- M1 motorway (Republic of Ireland)
-
M1 motorway
Route information Part of 

Length: 80 km (50 mi) History: Completion dates: Whitehall/Coolock 1983
Airport Motorway 1985
Dunleer Bypass 1993
Balbriggan Bypass 1998
Dunleer to Dundalk 2001
Drogheda Bypass 2003
Airport to Balbriggan 2003
Dundalk Bypass 2005Major junctions From: Dublin
(Turnapin)








To: Ballymascanlon Location Primary
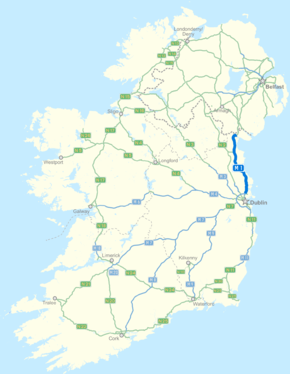
destinations:Dublin Airport, Swords, Balbriggan, Drogheda, Dundalk Road network The M1 motorway (Irish: Mótarbhealach M1) is a motorway in Republic of Ireland. It forms the large majority of the N1 national primary road connecting Dublin towards Belfast along the east of Ireland. The route heads north via Drogheda and Dundalk to the Northern Irish border just south of Newry in County Armagh, where it becomes the A1 and further on, the M1. It also forms a significant part of the road connection between Dublin and the Northern Irish cities of Newry, and Lisburn. The route is part of European route E01.
Contents
Route
 The Boyne River Bridge.
The Boyne River Bridge.
The N1 begins at Bachelors Walk, part of the Dublin quays, where it connects to the N4. From here it follows O'Connell Bridge, O'Connell Street, Parnell Street, Parnell Square West, Granby Row, Dorset Street Upper (and via North Frederick Street, Parnell Square East and Cavendish Row), Dorset Street Lower, Drumcondra Road and the Swords Road. At Whitehall, the road follows the route of the former M1 Airport Motorway (this section is now downgraded to single carriageway primary route following the construction of the Dublin Port Tunnel). At the Dublin Port Tunnel portals, the road follows the M50 motorway for 2 km, before the M1 motorway begins at M50 Junction 3. Almost the entire length of the N1 has been upgraded to motorway standard and is designated the M1 motorway. At 80 km it is the second longest stretch of motorway in Ireland, excluding connecting motorways. (The M8 is the longest.) It runs from the northernmost part of the M50 ring road in Dublin, north of Dundalk, bypassing the intermediate towns through which the original route travelled. The original N1 route now forms the R132.[1] On directional roadsigns along the N1 route, the N1 designation is only used for two relatively short sections: between Dublin city centre and Whitehall, and between Ballymascanlon and the Northern Irish border. The motorway section of the N1 uses the M1 designation. Small yellow route markers along the motorway route also read N1.
The motorway was built in several stages as short disconnected bypasses, replacing the original N1 route. The first section opened (in 1983) was from Whitehall to Coolock Lane followed (in 1985) by the Airport Motorway between Whitehall and Dublin Airport, only the third section of motorway opened in the Republic of Ireland. 1980s style direction signs were still intact on this route up until 2006. Part of this original M1 is now a spur to Dublin Airport, while another part between Whitehall to the Port Tunnel portals is now narrowed to two+one lanes (although still grade separated) as a result of the Dublin Port Tunnel work.
There are toll fees for use of the motorway between junctions 7 and 10, the section which forms the Drogheda bypass. Work began in 2004 on a bypass of Dundalk, and was completed three months ahead of schedule in 2005, extending the motorway to just south of the border.
Construction finished in 2007 on a cross-border stretch of grade-separated dual-carriageway linking the northern end of the M1 with the A1 near Newry in County Armagh. This was opened to traffic on 2 August 2007. Its length is 14 km, 4.6 km north of the border and 9.4 km south of the border. This allows traffic to flow freely from Dublin Port on motorway/dual-carriageway standard road to the Hillsborough Roundabout, located south of Lisburn.
