- Triptorelin
-
Piperazine 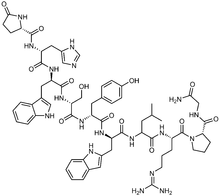
Systematic (IUPAC) name 5-oxo-D-prolyl-L-histidyl-Ltryptophyl-L-seryl-Ltyrosyl-3-(1H-indol-2-yl)-L-alanylleucyl-L-arginyl-L-prolylglycinamide Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information MedlinePlus a697045 Pregnancy cat. D Legal status ℞-only Routes Implant Pharmacokinetic data Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 57773-63-4 
ATC code L02AE04 PubChem CID 4837 DrugBank DB00592 ChemSpider 13835459 
UNII 9081Y98W2V 
KEGG D00807 
ChEBI CHEBI:28568 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201334 
Chemical data Formula C64H82N18O13 Mol. mass 1311.5 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Triptorelin, a decapeptide (pGlu-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-D-Trp-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2), is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist (GnRH agonist) used at the acetate or pamoate salts. By causing constant stimulation of the pituitary, it decreases pituitary secretion of gonadotropins luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Like other GnRH agonists, triptorelin may be used in the treatment of hormone-responsive cancers such as prostate cancer or breast cancer, precocious puberty, estrogen-dependent conditions (such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids), and in assisted reproduction. Triptorelin is marketed under the brand names Decapeptyl (Ipsen) and Diphereline and Gonapeptyl (Ferring Pharmaceuticals). In the United States, it is sold by Watson as Trelstar.In Iran Triptorelin is marketed under the brand name Variopeptyl® 0.1
During the treatment of prostate cancer it does cause a surge of testosterone (an initial uplevel of testosterone levels), known as a flare effect. In men a reduction of serum testosterone levels into the range normally seen after surgical castration occurs approximately two to four weeks after initiation of therapy. In contrast, gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists do not cause a surge, but a sudden reduction of testosterone levels.
Systematic IUPAC Name: [d-Trp6]GnRHReferences
- Lahlou N, Carel JC, Chaussain JL, Roger M (July 2000). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of GnRH agonists: clinical implications in pediatrics". J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 13 Suppl 1: 723–37. PMID 10969915.
- Padula AM (August 2005). "GnRH analogues—agonists and antagonists". Anim Reprod Sci 88 (1–2): 115–26. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2005.05.005. PMID 15955640.
Gonadotropins and GnRH (G03G) Gonadotropin
preparationsAgonistAntigonadotropinGnRH #WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III 
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
