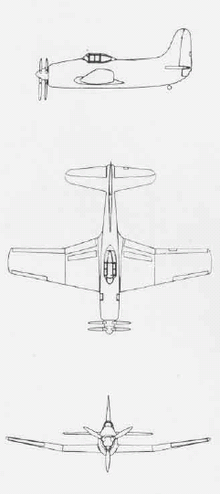
- Curtiss XBTC
-
XBTC A Curtiss XBTC-2 "Model B" in 1946 Role Attack aircraft National origin United States Manufacturer Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company First flight January 1945 (XBTC-2) Number built 2 The Curtiss XBTC was an experimental single-seat, single-engine torpedo bomber aircraft developed during World War II.
Contents
Design and development
The Curtiss XBTC-1 (Model 96) was a low-wing monoplane with retractable tailwheel landing gear which used a 2,200 hp (1,641 kW) Wright R-3350 radial engine. It was entered in a 1943 United States Navy competition against the Douglas XBTD-1 Destroyer II, Martin XBTM-1 Mauler, and Kaiser-Fleetwings XBTK-1. The BTC-2 should have used the Pratt & Whitney R-4360 engine, but problems with the Wright engine led to the further development of the BTC-2.[1] Despite its power and "first-class performance and weapon-carrying capacity",[2] it lost to the XBT2D-1 (redesignated as the AD-1 Skyraider) and the BTM-1 (similarly redesignated AM-1) Mauler, which were already building. Two VBTC-2s were built, each having a different wing. The "Model A" had a standard wing and flaps; the "Model B" featured a full span Duplex flap wing with a straight trailing edge and a swept-back leading edge. Both had the 3,000 hp (2,237 kW) Pratt & Whitney XR-4360-8A equipped with contrarotating propellers. The planes were delivered to the Naval Air Test Center at Patuxent River, Maryland (USA), in July 1946. One plane crashed in February 1947 the other in August 1947.[3]
The United States Army Air Force assigned the designation A-40 to a proposed 'de-navalised' version of the XBTC; however, the USAAF decided not to acquire any further single-engine attack aircraft and the project was cancelled.[citation needed]
Variants
- Curtiss XBTC-1 (Model 96) :
- Curtiss XBTC-2 (Model 98) :
Operators
Specifications (XBTC-2)
Data from Curtiss Aircraft 1907–1947[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 39 ft 0 in (11.89 m)
- Wingspan: 50 ft 0 in (15.24 m)
- Height: 12 ft 11 in (3.94 m)
- Wing area: 425 sq ft (39.5 m2)
- Empty weight: 13,410 lb (6,083 kg)
- Gross weight: 21,660 lb (9,825 kg) with one Mk 13 torpedo
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-4360-8A Wasp Major Radial engine, 3,000 hp (2,200 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 374 mph (602 km/h; 325 kn) at 16,000 ft (4,900 m)
- Cruise speed: 188 mph (163 kn; 303 km/h)
- Range: 1,835 mi (1,595 nmi; 2,953 km) at 188 mph (303 km/h)
- Service ceiling: 26,200 ft (7,986 m)
- Rate of climb: 2,250 ft/min (11.4 m/s)
Armament
- Guns: 4 × 20mm cannon
- Missiles: One torpedo
- Bombs: Up to 2,000 pounds (910 kg)
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- AD Skyraider
- AM Mauler
- Kaiser-Fleetwings XBTK
- Related lists
References
- Andrews, Hal. "XBTC-2". Naval Aviation News. November–December 1987. pp. 16–17.
- Bowers, Peter M. Curtiss Aircraft 1907–1947. London:Putnam, 1979. ISBN0-370-10029 8.
- Donald, David, general editor. Encyclopedia of World Aircraft. Etobicoke, Ontario: Prospero Books, 1997. ISBN 1-85605-375-X.
External links
Aircraft produced by Curtiss and Curtiss-Wright Manufacturer
designationsModel letters: C • D • E • F • G • GS • H • J • K • L • M • N • PN • JN • R • S
Model numbers: 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 23 • 24 • 26 • 28 • 31 • 32 • 33 • 34 • 35 • 36 • 37 • 38 • 39 • 40 • 41 • 42 • 43 • 44 • 47 • 48 • 49 • 50 • 51 • 52 • 53 • 54 • 55 • 56 • 57 • 58 • 59A/59B • 60 • 61 • 62 • 63 • 64 • 66 • 67 • 68 • 69 • 70 • 71 • 72 • 73 • 75 • 76 • 77 • 79 • 81 • 82 • 84 • 85 • 86 • 87 • 88 • 90 • 91 • 94 • 95 • 96 • 97 • 98 •
"CW" models: CW-1 • CW-2 • CW-3 • CW-4 • CW-5 • CW-6 • CW-7 • CW-8 • CW-9 • CW-10 • CW-11 • CW-12 • CW-14 • CW-15 • CW-16 • CW-17 • CW-18 • CW-19 • CW-20 • CW-21 • CW-22 • CW-23 • CW-24 • CW-25 • CW-27 • CW-29 • CW-32
By role Experimental: No. 1 • Model C • Tanager
Racing: No. 2 • CR • R2C • R3C
General utility: Model D • Model E • Model F • Robin • Thrush
Maritime patrol: Model H • HS-1L and -2L
Training: Model L • Model JN • Fledgling • AT-4 Hawk • AT-5 Hawk
Fighters: 18 • PW-8 • P-1 • P-2 • P-3 • P-4 • P-5 • P-6 • XP-31 • P-36 • P-40 • XP-46 • XP-53 • YP-60 • XP-62 • XP-71 • XP-87
Naval Fighters: HA • FC • F2C • F3C • F4C • F6C • F7C • F8C • F9C • F10C • F11C • XF12C • F13C • XF14C • XF15C
Airliners: Eagle • Condor II • Kingbird
Naval Scouts/Dive Bombers: CS • GS • S2C • XS3C • S4C • SC • SBC • SB2C • XSB3C • SOC • SO2C • SO3C
Observation: O-1 • O-12 • O-13 • O-16 • O-18 • O-26 • O-39 • O-40 • O-52
Naval Observation: OC • O2C • O3C
Naval Bombers: 24 • BFC • BF2C • XBTC • XBT2C
Ground Attack: A-3 • A-4 • A-5 • A-6 • A-8 • YA-10 • A-12 • YA-14 • A-25 • A-40 • XA-43
Licensed production: NBS-1
USN/USMC bomber designations 1931-1962 Bomber Great LakesBN
Bomber Drone BDRBomber Fighter Bomber Torpedo XBTC · XBT2C
Kaiser-FleetwingsBTK
USAAS/USAAC/USAAF/USAF attack aircraft designations 1924–1962 (A-1 not assigned) • XA-2 • A-3 • A-4 • A-5 • A-6 • XA-7 • A-8 • XA-9 • YA-10 • XA-11 • A-12 • YA-13 • YA-14 • XA-15 • XA-16 • A-17 • A-18 • A-19 • A-20 • XA-21 • A-22 • A-23 • A-24 • A-25 • A-26 • A-27 • A-28 • A-29 • A-30 • A-31 • XA-32 • A-33 • A-34 • A-35 • A-36 • XA-37 • XA-38 • XA-39 • A-40 • XA-41 • XA-42 • XA-43 • XA-44 • XA-45
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Curtiss aircraft
- United States attack aircraft 1940–1949
- United States bomber aircraft 1940–1949
- World War II torpedo bombers of the United States
- Carrier-based aircraft
- Single-engine aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.