Junctions
This is the National Roads Authority's Exit numbering scheme for the M1.[2] As of 2011[update] all junctions feature their number on road signs.

Northbound exits Junction Southbound exits Start of motorway 
Malahide (N32), ALL OTHER ROUTES (M50 )
Motorway continues as M50 for Dublin and Dublin PortDublin Airport, Swords (R132) 
Dublin Airport, Swords (R132) Swords (R125) No exit Skerries, Rush (R132) Swords, Malahide (R132 (R126)) Lusk services Services Lusk services Balbriggan (R132) Lusk, Rush (R132) Balbriggan, Naul (R132) Balbriggan, Naul (R132) Julianstown, Drogheda South (R132) Julianstown, Drogheda South (R132) 
Drogheda, Duleek (R152) No exit Drogheda, Donore Drogheda, Donore Drogheda North, Navan (N51) Drogheda North, Navan (N51) No exit Monasterboice (R132) Dunleer, Collon (R169) Dunleer, Collon (R169) Dunleer, Dromin (R170) No exit Ardee, Derry (N33 (N2)) Ardee, Derry (N33 (N2)) Castlebellingham, Tallanstown (R166) Castlebellingham, Tallanstown (R166) Castlebellingham Services Services Castlebellingham Services Dundalk, Mullingar (N52) Dundalk, Mullingar (N52) Castleblayney, Dundalk (N53) Castleblayney, Dundalk (N53) Dundalk, Ballymascanlon (N52) Dundalk, Ballymascanlon (N52) 
Northbound exits Junction Southbound exits No exit Ravensdale (R132) Jonesborough Note: Sliproad crosses the border half way up Jonesborough, Carrickcarnan (R132), Customs and Excise Entering Northern Ireland
Road continues as A1— Entering Republic of Ireland
Road continues as N1All-Ireland route
Main article: A1 road (Northern Ireland)The upgrade of the N1 is now complete in the Republic of Ireland, the first major route to be completely upgraded to motorway/dual carriageway standard (outside of Dublin city centre) as per the National Development Plan. The Northern Irish authorities have no plans to replace the A1 route (currently dual carriageway) with motorway, although many junctions have now been grade separated. Currently, to drive from Dublin city centre to Belfast, one travels along the N1, M1 (Republic of Ireland), N1, A1 and M1 (Northern Ireland).
Motorway Service Areas
The first official on-line Motorway service area in Ireland opened on the M1 on 8 September 2010, located near Lusk. A second near Castlebellingham (M1 North service area) opened on 29 September 2010. Each location has northbound and southbound facilities, with no connection across the motorway between each side. Open 24 hours a day, they provide fuel and food and are of a design similar to those found in other European countries. The service areas are run by a consortium of companies known as Superstop.
ITS on the M1
While some other sections of Irish motorways also feature Variable-message signs, the M1 is the only one connected to an Intelligent transportation system providing real-time journey time information for motorists. The system works by recognising vehicle number plates at intervals along the motorway, and uses this information to calculate average vehicle speeds and hence travel times. Northbound, VMSs near Malahide and Balbriggan provide information on the journey times to the Drogheda (J7) and Dundalk (J16) exits. Similar signs southbound provide information on the travel time to Dublin airport and the Dublin port tunnel.
