- Mersalyl acid
-
Mersalyl acid 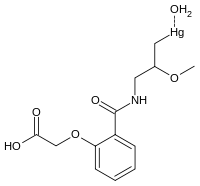
Identifiers CAS number 486-67-9 
PubChem 443130 ChemSpider 11337655 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201330 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O[Hg]CC(OC)CNC(=O)c1ccccc1OCC(O)=O
- InChI=1S/C13H16NO5.Hg.H2O/c1-9(18-2)7-14-13(17)10-5-3-4-6-11(10)19-8-12(15)16;;/h3-6,9H,1,7-8H2,2H3,(H,14,17)(H,15,16);;1H2/q;+1;/p-1

Key: HQRSUIDICNOLPX-UHFFFAOYSA-M
InChI=1/C13H16NO5.Hg.H2O/c1-9(18-2)7-14-13(17)10-5-3-4-6-11(10)19-8-12(15)16;;/h3-6,9H,1,7-8H2,2H3,(H,14,17)(H,15,16);;1H2/q;+1;/p-1/rC13H17HgNO6/c1-20-9(6-14-19)7-15-13(18)10-4-2-3-5-11(10)21-8-12(16)17/h2-5,9,19H,6-8H2,1H3,(H,15,18)(H,16,17)
Key: HQRSUIDICNOLPX-SCJHNVIKAK
Properties Molecular formula C13H18HgNO6 Molar mass 484.87512  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Mersalyl acid (Mersal) is a mercurial diuretic. It is only rarely used, having been superseded by diuretic medications that do not contain mercury and are therefore less toxic.
Antihypertensives: diuretics (C03) Sulfonamides
(except EA)Quinethazone • Clopamide • Chlortalidone • Mefruside • Clofenamide • Metolazone • Meticrane • Xipamide • Indapamide • Clorexolone • FenquizonePotassium-sparing (at CD) ESC blockersOsmotic diuretics (PT, DL) VAs (DCT and CD) Other 
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
