- Ganglionic eminence
-
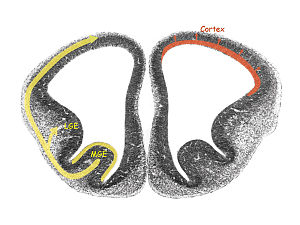 Coronal section in the forebrain of an embryonic mouse at 12.5 days of gestation (preplate stage), showing the lateral and medial ganglionic eminences (LGE, MGE) from which GABAergic interneurons migrate to the cortical anlage (left, yellow). Glutamatergic neurons destined for the cortex are generated locally in the cortical ventricular zone and migrate radially (right, red).
Coronal section in the forebrain of an embryonic mouse at 12.5 days of gestation (preplate stage), showing the lateral and medial ganglionic eminences (LGE, MGE) from which GABAergic interneurons migrate to the cortical anlage (left, yellow). Glutamatergic neurons destined for the cortex are generated locally in the cortical ventricular zone and migrate radially (right, red).
In neuroanatomy and neuroembryology, a ganglionic eminence (GE) is a transitory brain structure present in the embryonic and fetal stages of brain development. The eminences are found in the ventral part of the telencephalon, where they form bulges in the ventricles. These bulges develop into the basal ganglia.[1] They also contribute significantly in building up the GABAergic cortical cell population.
Categorization
Ganglionic eminences are categorized into three groups based on location:
- Lateral ganglionic eminences (LGE)
- Medial ganglionic eminences (MGE)
- Caudal ganglionic eminences (CGE)
In humans
In humans, ganglionic eminences serve as the source of GABAergic thalamic neurons, which migrate through another transient brain structure peculiar to humans, the gangliothalamic body (GTB). GEs also present an intermediate target for the axons growing from the thalamus into the cortex and vice versa. They disappear just before birth.
References
- ^ Purves, Dale, George J. Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, William C. Hall, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James O. McNamara, and Leonard E. White (2008). Neuroscience. 4th ed.. Sinauer Associates. pp. 555–8. ISBN 978-0-87893-697-7.
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of nervous system (GA 9.733 and GA 10.1002, TE E5.13-16) Neurogenesis Cranial neural crest (Cardiac neural crest complex) · Truncal neural crestRostral neuropore
Cephalic flexure · Pontine flexure
Alar plate (sensory) · Basal plate (motor)
Germinal matrixEye development Auditory development M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Neuroscience
- Neuroanatomy
- Embryology
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