Roadside Art on M1
Roadside art is funded under the Percentage For Arts Scheme where 1% of the scheme budget is allocated to roadside art with a cap of €63,000. The local authorities decide on a theme and are responsible for commissioning the work, usually by open competition.[3] There are several examples along the M1
- The Beehives. Three corbelled beehives on the Balbriggan bypass by artists Robert McColgan and Irene Benner made of cut stone in 2001 – Inspired by the tale of St. Molach, a beekeeper.[4]
- An Tarbh Donn, a three metre high bull on the Dundalk bypass by artist Micheál McKeown. Of metal mesh on a concrete base. Inspired by the Bull in the Táin Bó Cúailnge.[5]
See also
- Roads in Ireland
- Motorways in Ireland
- National secondary road
- Regional road
References
- ^ Roads Act 1993 (Classification of Regional Roads) Order 2006 – Department of Transport
- ^ Ordnance Survey Ireland Motorway Schemeta
- ^ http://www.arts-sport-tourism.gov.ie/pdfs/English-text5.htm
- ^ http://www.fingalarts.ie
- ^ http://www.createlouth.ie
Roads in Ireland Motorways National primary roads National secondary roads Regional roads (R101–R399) R101 · R102 · R103 · R104 · R105 · R106 · R107 · R108 · R109 · R110 · R111 · R112 · R113 · R114 · R115 · R116 · R117 · R118 · R119 · R120 · R121 · R122 · R123 · R124 · R125 · R126 · R127 · R128 · R129 · R130 · R131 · R132 · R133 · R134 · R135 · R136 · R148 · R149 · R150 · R151 · R152 · R153 · R154 · R155 · R156 · R157 · R158 · R159 · R160 · R161 · R162 · R163 · R164 · R165 · R166 · R167 · R168 · R169 · R170 · R171 · R172 · R173 · R174 · R175 · R176 · R177 · R178 · R179 · R180 · R181 · R182 · R183 · R184 · R185 · R186 · R187 · R188 · R189 · R190 · R191 · R192 · R193 · R194 · R195 · R196 · R197 · R198 · R199 · R200 · R201 · R202 · R203 · R204 · R205 · R206 · R207 · R208 · R209 · R210 · R211 · R212 · R213 · R214 · R229 · R230 · R231 · R232 · R233 · R234 · R235 · R236 · R237 · R238 · R239 · R240 · R241 · R242 · R243 · R244 · R245 · R246 · R247 · R248 · R249 · R250 · R251 · R252 · R253 · R254 · R255 · R256 · R257 · R258 · R259 · R260 · R261 · R262 · R263 · R264 · R265 · R266 · R267 · R268 · R277 · R278 · R279 · R280 · R281 · R282 · R283 · R284 · R285 · R286 · R287 · R288 · R289 · R290 · R291 · R292 · R293 · R294 · R295 · R296 · R297 · R298 · R299 · R310 · R311 · R312 · R313 · R314 · R315 · R316 · R317 · R318 · R319 · R320 · R321 · R322 · R323 · R324 · R325 · R326 · R327 · R328 · R329 · R330 · R331 · R332 · R333 · R334 · R335 · R336 · R337 · R338 · R339 · R340 · R341 · R342 · R343 · R344 · R345 · R346 · R347 · R348 · R349 · R350 · R351 · R352 · R353 · R355 · R356 · R357 · R358 · R359 · R360 · R361 · R362 · R363 · R364 · R365 · R366 · R367 · R368 · R369 · R370 · R371 · R372 · R373 · R374 · R375 · R376 · R377 · R378 · R379 · R389 · R390 · R391 · R392 · R393 · R394 · R395 · R396 · R397 · R398 · R399Regional roads (R400–R699) R400 · R401 · R402 · R403 · R404 · R405 · R406 · R407 · R408 · R409 · R410 · R411 · R412 · R413 · R414 · R415 · R416 · R417 · R418 · R419 · R420 · R421 · R422 · R423 · R424 · R425 · R426 · R427 · R428 · R429 · R430 · R431 · R432 · R433 · R434 · R435 · R436 · R437 · R438 · R439 · R440 · R441 · R442 · R443 · R444 · R445 · R446 · R448 · R449 · R458 · R459 · R460 · R461 · R462 · R463 · R464 · R465 · R466 · R467 · R468 · R469 · R470 · R471 · R472 · R473 · R474 · R475 · R476 · R477 · R478 · R479 · R480 · R481 · R482 · R483 · R484 · R485 · R486 · R487 · R488 · R489 · R490 · R491 · R492 · R493 · R494 · R495 · R496 · R497 · R498 · R499 · R500 · R501 · R502 · R503 · R504 · R505 · R506 · R507 · R509 · R510 · R511 · R512 · R513 · R514 · R515 · R516 · R517 · R518 · R519 · R520 · R521 · R522 · R523 · R524 · R525 · R526 · R527 · R548 · R549 · R550 · R551 · R552 · R553 · R554 · R555 · R556 · R557 · R558 · R559 · R560 · R561 · R563 · R564 · R565 · R566 · R567 · R568 · R569 · R570 · R571 · R572 · R573 · R574 · R575 · R576 · R577 · R578 · R579 · R580 · R581 · R582 · R583 · R584 · R585 · R586 · R587 · R588 · R589 · R590 · R591 · R592 · R593 · R594 · R595 · R596 · R597 · R598 · R599 · R600 · R601 · R602 · R603 · R604 · R605 · R606 · R607 · R608 · R609 · R610 · R611 · R612 · R613 · R614 · R615 · R616 · R617 · R618 · R619 · R620 · R621 · R622 · R623 · R624 · R626 · R627 · R628 · R629 · R630 · R631 · R632 · R633 · R634 · R635 · R637 · R638 · R639 · R659 · R660 · R661 · R662 · R663 · R664 · R665 · R666 · R667 · R668 · R669 · R670 · R671 · R672 · R673 · R674 · R675 · R676 · R677 · R678 · R679 · R680 · R681 · R682 · R683 · R684 · R685 · R686 · R687 · R688 · R689 · R690 · R691 · R692 · R693 · R694 · R695 · R696 · R697 · R698 · R699Regional roads (R700–R940) R700 · R701 · R702 · R703 · R704 · R705 · R706 · R707 · R708 · R709 · R710 · R724 · R725 · R726 · R727 · R729 · R730 · R731 · R733 · R734 · R735 · R736 · R737 · R738 · R739 · R740 · R741 · R742 · R743 · R744 · R745 · R746 · R747 · R748 · R749 · R750 · R751 · R752 · R753 · R754 · R755 · R756 · R757 · R758 · R759 · R760 · R761 · R762 · R763 · R764 · R765 · R766 · R767 · R768 · R769 · R770 · R772 · R773 · R774 · R801 · R802 · R803 · R804 · R805 · R806 · R807 · R808 · R809 · R810 · R811 · R812 · R813 · R814 · R815 · R816 · R817 · R818 · R819 · R820 · R821 · R822 · R824 · R825 · R826 · R827 · R828 · R829 · R830 · R831 · R833 · R834 · R835 · R836 · R837 · R838 · R839 · R840 · R841 · R842 · R843 · R846 · R847 · R848 · R849 · R851 · R852 · R853 · R854 · R855 · R857 · R858 · R859 · R860 · R863 · R864 · R865 · R866 · R867 · R868 · R870 · R871 · R873 · R874 · R875 · R876 · R877 · R880 · R883 · R884 · R885 · R886 · R887 · R888 · R889 · R890 · R891 · R895 · R896 · R898 · R899 · R900 · R901 · R902 · R903 · R904 · R906 · R907 · R908 · R909 · R910 · R911 · R913 · R914 · R915 · R916 · R917 · R918 · R919 · R920 · R921 · R922 · R923 · R924 · R925 · R926 · R927 · R928 · R929 · R930 · R931 · R932 · R933 · R934 · R935 · R936 · R937 · R940Transport in Dublin Air Rail Tram*Road Bus corridorsR101 · R102 · R103 · R104 · R105 · R106 · R107 · R108 · R109 · R110 · R111 · R112 · R113 · R114 · R115 · R116 · R117 · R118 · R119 · R120 · R121 · R122 · R123 · R124 · R125 · R126 · R127 · R128 · R129 · R130 · R131 · R132 · R133 · R134 · R135 · R136 · R148 · R156 · R403 · R445 · R761 · R810 · R817 · R821 · R822 · R824 · R825 · R826OtherWater CanalsPortsAgencies *=Tram systems no longer run. Information in parentheses shows the operator(s)Categories:- Motorways in the Republic of Ireland
- Roads in County Dublin
- Roads in County Louth
- Roads in County Meath
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.