- Nafarelin
-
Nafarelin 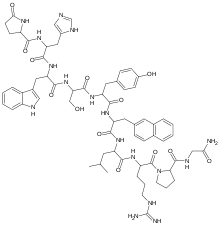
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2R)-N-[(2R)-5-carbamimidamido-1-[(2S)-2-[(carbamoylmethyl)carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]-2-[(2R)-2-[(2R)-2-[(2R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(2S)-2-[(2S)-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2R)-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]formamido}propanamido]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanamido]propanamido]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanamido]-3-(naphthalen-2-yl)propanamido]-4-methylpentanamide Clinical data Trade names Synarel AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a601082 Pregnancy cat. X Legal status ℞-only Routes Nasal spray Pharmacokinetic data Half-life 2.6 to 4 hours Excretion renal Identifiers CAS number 76932-56-4 
ATC code H01CA02 PubChem CID 25077649 DrugBank APRD01129 ChemSpider 10482014 
UNII 1X0094V6JV 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201309 
Chemical data Formula C66H83N17O13 Mol. mass 1321.6344 g/mol - InChI=1S/C66H83N17O13/c1-36(2)25-48(58(89)76-47(13-7-23-71-66(68)69)65(96)83-24-8-14-54(83)64(95)73-33-55(67)86)77-60(91)50(28-38-15-18-39-9-3-4-10-40(39)26-38)78-59(90)49(27-37-16-19-43(85)20-17-37)79-63(94)53(34-84)82-61(92)51(29-41-31-72-45-12-6-5-11-44(41)45)80-62(93)52(30-42-32-70-35-74-42)81-57(88)46-21-22-56(87)75-46/h3-6,9-12,15-20,26,31-32,35-36,46-54,72,84-85H,7-8,13-14,21-25,27-30,33-34H2,1-2H3,(H2,67,86)(H,70,74)(H,73,95)(H,75,87)(H,76,89)(H,77,91)(H,78,90)(H,79,94)(H,80,93)(H,81,88)(H,82,92)(H4,68,69,71)/t46-,47-,48-,49-,50+,51-,52-,53-,54-/m0/s1

Key:RWHUEXWOYVBUCI-ITQXDASVSA-N
 (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Nafarelin is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH agonist). By causing constant stimulation of the pituitary, it decreases pituitary secretion of gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Nafarelin may be used in the treatment of estrogen-dependent conditions (such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids), to treat central precocious puberty, and to control ovarian stimulation in IVF.
It is normally delivered via a nasal spray.
Nafarelin acetate is marketed by Searle (now part of Pfizer) under the brand name Synarel.
Side effects
Side effects of nafarelin are mostly related to the low estrogen state. Side effects include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, headaches, mood changes, and decreased interest in sex. Some patients may experience acne, muscle pain, reduced breast size, and irritation of the tissue inside the nose. These side effects should disappear after stopping the medication.
Gonadotropins and GnRH (G03G) Gonadotropin
preparationsAgonistAntigonadotropinGnRH Hypothalamic-pituitary hormones and analogues (H01) Hypothalamic Agonists: Lanreotide • OctreotideAnterior pituitary Agonists: Corticotropin • Cosyntropin • TetracosactideAgonists: ThyrotropinPosterior pituitary Agonists: Argipressin • Desmopressin • Felypressin • Lypressin • Ornipressin • Terlipressin
Antagonists: Conivaptan • Demeclocycline • Lixivaptan • Mozavaptan • Nelivaptan • Relcovaptan • Satavaptan • TolvaptanCategories:- GnRH agonists
- InChI=1S/C66H83N17O13/c1-36(2)25-48(58(89)76-47(13-7-23-71-66(68)69)65(96)83-24-8-14-54(83)64(95)73-33-55(67)86)77-60(91)50(28-38-15-18-39-9-3-4-10-40(39)26-38)78-59(90)49(27-37-16-19-43(85)20-17-37)79-63(94)53(34-84)82-61(92)51(29-41-31-72-45-12-6-5-11-44(41)45)80-62(93)52(30-42-32-70-35-74-42)81-57(88)46-21-22-56(87)75-46/h3-6,9-12,15-20,26,31-32,35-36,46-54,72,84-85H,7-8,13-14,21-25,27-30,33-34H2,1-2H3,(H2,67,86)(H,70,74)(H,73,95)(H,75,87)(H,76,89)(H,77,91)(H,78,90)(H,79,94)(H,80,93)(H,81,88)(H,82,92)(H4,68,69,71)/t46-,47-,48-,49-,50+,51-,52-,53-,54-/m0/s1
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
