →
→Coat of arms
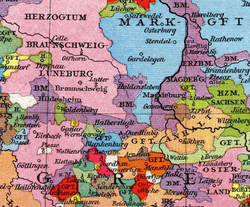
Prince-Bishoprics of Hildesheim, Halberstadt
and Magdeburg (violet), about 1250Capital Magdeburg
Halle (from 1503)Government Theocracy Historical era Middle Ages - Archbishopric founded
by Emp. Otto I
968- Conquered Jüterbog 1157 - Gained immediacy at
breakup of Saxony
1180- Subdued Halle 1478 - Lower Saxon Circle 1500 - Albert of Brandenburg
elected archbishop1513 - Secularization 1680 The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese and Prince-Bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 955 and established in 968, the archbishopric began to be ruled by administrators, some of whom were Lutheran, in 1545. The archbishopric was inherited by Brandenburg-Prussia in 1680 and, after being secularised, replaced with the Duchy of Magdeburg.
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Magdeburg is the modern diocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic church located in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.
Contents
History
After the wars of the years 940 and 954, when the Polabian Slavs, as far as the Oder, the Magyars had come far into Germany, that Augsburg was in danger. At the Battle of Lechfeld in 955 they were defeated and repelled. Immediately in 955 Otto the Great set to work to establish an archbishopric in Magdeburg, for the stabilisation through Christianisation of the eastern territories. He wished to transfer the capital of the diocese from Halberstadt to Magdeburg, and make it an archdiocese. But this was strenuously opposed by the Archbishop of Mainz, who was the metropolitan of Halberstadt. When, in 962, Pope John XII sanctioned the establishment of an archbishopric, Otto seemed to have abandoned his plan of a transfer. The estates belonging to the convents mentioned above (founded in 937) were converted into a mensa for the new archbishopric, and the monks transferred to the Berge Convent. The archiepiscopal church made St. Maurice its patron, and in addition received new donations and grants from Otto.
Its ecclesiastical province included the existing dioceses of Brandenburg and Havelberg and the newly founded dioceses of Merseburg, Zeitz, and Meißen. Lebus was added in 1424. The new archdiocese was close to the unsecured border regions of the Holy Roman Empire and Slavic tribes, and was meant to promote Christianity among the many Slavs and others. Then, on 20 April 967, the archbishopric was solemnly established at the Synod of Ravenna in the presence of the pope and the emperor. The first archbishop was Adelbert, a former monk of St. Maximin's at Trier, afterwards missionary bishop to the Russians, and Abbot of Weissenburg in Alsace. He was elected in the autumn of 968, received the pallium at Rome, and at the end of the year was solemnly enthroned in Magdeburg.
The Diocese of Magdeburg itself was small; it comprised the Slavonic districts of Serimunt, Nudizi, Neletici, Nizizi, and half of northern Thuringia, which Halberstadt resigned. The cathedral school especially gained in importance under Adalbert's efficient administration. The scholastic Othrich was considered the most learned man of his times. Many eminent men were educated at Magdeburg.
Othrich was chosen archbishop after Adalbert's death (981). Gisiler of Merseburg by bribery and fraud obtained possession of the See of Magdeburg, and also succeeded temporarily in grasping the Bishopric of Merseburg (until 1004). Among successors worthy of mention are the zealous Gero (1012–23); Werner (1063–78), who was killed in battle with Henry IV; St. Norbert, prominent in the 12th century (1126–34), the founder of the Premonstratensian order.
Archbishop Wichmann (1152–92) was more important as a sovereign and prince of the Holy Roman Empire than as a bishop; Albrecht II (1205–32) quarrelled with Otto II, Margrave of Brandenburg (1198–1215), because he had pronounced the pope's ban against the latter and this war greatly damaged the archbishopric. In 1208 he began to build the present Cathedral of Magdeburg, which was only consecrated in 1263, and never entirely finished; Günther I (1277–79) hardly escaped a serious war with the Margrave Otto IV, who was incensed because his brother Eric of Brandenburg had not been elected archbishop. The Brandenburgers succeeded in forcing Günther and Bernhard (1279–1281) to resign and in making Eric archbishop (1283–1295).
Cardinal Albert of Brandenburg (1513–45), on account of his insecure position, as well as being crippled by a perpetual lack of funds, gave some occasion for the spread of Lutheranism in his diocese, although himself opposing the Protestant Reformation. It is not true that he became a Lutheran and wished to retain his see as a secular principality, and just as untrue that in the Kalbe Parliament in 1541 he consented to the introduction of the Reformation in order to have his debts paid. His successors were the zealous Catholics John Albert of Brandenburg-Ansbach (1545–1550), who however could accomplish very little, and Frederick IV of Brandenburg, who died in 1552.
Administrators who were secular princes now took the place of the archbishop, and they, as well as the majority of the cathedral chapter and the inhabitants of the diocese, were usually Protestant. They belonged to the House of Brandenburg. Christian William was taken prisoner in 1631, and went over to the Catholic Church in Vienna. At the time of the Peace of Prague (1635), the Archbishopric of Magdeburg fell to August, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels. In the Treaty of Westphalia (1648), the expectancy to the archbishopric was promised to Brandenburg-Prussia upon the death of August. When the Saxon prince died in 1680, the archbishopric was secularised by Brandenburg and replaced with the Duchy of Magdeburg.
The remaining Catholic parishes and abbeys in the area of the former archdiocese were put under supervision of the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1648. In 1821, the area was transferred to the Diocese of Paderborn. In 1994, the Diocese of Magdeburg was founded in the area.
