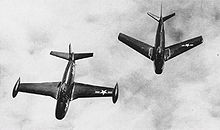
- North American FJ-1 Fury
-
FJ-1 Fury An FJ-1 Fury in 1947 Role Fighter aircraft National origin United States Manufacturer North American Aviation First flight 11 September 1946 Introduction October 1947 Primary users United States Navy
United States Marine CorpsNumber built 31 (including prototype) Developed into North American F-86 Sabre The North American FJ-1 Fury was the first operational jet aircraft in United States Navy service, and was developed by North American Aviation as the NA-135.[1] The FJ-1 was an early transitional jet of limited success which carried over similar tail surfaces, wing and canopy derived from the piston-engined P-51 Mustang. The evolution of the design to incorporate swept wings would become the basis for the land-based XP-86 prototype of the United States Air Force's enormously influential F-86 Sabre, which itself formed the basis for the Navy's carrier-based North American FJ-2/-3 Fury.
Contents
Design and development
Ordered in late 1944 as the XFJ-1 in competition with proposals from Douglas and Vought, the Fury began as a straight-wing, tricycle gear fighter with a single turbojet passing through the fuselage. The wing, empennage and canopy strongly resembled that of the piston-engined P-51 Mustang, North American Aviation's highly successful World War II fighter.
Operational history
 An Oakland Naval Air Reserve FJ-1 over Oakland, California, in 1950.
An Oakland Naval Air Reserve FJ-1 over Oakland, California, in 1950.
The first flight of the prototype XFJ-1 took place on 11 September 1946, with the first of 30 deliveries beginning in October 1947. Flown by Navy squadron VF-5A, the FJ-1 made the USN's first operational aircraft carrier landing with a jet fighter at sea[N 1] on 10 March 1948 aboard USS Boxer, pioneering jet-powered carrier operations and underscoring the need for catapult-equipped carriers. The Fury was capable of launching without catapult assistance, but on a crowded flight deck the capability was of small practicality. In reality, taking off without a catapult launch, pitched the FJ-1 into a perilous, slow climb that was considered too risky for normal operations.[2]
As straight wings were seen at the time as the only way to ensure the low speed and stability needed for carrier landings, the FJ-1 used a straight wing. No provision for wing-folding had been made as dive brakes mounted in the wings made that option unfeasible. In order to conserve carrier deck space, a unique "kneeling" nose undercarriage along with a swivelling "jockey wheel" allowed the FJ-1 to be stacked tail-high, close to another FJ-1.[3]
Although ordered into production, the initial order for 100 units was trimmed to only 30 aircraft which were mainly used in testing at NAS North Island. VF-5A, soon redesignated as VF-51, operated the type in service beginning in August 1948. Although VF-51 went to sea on Boxer by May 1949, the FJ-1s were phased out in favor of the new F9F-2 Panther.[4]
Ending its service career in US Naval Reserve units, the FJ-1 eventually was retired in 1953. The one highlight in its short service life was VF-51's win in the Bendix Trophy Race for jets in September 1948. The unit entered seven FJ-1s, flying from Long Beach, California to Cleveland, Ohio, with VF-51 aircraft taking the first four places, ahead of two California ANG Lockheed F-80 Shooting Stars.[1]
Variants
- XFJ-1
- Prototype aircraft, powered by a 3,820 lbf (17 kN) General Electric J35-GE-2 turbojet engine, three built.
- FJ-1 Fury
- Single-seat fighter aircraft, powered by a 4,000 lbf (17.8 kN) Allison J35-A-2 turbojet engine, armed with six 0.50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns, 30 built.
Operators
Main article: List of Fury units in US Navy & Marine CorpsSurvivors
- FJ-1 BuNo. 120349 is under restoration at Yanks Air Museum in Chino, California. [5]
- An FJ-1 is in storage at the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C. [6]
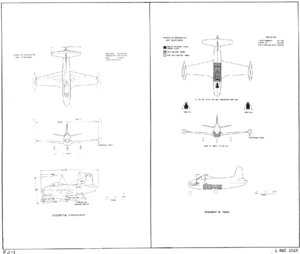
Specifications (FJ-1)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 34 ft 5 in (10.48 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 2 in (11.63 m)
- Height: 14 ft 10 in (4.52 m)
- Wing area: 221 ft² (20.5 m²)
- Empty weight: 8,843 lb (4,010 kg)
- Loaded weight: 15,118 lb (6,854 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Allison J35-A-2 turbojet, 4,000 lbf (17.8 kN)
- Fuel provisions Internal fuel load: 465 gal (1,743 l), Wing Tip Tanks: 2 × 170 gal (644 l)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 547 mph at 9,000 ft (880 km/h at 2,743 m)
- Range: 1,496 mi, (2,407 km) 1,496 mi (2,407 km) with external tanks
- Service ceiling: 32,000 ft. (9,753 m)
- Rate of climb: 3,300 ft/min at sea level (1,005 m/min)
- Thrust/weight: 0.38
- Stalling speed (power off): 121 mph (106 kn, 194 km/h)
Armament
- Guns: 6 × 0.50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns (1,500 rounds in total)
See also
- Related development
- North American P-51 Mustang
- North American T-2 Buckeye
- North American F-86 Sabre
- North American FJ-2/-3 Fury
- North American FJ-4 Fury
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- de Havilland Sea Vampire
- Hawker Sea Hawk
- McDonnell FH Phantom
- Supermarine Attacker
- Vought F6U Pirate
- Related lists
- List of fighter aircraft
- List of military aircraft of the United States
- List of Sabre and Fury units in US military
References
- Notes
- ^ The first all-jet aircraft to take off and land from an American carrier was a McDonnell XFD-1 Phantom on 21 July 1946 from USS Franklin D. Roosevelt, but the tests were not conducted under operational conditions.
- Citations
- ^ a b "The FJ-1 Fury." f-86.tripod.com. Retrieved: 29 April 2008.
- ^ "North American FJ-1 Fury – carrier-borne fighter." aviastar.org. Retrieved: 29 April 2008.
- ^ "FJ Fury." boeing.com. Retrieved: 29 April 2008.
- ^ "FJ Fury." globalsecurity.org. Retrieved: 29 April 2008.
- ^ "Boneyard Tarmac". Yanks Air Museum. Retrieved: 17 January 2011.
- ^ "FJ-1 Fury". NASM. Retrieved: 17 January 2011.
- Bibliography
- Taylor, John, W.R., ed. Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1965-1966. London: Jane's All the World's Aircraft, 1967. ISBN 0-71061-377-6.
- Wagner, Ray. The North American Sabre. London: Macdonald, 1963. No ISBN.
- Winchester, Jim, ed. Military Aircraft of the Cold War (The Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2006. ISBN 1-84013-929-3.
External links
USN fighter designations pre-1962 General Aviation
BrewsterBoeing Curtiss Douglas
McDonnellGrumman Eberhart
GoodyearHall
McDonnellBerliner-Joyce
North American AviationLoening
BellGeneral Motors Seversky FN
Lockheed Ryan FR • XF2R
Northrop Vought Lockheed Wright Convair Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- North American Aviation aircraft
- Carrier-based aircraft
- United States fighter aircraft 1940–1949
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.