Archbishops and administrators
Archbishops of Magdeburg
- Adalbert 968–981
- Giselmar 981–1004
- Tagino 1004–1012
- Waltaro 1012
- Gero 1012–1023
- Humfrid 1023–1051
- Engelhard 1052–1063
- Werner of Steutzlingen 1064–1078
- Hartwig of Spanheim 1079–1102
- Henry I of Assel 1102–1107
- Adalgod of Osterberg 1107–1119
- Rudigar of Baltheim 1119–1125
- Norbert of Xanten 1126–1134
- Conrad I of Querfurt 1134–1142
- Frederick of Wettin 1142–1152
- Wichmann von Seeburg 1152–1180; prince-archbishop to 1192; Bishop of Naumburg, 1150–54
1180: Gained Imperial immediacy on breakup of duchy of Saxony
Prince-archbishops of Magdeburg
- Wichmann von Seeburg 1180–1192; archbishop from 1152
- Ludolf of Koppenstedt 1192–1205
- Albert I of Käfernburg 1205–1232
- Burkhard I of Woldenberg 1232–1235
- Wilbrand of Kasernberg 1235–1254
- Rudolf of Dinselstadt 1254–1260
- Rupert of Mansfeld 1260–1266
- Conrad II of Sternberg 1266–1277
- Günther I of Schwarzenberg 1277–1279
- Bernhard of Wolpe 1279–1282
- Eric of Brandenburg 1282–1295
- Burkhard II of Blankenburg 1295–1305
- Henry III, Prince of Anhalt-Aschersleben 1305–1307
- Burkhard III of Mansfeld-Schrapglau 1307–1325
- Heideke of Erssa 1326–1327
- Otto of Hesse 1327–1361
- Dietrich Kagelwit 1361–1367
- Albert II of Sternberg 1367–1372
- Peter Gelvto 1372–1381
- Ludwig of Meissen 1381–1382
- Frederick II of Hoym 1382
- Albert III of Querfurt 1382–1403
- Günther II of Schwarzburg 1403–1445
- Frederick III of Beichlingen 1445–1464
- John II of Palatinate-Simmern 1464–1475
- Ernst of Saxony 1475–1480; prince-archbishop to 1513
1480: Bishopric of Halberstadt administered by archbishops of Magdeburg
Prince-archbishops of Magdeburg, administrators of Halberstadt
- Ernst of Saxony 1480–1513; prince-archbishop from 1475
- Albert IV of Brandenburg 1513–1545; also archbishop-elector of Mainz from 1514–54
- John Albert of Brandenburg-Ansbach 1545–1551
- Frederick IV of Brandenburg 1551–1552; Frederick III as administrator of Halberstadt
1552: Archdiocese ruled by Lutheran administrators
Administrators of Magdeburg
- Sigismund of Brandenburg 1552–1566; also titled prince-archbishop
- Joachim Frederick of Brandenburg 1566–1598
- Christian Wilhelm of Brandenburg 1598–1631
- Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria, Catholic administrator, 1631–1638; also prince-bishop of Passau (1625–62), Strasbourg (1626–62), Halberstadt (1628–48), Olmütz (1632–62) and Breslau (1656–62) and de jure prince-archbishop of Bremen (1635–45)
- Augustus, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels, Count of Barby, 1638–1680
1680: Archbishopric secularised to duchy
Ecclesiastical Province of Magdeburg
The archbishop of Magdeburg was the metropolitan of the Ecclesiastical Province of Magdeburg (de facto dissolved in 1648), with the archbishops also holding – besides the archbishop-elector of Mainz – the honary title Primas Germaniae. The suffragans of Magdeburg were:
- Diocese of Brandenburg, Lutheran since 1539, the pertaining prince-bishopric secularised and merged into the Electorate of Brandenburg in 1571.
- Diocese of Havelberg, Lutheran since 1558, the pertaining prince-bishopric secularised and merged into the Electorate of Brandenburg in 1598.
- Diocese of Lebus since 1424 (before suffragan to Gniezno), Lutheran since 1555, pertaining temporalities (County of Beeskow) secularised and merged into the Electorate of Brandenburg in 1598.
- Diocese of Merseburg, Lutheran since 1544, the pertaining prince-bishopric secularised and merged into the Electorate of Saxony in 1565
- Diocese of Naumburg, Lutheran between 1542 and 1547 and from 1562 on, the pertaining prince-bishopric secularised and merged into the Electorate of Saxony in 1615
See also
References
 "Magdeburg". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.
"Magdeburg". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Magdeburg". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Magdeburg". Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company. Lower Saxon Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman Empire
Lower Saxon Circle (1500–1806) of the Holy Roman EmpireEcclesiastical 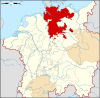
Secular Bremen (from 1648) · Brunswick (Blankenburg (until 1731) · Calenberg2 · Grubenhagen (until 1596) · Wolfenbüttel) · Hanover (from 1708) · Holstein (Glückstadt · Gottorp) · Lüneburg2 · Mecklenburg (Güstrow (until 1695) · Schwerin · Strelitz (from 1701)) · Rantzau (until 1734) · Regenstein · Saxe-Lauenburg2Cities 1 until 1648. 2 until 1705.Categories:- Former theocracies
- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1180
- States and territories disestablished in 1680
- Archbishops of Magdeburg
- Magdeburg
- Prince-Bishops of Germany
- History of Saxony-Anhalt
- 968 establishments
- 1680 disestablishments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.